Favorable Outcome of Fournier Gangrene in Two Patients with ...
Fournier Gangrene-A Flesh Eating Disease
-
Upload
dr-diana-enachescu -
Category
Documents
-
view
1.362 -
download
10
description
Transcript of Fournier Gangrene-A Flesh Eating Disease

FOURNIER’S GANGRENE
A FLESH EATING DISEASE
Author : Biru Diana-MadalinaCo-authors: Pricop Mariana, Pricop DanielaScientific Coordinator: Dr.Nutu Vlad

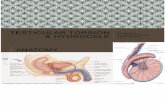
Fournier’s Gangrene
Fournier’s gangrene is a rapidly progressive fasciitis of the perineum. It was described in 1883 by Jean
Alfred Fournier, a French venereologist . Although most cases described occur in diabetic men 50–70 years old, Fournier gangrene also has been described in women. The rate of fascial necrosis has been documented to be as rapid as 2–3 cm/h .

The chart above shows the there has been an increase in the number of cases reported in the literature over the last decade.This probably is because of better recognition of this condition and an increase in the reporting of this condition in the medical literature.
Epidemiology of FG

Clinical case study
P.G. is a 51-year-old man without any significant pathology who presented himself to his primary care
doctor after 7 days of:
progressive pain swelling in his genital region low-grade fever asthenia

Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis for acute scrotal pain includes testicular traumatesticular torsionacute epididymo-orchitisFournier’s gangrene.

Clinical case study
There was no history of similar symptoms.
He denied recent trauma.
He had no nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, melena, or hematochezia.
He had dysuria.
Notably, he reported a 20 kg weight loss over the last year.

Physical examination
The patient was a mildly ill-appearing man in a severe sepsis shock and with acute renal failure.
He was awake and alert.
His vital signs included:

He was 1.67 cm tall and weighed 45 kg.
Head, eyes, ears, nose, and throat were normal.
Lungs were clear.
Heart was tachycardic with a normal s1 and s2 with no murmurs or gallops and no rub.
Abdomen was nontender and distended with normal bowel sounds and it revealed a palpable urinary bladder size 40x20 cm.
His extremities had no edema, and pulses were normal bilaterally.
Physical examination

Genital examination
Diffuse erythema ,fluctuance, edema of his scrotum,penis and perineal area, along with severe tenderness, measuring almost 10 x 20 cm with the development of a crepitus of the inflamed tissues.
There was a necrosis area measuring 4-5 cm in the center involving a part of the scrotum but sparing the penis. At compresion the necrotic area eliminated a foul
smelling, suggesting a microbial infection with anaerobic.
His perirectal area was erythematous, but there was no
evidence of fissures, ulcerations, or crepitus .

Fournier’s Gangrene Clinical Signs
Patients have a sudden onset of perineal pain and swelling.
Fever and leukocytosis.
Physical examination reveals • pain, • redness• swelling of the perineal area.
Crepitus from the soft-tissue gas can be palpated.

Digital rectal examination
On the posterior side of the rectum a necrosis area within 2x2 cm which eliminates gases with a fetid odor and pus.
The posterior part of the anal area revealed 4 warts which leaded to the presumtion of a condyloma acuminatum or a anal cancer.A biopsy was performed for diagnostic purposes

Fournier’s Gangrene Aetiology
The bugs: Staphylococcus aureus Streptococci Enterococci Escherichia coli Peptostreptococcus Preveoella and Porphyromonas Klebsiella Pneumonie Bacteroides fragilis Clostridium

Comorbid risk factors

Aetiology of FG
Anorectal or urogenital and perineal trauma, including pelvic and perineal injury or pelvic interventions are other causes of FG.


Investigations

Laboratory data

Laboratory data

Evolution27.03
28.03
29.03
30.03
31.03
2.04
3.04 4.04 7.04
8.04 9.04
11.04
Glucose
307 248 442 360 245 150 170 139 94 191 86Na 134 135 130 134 133 136 137
K 4,19
4,8 3,9 4,9 2,9 3,3 3
Cl 103 113 108 103 110 111 115
FA 228 149 240 185 220 163 330
Creatinine
4,99
3,98
3,02 2,62 2,22 2,46 1,93 2,11
1,82
Urea 114 105 94 79 67 80 81 61 36

Evolution
27.03 28.03 29.03 30.03 2.04 3.04 4.04 8.04 11.04
Hb 9,1 8,2 8,4 7,9 6,3 7 7,95 8 7,2
Ht 26,2 23,1 23,7 23,2 18,4 20,7 23,1 23 21,9
Leu 35600 31600 26900 19500 26500 22000 18700 11900 10200
Tr 484000 485000 497000 520000 595000 516000 629000 492000 470000

Diagnosis
PG’s. was diagnosed as having type 2 diabetes and Fournier’s Gangrene.

