Chemical concentration, activity, fugacity, and toxicity: dynamic
Fugacity-based environmental modelsmodels Level 1--the equilibrium distribution of a fixed quantity...
-
Upload
merryl-mckinney -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
Transcript of Fugacity-based environmental modelsmodels Level 1--the equilibrium distribution of a fixed quantity...

Fugacity-based environmental models• Level 1--the equilibrium distribution of a fixed quantity of conserved chemical, in a
closed environment at equilibrium, with no degrading reactions, no advective processes, and no intermedia transport processes (eg. no wet deposition, or sedimentation).
• Level 2-- describes a situation in which a chemical is continuously discharged at a constant rate and achieves a steady-state and equilibrium condition at which the input and output rates are equal. Degrading reactions and advective processes are the loss or output processes treated. Intermedia transport processes (eg. no wet deposition, or sedimentation) are not quantified.
• Level 3--A Level III simulation describes a situation which is one step more complex and realistic than the Level II model. Like the Level II model, chemical is continuously discharged at a constant rate and achieves a steady state condition in which input and output rates are equal. The loss processes are degrading reactions and advection. Unlike the Level II model, equilibrium between media is not assumed and, in general, each medium is at a different fugacity. A mass balance applies not only to the system as a whole, but to each compartment. Rates of intermedia transport are calculated using D values which contain information on mass transfer coefficients, areas, deposition and resuspension rates, diffusion rates, and soil runoff rates. It is now essential to define inputs to each medium separately, whereas in Level II only the total input rate was requested.

Level 1 program• Physical-chemical properties are used to quantify a chemical's behavior in an
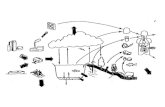
evaluative environment. Three types of chemicals are treated in this model: chemicals that partition into all media (Type 1), involatile chemicals (Type 2), and chemicals with zero, or near-zero, solubility (Type 3). The Level I Program assumes a simple, evaluative, closed environment with user-defined volumes and densities for the following homogeneous environmental media (or compartments): air, water, soil, sediment, suspended sediment, fish and aerosols.
• This model is useful for establishing the general features of a new or existing chemical's behaviour. A Level I calculation gives the general impression of the likely media into which a chemical will tend to partition and an indication of relative concentrations in each medium. The results of changes in chemical and environmental properties may be explored.

Air
Fish
Soil
Sediment
Suspended SedimentWater
Chemical:LEVEL I
Aerosols
LEGEND
EQUILIBRIUM
1
3 2
4
7
5
6

Inputs and outputs
The required input data are:
Chemical Properties:
chemical name
molecular mass
data temperature
Type 1 chemicals
- water solubility
- vapor pressure
- log Kow
- melting point
Type 2 and 3 chemicals
- partition coefficients
Environmental Properties: volumes for all 7 media densities for all 7 media organic carbon content (soil, sediment &
suspended sediment only) fish lipid content (Type I chemicals only)
Emissions: chemical amount
Model Output: partition coefficients (Type 1) Z values fugacity of the system concentrations and amounts for each
compartment a summary diagram

Z = “fugacity capacity”C = Z f
concentration = Z fugacity
units: mol/m3 = mol/m3Pa Palike Henry’s law, Z could also be dimensionless
At eqbm, f is equal in all phases:
f1 = f2= C1/Z1 = C2/Z2 so K12 = C1/C2 or Z2/Z1
all these parameters (C, Z, K) depend on T, P, properties of solute/solvent, etc.

Z is like C (heat capacity)
• At equilibrium, all phases will have same fugacity (temperature).
• C (heat capacity) = amount of heat (energy in J/unit volume)/Temperature
• Z = amount of chemical (moles per unit volume)/fugacity

Types of chemicals
• Type 1: chemicals that partition into all media– input VP, solubility, program calculates Kh
– Z factor of air is one (1/RT to convert units)
• Type 2: involatile chemicals – VP not available, so input everything as partition coefficients
– Z factor of water is one
• Type 3: chemicals with zero, or near-zero, solubility– Solubility not available, so input everything as K’s
– Z factor of air is one (1/RT to convert units)
All K’s must be internally consistent if everything is at equilibrium

Air
Water
Octanol
A gas is a gas is a gasT, P
Fresh, salt, ground, poreT, salinity
NOM, biological lipids, other solvents
Pure Phase(l) or (s)
Ideal behavior
PoL
Csatw
Csato
KH = PoL/Csat
w
KoaKH
Kow = Csato/Csat
w
Kow
Koa = Csato/Po
L

The fact that these are the same is anartifact, arising because the ratio of Kow to VP is the same for both PCB 52 and pyrene
INPUTS: pyrene PCB 52MW (g/mol) 202.3 292Data T (C) 25 25Log Kow 5.18 6.10water sol. (g/m3) 0.132 0.03VP (Pa) 0.00060 0.00490Melting pt. (C) 156 87
CALCULATED:Kh (Pa m3/mol) 0.92 47.7Sub-cooled liquid VP 0.0119 0.0201
Fugacity (Pa) 1.64E-08 7.09E-08Total VZ Products 3.01E+13 4.83E+12Amt of chem (mol) 4.94E+05 3.42E+05
% in each compartmentair 0.13 0.84water 0.72 0.087soil 97 97sedmt. 2.15 2.15susp. Sedmt. 0.067 0.067fish 0.0055 0.0055aerosol 0.0014 0.005