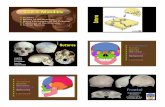
Functions of mandible
-
Upload
zeeshan-ali -
Category
Documents
-
view
232 -
download
0
Transcript of Functions of mandible

8/7/2019 Functions of mandible
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/functions-of-mandible 1/23
Functions of mandible

8/7/2019 Functions of mandible
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/functions-of-mandible 2/23
Osteology of the mandible
body
angle
ramus
Coronoid
process
body
condylar
process
head
neck
Mentalforamen
mandibular foramen
Mylohoid
line
Mylohoidgroove
Subamndibular fossa
Sublingual
fossa
Digastricfossa
Genialtubercles
Pterygoid fossa
notch

8/7/2019 Functions of mandible
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/functions-of-mandible 3/23
Temporal fossa
� Bounded by the superior andinferior temporal lines.
� Inferiorly, the infratemporalcrest separates it from theinfratemporal fossa.
� The floor is formed by parts of
the four bones that form thepterion.
Superior temporalline
Inferior temporal
line
Infratemporal crest
frontal parietal
temporalsphenoid
pterion

8/7/2019 Functions of mandible
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/functions-of-mandible 4/23
Temporal fossa� Roof: temporal fascia.
± Attached to the superior temporal lineand passes down to the upper borderof the zygomatic arch.
� Superficial temporal vessels andauriculotemporal nerve are superficialto the temporal fascia.
� The deep temporal vessels and nerves
are deep to the temporal muscle
Temporal fascia
Superficialtemporal vessels
Auriculo-temporalnerve

8/7/2019 Functions of mandible
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/functions-of-mandible 5/23
Muscles of mastication:
� Temporalis
� Masseter
� Medial pterygoid
� Lateral pterygoid
All are attached to the mandible All receive motor supply from the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (the only
division that carries motor fibers).

8/7/2019 Functions of mandible
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/functions-of-mandible 6/23
Muscles of mastication: temporalis� Fan shaped
(triangular) muscle,attached to the
temporal fossa and
temporal fascia.
� Inserted into the
coronoid process
of the mandible
� The upper and anterior fibers elevate the mandible
(close the jaws).� The posterior fibers retract the mandible, they are
the only fibers to do so.
temporalis
Deeptemporalnerves and
vessels
Temporal fascia
Coronoidprocess

8/7/2019 Functions of mandible
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/functions-of-mandible 7/23
Muscles of mastication: masseter� Quadrate muscle
� Between the zygomatic arch and the angle and
lateral surface of the ramus of the mandible.
� It acts to close the jaws and contributes to
protrusion.
masseter

8/7/2019 Functions of mandible
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/functions-of-mandible 8/23
Lateral pterygoid muscle� Has two heads:
± lateral surface of the
lateral pterygoid plate
(inferior head)
± infratemporal surface of
the greater wing of the
sphenoid (superior head).
� Inserted into the neck of themandible and the capsule and
intra-articular disk of the TMJ.
� The muscle draws the condyle
and intra-articular disc
forwards from the glenoid
fossa down the slope of
articular eminence: Active
opening of the mouth.
Superior head
Inferior head
Intra-articular disc

8/7/2019 Functions of mandible
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/functions-of-mandible 9/23
Medial pterygoid muscle
� Medial surface of the lateral
pterygoid plate (deep head).
� Tuberosity of the maxilla
(superficial head).
� Muscle fibers run downwards,
backwards, and laterally to beinserted into the deep surface of
the angle of the mandible
(opposite the insertion of
masseter).
Superficialhead
deep head
Medialpterygoid
� The muscle thus moves themandible upwards, forwards, and
medially (i.e. closes the mouth and
when acting on one side it moves
the mandible to the opposite side).

