GEOLOGIC TIME “HISTORY OF THE EARTH”. LEARNING TARGETS 2a) I can distinguish between eons, eras,...
-
Upload
benjamin-adams -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
0
Transcript of GEOLOGIC TIME “HISTORY OF THE EARTH”. LEARNING TARGETS 2a) I can distinguish between eons, eras,...

GEOLOGIC TIME“HISTORY OF THE EARTH”

LEARNING TARGETS
2a) I can distinguish between eons, eras, periods, and epochs (DOK 1).
2b) I can identify the order of the eras and the relative length of the eras (DOK 1).
2c) I can identify key geological and biological features of the 4 different eras (DOK 1).

ESSENTIAL QUESTION
How is Earth’s history organized?

HOW OLD IS THE EARTH?About 4.6 billion years old

HOW WAS EARTH FORMED?
13.7 bya-BIG Bang Explosion of atomic particles Cooling to form clouds of H and He Star formation Galaxies Clusters
4.5 bya-Solar System Forms (Nebular Hypothesis)
Solar nebula (rotating cloud dust/gas)Planetesimals (clumps formed in spinning disk of matter)
8 Protoplanets & moonsEarly Earth impact moon

HOW IS EARTH’S HISTORY ORGANIZED?
Scientist use fossils and other clues to organize the events in Earth’s history into a timeline.
Geologic time is organized into lengths of time based on life forms present and events such as extinctions.
There are 5 mass extinctions that scientist know about throughout history.
-Cretaceous-Tertiary (KT) extinction, 65 mya- Killed the dinosaurs.
- Permian-Triassic (PT) extinction, 251 mya– Killed about 95 % of all species.

WHEN WERE THE MASS EXTINCTION EVENTS?
Mass Extinction Event
Time Frame (mya)
Types of Life Effected
Late/End Ordovician 443 mya Many species of Trilobites, Brachiopods, Graptolites, Echinoderms and Corals
Late/End Devonian 354 mya Many marine families on tropical reefs, Corals, Brachiopods, Bivalves, Sponges
Late/End Permian 248 mya 57% of all marine families, Trilobites, Eurypterids, Mollusca devastated along with Brachiopods. Many vertebrates
Late/End Triassic 206 mya Mollusca phyla, Sponges, marine vertebrates, large amphibians, many mammal-like reptiles
Late/End Cretaceous
65 mya Ammonites, Marine reptiles, dinosaurs, pterosaurs, microscopic marine plankton, Brachiopods, bivalves, and echinoderms

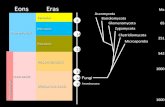
WHAT ARE THE DIVISIONS OF GEOLOGIC TIME?Geologic time is divided into:EonsErasPeriodsEpochs



WHAT ARE THE FOUR ERAS?
1. Precambrian Era (4600-544 mya) Longest era, bacteria-like life forms present.

WHAT ARE THE FOUR ERAS?
2. Paleozoic Era (544-248 mya) Broken down into 7 periods. 1st plants, fish, reptiles, amphibians, and insects.

WHAT ARE THE FOUR ERAS?
3. Mesozoic Era (248-65 mya) Broken down into 3 periods. Era of the dinosaurs and first mammals and birds.

WHAT ARE THE FOUR ERAS?
4. Cenozoic Era (65 mya – present) 2 periods, mammals are abundant. Homo sapiens evolve.

CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING
Write a paragraph that covers the following:
How Earth was formed
How Earth’s history is organized
The divisions of time that is used for Earth’s history
A summary of the four eras