Functional neuroanatomy of the neurological examination: Cranial...
Transcript of Functional neuroanatomy of the neurological examination: Cranial...

1
Functional
neuroanatomy of
the neurological
examination:
Cranial nerves
Chris Thomson
BVSc(Hons), Dip ACVIM (Neurol), Dip ECVN, PhD
Associate Professor Neurobiology,
Dept. of Vet. Med.,
University of Alaska, Fairbanks,
Alaska.
Ref: Parry and Volk: Imaging the cranial nerves.
Vet Radiol & US, 2011, 52, 1, Suppl 1, pp S32-S41

2
General principles– Sensory, motor, or mixed
– Parasympathetic – CNN III, VII, IX, X
– Sensory (afferent) connections
• Reflex function
• Sensory nucleus – trigeminal sensory complex
• Sensory perception – somatosensory cortex, cerebellum
– Motor
• LMN – somatic or visceral (autonomic)
– Nuclear arrangement in brainstem
• Ξ to fragmented spinal cord columns
– Only one CN that is pure CNS
– Attachment mainly ventral/ventrolateral
• except ???
Which cranial nerve is affected?

3
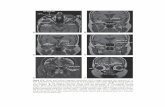
Fig 1.7 Thomson and Hahn
Fig 10.2 Thomson and Hahn,
Functional CNN nuclear columns in the brainstem

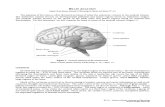
4Fig 10.1 Thomson and Hahn
Dog brain, ventral aspect, cranial nerves

5
Cranial nerve Brain attachment Function
sensory, parasympathetic, motor
I Olfactory Telencephalon Olfaction
II Optic Diencephalon Vision
III Oculomotor Mesencephalon Pupil constriction, extraocular muscles (which
ones?)
IV Trochlear Mesencephalon Extraocular muscles (which ones?)
V Trigeminal Pons/myelencephalon Facial sensation, masticatory muscles (which
ones?)
VI Abducens Myelencephalon Extraocular muscles
VII Facial Pons/myelencephalon Taste, GVA head, salivary, lacrimal glands,
Muscles of facial expression
Masticatory muscle (which one?)
VIII Vestibulocochlear Pons/myelencephalon Hearing, balance
IX Glossopharyngeal Myelencephalon Taste, salivary glands, Swallowing,
X Vagus Myelencephalon Taste, parasympathetic to body viscera
swallowing, laryngeal,
XI Accessory Myelencephalon Laryngeal function, neck muscles
XII Hypoglossal Myelencephalon Tongue muscles
Cranial nerves, attachment and main functions

6
To move both eyes to the right
requires stimulation of …
http://londonbeep.com/

7
Vision –
CN II
• Optic nerve– Visible CNS
• Optic chiasm– Variable degree of cross over
• Herbivores 80-90%
• Cats 65%
• Inversely related to stereoscopic vision– The more overlap of the visual fields, the less decussation at the optic chiasm
Fig 10.5 Thomson and Hahn,
Optic pathway and binocular vision

8
Vision• Pathway (cat)
– 80% fibres
-> Lateral geniculate nucleus
-> Optic radiation
-> Visual cortex
– 20% fibres to the midbrain
• Visual reflexes e.g. PLR and
head / eye turning
• Cerebral cortex – midbrain connections
– Required for
• Perception of movement
• Spatial orientation

9
Visual
Reflexes
• Rostral colliculus
– Tectonuclear (bulbar) – extraocular muscles
– Tectospinal – cervical muscles
– Function???
Fig 10.9 Thomson and Hahn,
Optic pathway and its connections

10
Pupillary light
reflex
Consensual reflex strength
inversely proportional to
degree of decussation at
the optic chiasm
- More decussation, the
stronger direct PLR
e.g. cat versus horse
Swinging light test
Fig 10.8 Thomson and Hahn,
Pupillary light reflex pathway

11
Menace Response• CN II, CN VII
• Menace deficit in cerebellar disease
– Mechanism?• Pathway? – visual cortex,
cerebellum, facial nucleus
• Cerebellar influence on cortex permitting the response?
– Ipsilateral cerebellar and menace deficit
Fig 13.8 Thomson and Hahn

12
The menace response appears in
kittens / puppies by _______
weeks of age

13
Somatosensory input from head
Fig 10.6 Thomson and Hahn, trigeminal sensory complex
Fig 10.6 Thomson and Hahn,
spinal cord, XS; What level?
Afferents: CNN V, VII, IX, X
To the trigeminal sensory complex
• Mesencephalon
• Pons
• Myelencephalon
Projects to contralateral somatosensory cortex
Substantia
gelatinosa.

http://www.winslowvetmobile.com/
http://www.saltoftheearth.
What cranial nerve is being
assessed in these images?

15
Vestibular System
Proprioceptors
• Hair cells with microvilli
• Location
– Membranous labyrinth inner ear/petrous temporal bone
• Function to maintain posture
– Head, neck, trunk, limbs, eyes
– During rest and motion
– Anti-gravity function
• Facilitate extensor muscle activity
Fig 8.8 Thomson and Hahn

16
Fig 8.1 Thomson and Hahn
X 3
Static equilibrium
Dynamic equilibrium

17
Hair cell function in head equilibrium
(balance)
• Deflection of microvilli
– towards/away from kinocilium
– Stimulates sensory nerve endings of vestibular portion CN VIII
• Static head equilibrium
– Detection by hair cells in sac structures
• Saccule – sagittal/vertical plane
• Utriculus – dorsal/horizontal planes
– Detect effect of gravity; constant tonic discharge
• Dynamic head equilibrium
– Angular acceleration/deceleration
– Detection by hair cells in semi-circular ducts
• Ducts in three planes: x, y, z
– Detect effect of acceleration in 3 planes