8/7/2019 Functions of mandible
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/functions-of-mandible 10/23
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ)� Type: A modified hinge type of synovial
joint� Articulation: between the condyle of the
mandible on one side and the articular
tubercle and mandibular fossa of the
temporal bone on the other side.
Mandibular fossa
Articular tubercle
Mandibular head

8/7/2019 Functions of mandible
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/functions-of-mandible 11/23
TMJ- intra-articular disc
� Made of fibrocartilage.� Covers both the mandibular fossa and the articular eminence in front of it (so that it is
shaped like a jockey¶s cap).
� Its circumference blends with the capsule.
� It divides the joint into a superior and inferior compartments.
� The gliding movements of protrusion and retrusion occur in the superior compartment.
� The hinge movements of depression and elevation occur in the inferior compartment.
Mandibular
fossa
Articular tubercle
Mandibular head
Articular disc

8/7/2019 Functions of mandible
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/functions-of-mandible 12/23
Ligaments� The lateral ligament
(temporomandibular):intrinsic, very strong.
± Prevents posterior dislocationand fracturing the tympanicplate when a severe blow fallson the chin.
� Two other ligaments (extrinsic) neither of them provides muchstrength to the joint.
± Stylomandibular ligament(thickened band of parotidfascia) runs from the styloidprocess to the angle of themandible.
± Sphenomandibular ligamentruns from the spine of the
sphenoid to the lingula of themandible.
Lateral lig.
stylomandibular lig.
sphenomandibular lig.
Tympanic plate

8/7/2019 Functions of mandible
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/functions-of-mandible 13/23
Movements
� Opening-closing
� Protraction-retraction
� Side to side movements

8/7/2019 Functions of mandible
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/functions-of-mandible 14/23
Movements� Opening-closing
the head of the mandible rotates on
the disk like the movement of a hinge
joint (lower compartment of the joint).
In addition to the simplehinge movement, the
disc carrying the head
with it glides forward
(upper compartment of
the joint).

8/7/2019 Functions of mandible
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/functions-of-mandible 15/23
Movements� The forward movement of the
mandibular head can be easily felt byplacing a finger in front of or in the
external acoustic meatus.
� Opening of the mouth:
± Passive: produced by gravity (a
simple hinge). The falling open
of the jaw during sleep illustrates
the effect of gravity. ± Active: produced by
submandibular muscles
(digastric, mylohyoid, and
geniohyoid) + lateral pterygoid
(being attached to the neck,
capsule and disc) producing the
foreword movement (a
compound hinge and gliding).
� Closure of the mouth is produced by
temporalis, masseter, and medial
pterygoid.
� Closure is therefore much more
powerful than opening
Mandibular head
Mandibular fossa
Mandibular head
Mandibular fossa
Mouth closed Mouth open
Lateral view of TMJ

8/7/2019 Functions of mandible
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/functions-of-mandible 16/23
Movements� Protraction-retraction
± Occurs in the upper compartment
of the joint
± Protraction: masseter, lateral and
medial pterygoid.
± Retraction: posterior fibers of
temporalis.� Side to side movements
± Occur in the upper compartment
± Produced by the pterygoids acting
on either side alternately.

8/7/2019 Functions of mandible
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/functions-of-mandible 17/23
17
Types of Mandibular Movement
� Rotational movement
± Horizontal axis of rotation
± Frontal (vertical) axis of rotation
± Sagittal axis of rotation
� Translational movement

8/7/2019 Functions of mandible
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/functions-of-mandible 18/23
18
Rotational Movement
� Around the horizontal axis (hinge axis)

8/7/2019 Functions of mandible
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/functions-of-mandible 19/23
19
Rotational Movement
� Around the frontal (vertical) axis

8/7/2019 Functions of mandible
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/functions-of-mandible 20/23
20
Rotational Movement
� Around the sagittal axis

8/7/2019 Functions of mandible
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/functions-of-mandible 21/23
21
Translational movement

8/7/2019 Functions of mandible
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/functions-of-mandible 22/23
TMJ dislocation
� When the mouth is open, the TMJ is very unstable.
� A blow on the mandible may cause anterior
dislocation bringing the condylar process in front of
the articular tubercle.Mouth open
Blow
Anterior
dislocation

8/7/2019 Functions of mandible
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/functions-of-mandible 23/23
TMJ dislocation
� Posterior dislocation isuncommon being resisted by thepostglenoid tubercle and thestrong lateral ligament.
Lateral lig.