gcse nervous system
description
Transcript of gcse nervous system

BODY SYSTEMS BODY SYSTEMS

NERVOUS SYSTEM

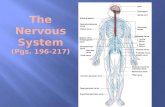
The Nervous System
• A network of billions of nerve cells linked together in a highly organized fashion to form the rapid control center of the body.
• Functions include:– Integrating center for homeostasis (the
maintenance of our internal processes), – Movement– and almost all other body functions.

DO YOU KNOW ANY PARTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?

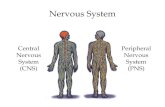
Organization of the Nervous System
Together, the spinal cord and the brain make up the Central Nervous System (CNS).
• The brain receives information, makes a decision and then sends instructions.
• The spinal cord is made up of sensory and motor nerves and sends messages from the brain to the body.

Peripheral Nervous System
• Responsible for communication between the CNS and the rest of the body. Can be divided into:
• Sensory Division Conducts impulses from receptors ( eyes, ears,
heart, muscles ect) to the CNS Informs the CNS of the state of the body interior and
exteriorSensory nerve fibers can be somatic (from skin,
skeletal muscles or joints) or visceral (from organs w/i the ventral body cavity
• Motor DivisionConducts impulses from CNS to the muscles and
organs.

Motor Efferent Division• Can be divided further:
– Somatic nervous system • VOLUNTARY (generally)• Somatic nerve fibers that conduct impulses from
the CNS to skeletal muscles
– Autonomic nervous system• INVOLUNTARY (generally)• Conducts impulses from the CNS to smooth
muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands.

Importance of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord acts as the primary information pathway between the brain and all the other nervous systems of the body. It receives sensory information from the skin, joints, and muscles of the trunk, arms, and legs, which it then relays upward to the brain. It carries messages downward from the brain to the PNS, and contains motor neurons, which direct voluntary movements and adjust reflex movements. Because of the central role it plays in coordinating muscle movements and interpreting sensory input, any kind of injury to the spinal cord can cause significant problems throughout the body.

Skeletal System
• The four functions of the skeletal