Geology 12 Presents UNIT 3 Chp 10 Earth’s Interior and Isostacy Chp 11 Ocean Basin Chp 12 Plate...
-
Upload
mervyn-stone -
Category
Documents
-
view
235 -
download
4
Transcript of Geology 12 Presents UNIT 3 Chp 10 Earth’s Interior and Isostacy Chp 11 Ocean Basin Chp 12 Plate...

Geology 12Geology 12
PresentsPresents

UNIT 3UNIT 3
• Chp 10 Earth’s Interior and Isostacy
• Chp 11 Ocean Basin
• Chp 12 Plate Tectonics
• Chp 9 Seismology
• Chp 13 Structure
Handout WS 10.1 Note Helper

Chapter 10
Earth’s Interior and Isostacy
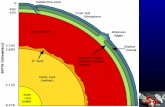
atmosphere
Lower mantle
hydrospherecontinental
crust oceanic crust
Lith
osph
ere
Upper mantle
MohoAsthenosphere
Outer coreInner
core

Earth’s InteriorEarth’s Interior



Layer Vol Density Composition
% gms/cm3
Oceanic Crust 0.16 3.0 upper: basalt
lower: gabbro
Continental Crust 0.44 2.7 granodiorite
Mantle 83 3.3 – 5.7 peridotite
Outer Core 15.7 9.9 – 12.2 88%Fe, +S,O2,Ni, K
Inner Core 0.7 12.6 – 13.0 80 - 90% Fe, +Ni


How Layers of Earth was Determined
1. Seismic
2. Heat Flow
3. Gravity
4. Magnetic Field

1. Seismic
• Seismic waves that travel through the Earth
• Caused by earthquakes or underground nuclear tests
• Two types
1. Surface waves
2. Body waves

1. Surface Waves
– Travel on the surface
– 2-3 km/sec
• Rayleigh and Love waves (more on this in Chp 9)
EQ
Surface waves Body
waves

1. Surface Waves
– Travel on the surface
– 2-3 km/sec
• Rayleigh and Love waves (more on this in Chp 9)

2. Body Waves– Travel inside the Earth– a) P-waves/Primary waves
• Fastest (7-13 km/sec)• A compressional/pull-push wave
like sound• Travel through everything (rock,
magma, water, air ( can sometimes hear EQ!)


– B) S-waves/Secondary waves
• slower (3 - 7 km/sec)
• Are shear waves because they move perpendicular to direction of travel
• Travel only through solids (not fluids)



• Wave velocity affected by:i) rock density: higher density speeds waves(ex: Earth’s density increase towards the core:
S-waves travel faster at the bottom of the mantle)
ii) Rock elasticity = tendency to return to original shape
higher elasticity increases wave speed(ex: P-waves travel slow through liquid outer
core than through solid inner core)Discontinuity = marked change in wave
velocity• Basis for dividing Earth into its layers.

• Please now refer to WS 10.1 top of page 2 of note helper

Low
vel
ocity
zon
e =
ast
heno
pher
e
crust
Gut
enbu
rg D
isco
ntin
uity


• Upon EQ/nuclear detonation, waves travel outward and inward in every direction (like ripples on a pond)
• Waves’ direction of travel:– Refracted (bent) away from more dense/more
elastic rocks back to surface• Most energy is refracted
– Reflected (change direction) at major rock boundaries (discontinuities)
• Reflected waves (wave velocity) + time to travel = depth to layer) gives us depth to layers (d = vt)
• GEOPHYSICS

Wave Refraction
EQ
Wave Reflection

Layers of the Earth Found
• 1. Core
– a) Outer Core & S-waves
Liquid
Outer

b) Inner Core & P-waves
•Inner core is solid because higher pressure increases melting temperature
•Inner core rotates 20 km/yr faster than outer core


2. Mantle•1909 Andrija Mohorovicic detected a seismic disontinuity (Moho) at about 30 km.

• P-waves travel faster (8 km/sec) in mantle than in crust (6.75 km.sec)
• Moho – bottom of crust– Below continents: 2- 90 km (aver’ 35 km)– Below seafloor: 5 -10 km.
Please refer to WS 10.1, p.2 of notehelper, bottom diagram.



M .
C .
Low velocity zone = Asthenosphere
Upper mantle
Transition Zone
Lower Mantle

Upper Mantle

Seismic Tomography
• Numerous seismic waves are analyzed to give a “CAT-scan” of the Earth
• Hot and cold areas of the mantle have been detected by measuring wave velocities (hot rock is less elastic = lower velocity)
• Depressions and rises have been detected where rising and sinking mantle deforms the mantle and core.

Seismic Tomography



3. Crust
• a) Continental Crust: – mainly granodiorite (P-waves 8 km/sec)– 35 km aver’ thickness– 20 km at rifts– 90 km at Himalayas

• b) Oceanic Crust– Top 1/2 : basalt– Bottom ½: gabbro– 5 km thick at spreading ridges– 10 km thick where it is oldest

3. Crust



How Layers of Earth was How Layers of Earth was DeterminedDetermined
1. Seismic
2. Heat Flow
3. Gravity
4. Magnetic Field
Hand out WS 10.2 Note Helper

2: Heat Flow
• Is very low (Earth is a good insulator/poor conductor)
• Is measured with very sensitive instruments



• Highest at spreading centres and areas of recent volcanism; lowest at trenches
Hea
t flo
w C
al/c
m2 /
sec 4
3
2
1
0
Island arc (volcanoes)
World average
Oceanic ridge
trenchnew crustold crust

• 70% of heat is lost through oceans
• Earth has been cooling off (less and less radioactive fuel) since its beginning.
• Most heat created by radioactive decay of U, Th and K


• Geothermal Gradient = rate of increase in temperature with depth– Highest at spreading ridge; lowest in mtns’
Region Temperature Geothermal Gradient
Crust base: 800- 1200 25
Mantle base: 3500-5000 1
Core base: 6500 <1
Remember Chp 7!

