Geodetic Geocentric
Transcript of Geodetic Geocentric

Geodetic and Geocentric LatitudeASEN 3200
George H. Born
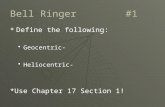
Figure 1 Reference Ellipsoid representing the Earth
Geocentric Latitude – The acute angle measured perpendicular to the equatorial
plane and a line joining the center of the earth and a point on the surface of the reference
ellipsoid. ( )
Geodetic Latitude – The acute angle between the equator and a line drawn
perpendicular to the tangent of the reference ellipsoid. Map coordinates are given as
longitude and geodetic latitude.
Reduced Latitude – See figure 1 for definition
Reference : P.R. Escobal, “Method of Orbit Determination”, John Wiley & Sons, NY,
1965 # Page 24-29 and 135-136.
1
2/6/2001
R+
xy
z
b
a
CircumscribingCircle
Cross section of ellipse
NorthObserver
Equator

Useful Equations
= = ; =
cos = = ; =
In terms of geocentric latitude, we have
x = , r = =
z =
Where e is the eccentricity and f is the flattening of the ellipsoid.
For the World Geodetic Survey (WGS-84)
, = , = , e = 0.0818191
In terms of geodetic latitude, we have
=
=
x = , z = , r =
Note that if we wish to find x and z for a tracking station located at height H above the
reference ellipsoid we must add (H cos ) to x and (H sin ) to z (see Eqn. 2.8-7 in Bate
Mueller and White).
The relation between and is given by
2

=
3