Geography Honors Europe. Map Work Atlas Work- Introduction to Europe Fill out a political map of...
-
Upload
jemima-rose -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
2
Transcript of Geography Honors Europe. Map Work Atlas Work- Introduction to Europe Fill out a political map of...
- Slide 1
- Geography Honors Europe
- Slide 2
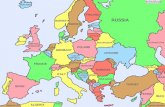
- Map Work Atlas Work- Introduction to Europe Fill out a political map of EuropePlace countries and capitals on the map. Do not forget Andorra, Vatican City, Monaco, San Marino (do not need to find a capital for these countries) Use blue or black ink Color each country to show boundary lines, do not use the same color to countries next to each other. Physical map: answer questions on the Physical Feature of Europe worksheet, and then place those physical features on the physical map. Also locate the Rhine River Use blue or black ink Shade or outline where the physical features are; do not have to color the water.
- Slide 3
- Physical Geography Relative Location? Europe is physically smaller than the United States, but has nearly twice the population. The majority of Europe is highly urbanized and densely settled. Climate Europe has an advantage Europes overall climate is relatively mild considering its high latitude. Prevailing Westerly winds and the North Atlantic Drift; winds blowing off warmer water bring mild, humid conditions to a large portion of Europe.
- Slide 4
- Scandinavia and much of southern Europe are hilly or mountainous, especially in the Alps, Pyrenees, and Carpathian mountains. Between these rugged areas lies the immense and agriculturally fertile North Europe Plain. Most important rivers are the Rhine and Danube. Pg. 62 and 115
- Slide 5
- Historical Impact Until the 15 th century, Europe played a minor role in world affairs, but the Age of Discovery began establishing Europe as a center of colonization, trade, and technological innovation. European nations wound up colonizing, settling, and profoundly altering much of the rest of the world. Industrial Revolution originated in Europe. Europes dominance began unraveling in the 20 th century, after two devastating world wars fought mainly on European soil and the loss of many European colonies. Also, the rise of Nationalism. Europe continues to be an important and wealthy region and moving into a postindustrial economy.
- Slide 6
- Cultural and Historical Homework: Read 3.3 and answer questions Examine, language and religion Review devolution and articles provide examples within Europe. Due Monday
- Slide 7
- European Union Round Table Read European Union section in book and the articles. What countries are part of the European Union? What is the main goal of the European Union? Why was it created? How do you become a member of the European Union? What countries are on the waiting list? Any Problems? Homework: Chapter 4 worksheet
- Slide 8
- Europe: Regions European CoreWestern Europe Mediterranean EuropeSouthern Europe Eastern Europe Northern Europe Comparison Chart: Create four boxes that represent each region. Mention the countries within each region, physical traits (climate, vegetation, etc.), cultural traits, and historical impacts. Brainstorm as well, what do you know about the countries within each region? You may bullet statements, but each still needs to be in complete sentences, except the list of countries.
- Slide 9
- European Core Middle Ages Feudalism Magna Carta parliament Protestant Reformation Martin Luther French Revolution Napoleon Industrial Revolution Started in England and spread to France and Germany. Later spread to colonies such as North America. Imperialism World War I and II Cold WarBerlin Wall
- Slide 10
- Slide 11
- Northern Europe Five Themes assignment Pick one Northern European country to create a small five theme essay to describe the country. You may select a Benelux country as well.
- Slide 12
- Eastern Europe Byzantine Empire Crusades Cold War.satellite nations Balkanization nationalism Article on Serbia
- Slide 13
- Southern/Mediterranean Europe Greek Empire Roman Empire Crusades Renaissancestarted in Italy HEI exampleVenice
- Slide 14
- Venice Humans created this unique environment. Venice, Italy is made of about 120 islands and part of the mainland. A broad waterway called the Grand Canal flows between these islands There are 150 canals that snake around the city. You can either walk or take a boats to travel around Venice. How was Venice built? Builders sunk wooden pilings into the ground to help support the structures above. So much wood was needed many parts of Northern Italy was flattened. Weight of buildings is so great that it has compressed the underlying ground. This is one of the reasons why Venice is gradually sinking. Other reasons include rising sea levels and the removal of too much groundwater by pumping.
- Slide 15
- Venice Problems: There is severe water pollution that threatens historic buildings. Pollution includes: Industrial waste and sewage Algae is created and when algae decays buildings it uses up oxygen which destroys fish
- Slide 16
- Research Paper Go over instructions Two days in library 110 points Pick topic by Monday