Fig 18.7 Uemura

19
Effect of gravity or linear acceleration on macula of sacculus or utriculus
Deflection of microvilli
• towards kinocilium – depolarisation (stimulation)
• away from kinocilium – hyperpolarisation (inhibition)
Saccule – sagittal/vertical plane Utriculus – dorsal/horizontal plane
Fig 8.2 Thomson and Hahn

20
Fig 8.3 Thomson and Hahn, effect of acceleration on SCD
– Head rotation
• Causes endolymph flow in 1+ pairs of ducts
• Deflects cupula -> bending microvilli
• Stimulating or inhibiting sensory nerve ending
• Microvilli deflected
– Towards kinocilium stimulates nerve endings
– Away from kinocilium, inhibits neural discharge

21
What are the effects of vestibular nuclei stimulation?

22
Fig 8.5 Thomson and Hahn
Vestibular nuclei connections
Fig 8.6 Thomson and HahnTo temporal lobe

Consequences of peripheral vestibular
apparatus input
• Vestibular portion of CNVIII
– Input to vestibular nuclei
• 4 pairs in myelencephalon
– Output to
• Spinal cord – postural
adjustment
• Extraocular muscles – eye
movement and position
• Cerebellum – head
proprioception
• Forebrain – conscious
perception
• Reticular formation
– Including vomiting centre

24
Fig 8.9 Thomson and Hahn
Effect of vestibular lesions; uneven stimulation of VN at rest,

What signs occur with abnormal
vestibular function?

26
Distance penlight test: for subtle anisocoria and strabismus

Differentiating VD
• Depends on what other structures are
– compromised (collateral damage)
– not compromised
– Other structures
• Inner/middle ear – peripheral VD
• Brainstem – central VD
• Cerebellum – paradoxical VD
27Fig 13.1 Thomson and Hahn

28
Paradoxical Vestibular Disease
• Lesion in caudal cerebellar peduncle or flocculonodular lobe
• Loss of inhibitory output to vestibular nuclei;
• XS stimulation on side of the lesion
Fig 8.10 Thomson and Hahn

Paradoxical Vestibular
Disease
• Signs– Head tilt to opposite side from lesion
– Nystagmus to side of lesion
– Ipsilateral ataxia and proprioceptive deficits
• Lesion location– Vestibulocerebellum or caudal cerebellar
peduncle• (see de Lahunta and Glass for more detail)
• Mechanism– Loss of inhibition of vestibular nuclei

30
Fig 10.15 Thomson and Hahn
Hearing – CN VIII

31
Mouse cochlea,
https://www.best.edu.au
SV
ST
Stria vascularis
BM
CD
Spiral
ganglion

Tortora, Fig 17-22

33
Hearing – CN VIII • Conscious hearing
– auditory cortex, temporal lobe
• Reflex function
– Muscles of the middle ear
• CN V to tensor tympanii and CN VII to stapedius mm.
– (t for trigeminal, s for seven)
• Muscle contraction affects compliance of tympanum (tympanometry)
– Caudal colliculus
• Head/eye turning in response to auditory stimuli
• Tectonuclear (bulbar) – extraocular muscles
• Tectospinal – cervical muscles
http://vethospital.tamu.edu
What animal type?

Onset of hearing, deafness• Onset of hearing
– Kittens 5 days
– Puppies 14 days
• normal by 4-5 weeks
• Deafness
– Conduction
• Otitis externa/media
– Sensorineural
• Congenital
– White coat blue eyes, some merle dogs
» ↓ melanocytes → stria vascularis and hair cell
degeneration
– Albinos OK
• Acquired
– damage to hair cells
» inflammation, neoplasia, ototoxicity
https://s-media-cache-ak0.pinimg.com https://upload.wikimedia.org

35
Fig 10.17 Thomson and Hahn
Auditory pathway in the brain
Fig 10.18 Thomson and Hahn
Brainstem auditory evoked reflex
I spiral ganglia, CN VIII
II cochlear nuclei
III dorsal nucleus of trapezoid body
IV ? (lateral lemniscus and nucleus)
V caudal colliculus
VI ? (medial geniculate nucleus)
VII ?

36
What else can BAER be used for?

37
A curious fact about CN VIII
http://upsidedowndogs.com
It’s only an afferent nerve – right?
• Olivocochlear reflex
(superior olivary nucleus = nucleus of the trapezoid body)
• Protective
– hyperpolarisation of hair cells
Discriminative
– neutralises background noise

38
Other CNN nuclei (VII, IX, X, XI)
Solitary tract and nucleus – sensory input: taste, carotid sinus, thoracic and
abdominal viscera
•Parasympathetic nucleus of VII and IX (Salivatory n.) – efferent to salivary glands
•Parasympathetic nucleus of X – Visceral efferent to thoracic and abdominal viscera
•Nucleus ambiguus – somatic efferent to larynx and pharynx
Fig 10.2 Thomson and Hahn

Recurrent laryngeal nerve damage can cause paralysis of
the ____ muscle and failure of glottal opening
Fig 10-20 Thomson & Hahn

40
Fig 10.19 Thomson and Hahn, Innervation
of the pharynx and larynx
Dyce, Figs 4-12 (2) and 4-14 (5)

41Fig 10.21 Thomson and Hahn,
Which cranial nerves innervate the
following function of the tongue?
– Motor
– Sensory (touch)
– Taste

42
Autonomic innervation of the head
• Parasympathetic (craniosacral origin)
– CNN III, VII, IX, X
– Functions?
• Sympathetic = (thoracolumbar origin)
– T1-3 (C8-T5)
– Not via CNN
– via sympathetic fibres from the cranial thorax
– Functions?

43