How Layers of Earth was How Layers of Earth was DeterminedDetermined
• Seismic
• Heat Flow
• Gravity
• Magnetic Field



3: Gravity
• Exists because mass attracts mass
• We are attracted towards the centre of the Earth
• F = Gm1 x m2
d2
Double the distance = ¼ the gravity

• Gravity varies by:
1. Distance between masses (greater distance = less gravity
a) Earth is not round: less gravity at equator
6378 km
6357 km

b) less gravity at high altitudes

2. Centrifugal force at equator “throws” you away from Earth = less gravity
•Generally. Gravity varies with latitude and altitude

3. Density of rock below
• Gravity is measured with a gravimeters(Positive gravity anomaly = more gravity)
• Important for Olympic records
• If you want to weigh less:– Drive fast east at the equator on top of a
mountain over top of low density rock.



Centrifugal Force is seen here with indirect high tides


Please refer to WS 10.2 Note Helper, Please refer to WS 10.2 Note Helper, bottom of page 1.bottom of page 1.

Ore deposit
Low density sedments Salt dome
(low density
Mountain
Positive gravity
anomaly
Negative gravity
anomaly

• Principle of Isostacy is Earth’s crust is “floating” on denser mantle.
– Like an iceberg, only 10% is above the water no matter the size of the iceberg
Crust
root
Mountain
Mantle


Isostacy



• Crust floats like a raft:– It sinks if:
a) glaciers/ice age
b) sediments accumulates in a delta or basin
(Evidence: sunken cities, docks, forests, beaches)
– If rises = isostatic rebound if:
a) glaciers melt/recede
b) erosion of a mountain
(Evidence: above sea-level: docks, beaches, marine fossils)

1.
2.
3.
4.
Glacial ice
Ice melts (i.e. Hudson’s Bay

Mtn’
erosion
Low density root
deposition deposition
erosiondeposition deposition


See question 11, WS 12.2

See question 16, UNIT 3 Review WS

How Layers of Earth was How Layers of Earth was DeterminedDetermined
• Seismic
• Heat Flow
• Gravity
• Magnetic Field

4. Magnetic Field
• Earth is dipolar = N & S pole
• Magnetic Filed is generated by electric currents in outer core
• Rocks with magnetic substances (iron, nickel) that cool below the Curie Point (580’C for magnetite) “lock-in” the present magnetic field.

4. Magnetic Field4. Magnetic Field

• Magnetic Inclination = deviation in magnetic field from horizontal
• Compass wants to point down at north end; up at south end.
Magnetic pole
True north pole
Lines of magnetic
force
Inclination/tilt of compass
needle

• Inclination can tell us the latitude of the continents/terranes at the time of Curie.– i.e. many of the BC terranes formed about 30’
latitude.

MagneticMagnetic InclinationInclination

• Magnetic Declination = angle between true north pole and magnetic north pole
True north pole (Santa’s home) magnetic north
pole
Chilliwack
19’ EastImportant for surveying…more on this in Chp 13
1290 km
compass

Magnetic DeclinationMagnetic Declination



The Magnetic The Magnetic Pole moves Pole moves clockwise clockwise
(precesses) CW (precesses) CW around and around and
generally near generally near the True Pole. the True Pole. The large scale The large scale movement of movement of the magnetic the magnetic pole/magnetic pole/magnetic field indicates field indicates
plate movementplate movement

• Magnetic Anomalies = variations in normal strength of magnetic field– Measured with magnetometer.– Positive anomaly = stronger magnetism
• Iron ore area (Great Lake region)• Lava flows (mafic rx) (Columbia basalts)• submarine, ship• Diamond mine/volcanic pipe
– Negative anomaly• Sedimentary rock• Salt dome, coral reef
See WS 10.2 Note helper, top of page 2.

+ mag’ anom’
- mag’ anom’
Sed’ rx Lava flow/ diamond
pipeSalt dome/
reef
Fe ore

• Magnetic Reversals: the magnetic field periodically weakens and reverses N to S and S to N. This is recorded in igneous rx that cooled below the Curie Point

• The magnetic field has weakened 5% in the last 100 yrs (15% in last 200), and is predicted to be nil in a few 1000 years, then will reverse, and build up again.– Last switched 70,000 yrs ago.
• Paleomagnetism: study of ancient magnetism.

Reversal of Earth’s Reversal of Earth’s
Magnetic FieldMagnetic Field AnimationAnimation

Do WS 10.3Do WS 10.3Look at Unit 3 Review WS. There is a Look at Unit 3 Review WS. There is a
“bottleneck” at the end of Unit 3, so “bottleneck” at the end of Unit 3, so do NOT leave the Unit 3 Review WS do NOT leave the Unit 3 Review WS to the last few days. You have been to the last few days. You have been warned!warned!