Pathological features

Normal skin is held tightly by proteins that make up the connective tissue that keep the dermis, epidermis and the muscle tightly connected.
But when bacteria invades the skin through open wounds and punctures of the skin, they cause devastating results by “eating” the protein and the connective tissue.
Pathological features
If left untreated the Bacteria will continue eating and destroying the skin and tissue beneath it until the muscle is infected, when this happens there is no hope of saving the person unless the infected area is surgically removed to keep the bacteria from spreading.
Normal skin Early stage Advanced stage

Photomicrograph showing presence of ulcerated epidermis. The dermis shows presence of thrombosed blood vessel and bacterial colonies (H&E, X200)
Pathological features

Pathogenesis
Thrombosis of subcutaneous and cutaneous blood vessels produces gangrene, but the fascial necrosis is usually more extensive than the visible gangrene suggests.
Classic findings are necrosis of the superficial and deep fascial planes, fibrinoid coagulation of the nutrient arterioles, polymorphonuclear cell infiltration, and positive microorganism culture of involved tissues.

Pathogenesis
The synergistic activity of aerobes and anaerobes lead to the production of various exotoxins and enzymes like collagenase, heparinase, hyaluronidase, streptokinase, and streptodornase, which aid in tissue destruction and spread
of infection.
The platelet aggregation and complement fixation induced by the aerobes and the heparinase and collagenase lead to microvascular thrombosis and dermal necrosis. In addition the phagocytic activity is impaired in the necrotic tissue, aiding in further spread of the infection.

Paraclinical signs

Treatment-4 main principles

Treatment –Resuscitation and Antibiotics
The patient was hemodynamically stabilized.
Resuscitation with normal saline and broad-spectrum antibiotics (ciprofloxacin,peniciline and metronidazole) was commenced immediately.
A Foley catheter was used to drain urine and the pacient eliminated 3500 ml of urine along with hematuria at the end.

Consent for radical DEBRIDEMENT, as well as possible colostomy.
Radical surgical excision of the entire necrotic tissue
Frequent wound dressings with hypertonic saline
His testicles were preserved and he required a colostomy.
He received diabetes education and performed self-monitoring of blood glucose four times a day. He was treated with insulin. His diabetes was then managed as an outpatient with no subsequent readmissions.
Treatment - Debridment

Treatment - Debridment
After a week, the denuded area was covered with healthy granulation tissue.

Treatment – wound dressing
Frequent wound dressings with hypertonic saline

Treatment - Reconstruction
The patient was sent to the Plastic Surgery Clinic for skin grafing.
Split-thickness skin grafting (STSG) is a safe and easy method to cover these raw areas. However, stabilizing the grafts may be difficult due to free mobility of the testicles. STSG can be done by using stamp-sized grafts or by the mesh technique. Mesh skin grafting offers the advantage of covering a large area with a small sheet of donor skin but needs specialized equipment, i.e., mesh graft plate and roller.
In our patient, we used stamp sized multiple skin grafts to achieve maximum coverage of the denuded area of the perineum and scrotum.

Conclusions
Fournier's gangrene is an abrupt, rapidly progressive, gangrenous infection of the external genitalia and perineum and a realy life threatning disease.
Prompt diagnosis and early surgical intervention is required for a better outcome of these patients.
Resuscitation and corection of electrolyte disturbances is very important
Empiric broad spectrum antibiotics must be used
Urgent surgical debridment remains the cornerstone of the treatment
Fecal and urinary diversion might be necessary to avoid wound contamination or to facilitate the treatment of underlying pathology or both
Continued medical care in the form of a multidisciplinary approach is necessary as these patients may require reconstructive procedures in the future.
Proactive management of the diabetic and immunosuppressed patients with perineal infections is of extreme importance to prevent the development of the condition in the first instance as this condition in the presence of such comorbidities is associated with high mortality.

Thank you!