Gas Exchange not just in the lungs. Gas exchange starts in the lungs......but it happens everywhere!...
-
Upload
damian-cross -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
4
Transcript of Gas Exchange not just in the lungs. Gas exchange starts in the lungs......but it happens everywhere!...
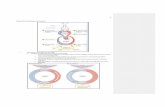
Gas exchange starts in the lungs...
...but it happens everywhere! The heart and blood vessels make up the cardiovascular system, which takes oxygen nearly everywhere in the body.
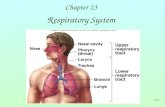
Inspiration (inhale)
● lungs fill with air● air moves through
bronchi into alveoli
● oxygen moves down concentration gradient into the blood stream
Concentration Gradient Review
There are differences in “concentration” within and between cells- different numbers of molecules in a given space. Molecules will try to distribute themselves evenly, even on different sides of membranes. It takes energy to move a molecule against its concentration gradient!
Circulation
● Oxygen binds with hemoglobin, which is located in red blood cells (RBCs)
● Now we’ll trace an RBC through circulation
● From the lungs, the RBC moves through the pulmonary veins to the heart
O2 is blue, bound in center of hemoglobin molecule
Sending oxygen to the hand
Our RBC exits the left ventricle, travels up the aorta, through the brachial (latin for ‘arm’) artery, and on to the hand.
Blood vessels permeate muscle tissue
● The RBC reaches the tiniest blood vessels, known as capillaries
● Concentration gradients are now the opposite of what they were in the lungs- lots of CO2 in the tissue and O2 in the blood stream
● Both move down their concentration gradients
CO2 crosses membranes
CO2 delivered to RBCs
CO2 delivered to lungs for expiration
From cells in organ tissue to capillaries, CO2
moves down its concentration gradient and enters RBCs.
capillary in skeletal muscle
Our RBC now carries CO2- “deoxygenated”
● The RBC travels back through veins towards the heart
● Once back in the heart, the heart pumps it back to the lungs
Expiration (Exhaling)
CO2 moves down its concentration gradient, into the alveoli of the lungs. O2 is moving from alveoli into the bloodstream. We’re back at the start!