FOOD PRESERVATION
-
Upload
airtel -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
201 -
download
1
Transcript of FOOD PRESERVATION

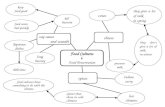
What is Food Preservation
A process by which certain foods like fruits and vegetables are prevented from getting spoilt for a long period of time. The colour, taste and nutritive value of the food is also preserved.When you keep fruits, vegetables or left over dal in therefrigerator or in a cool place, will this be called food preservation? No, because you can store fruits and vegetables or left over dal in this state for a few days onlyThe definition of food preservation states that the preserved food should retain their colour and taste. This means that the colour and taste of food which is present at the time of preservation should not change

Preserving food involves creating environments that microorganisms do not like.
*Preservation Techniques:
1. Drying
2. Smoking
3. Salting
4. Pickling
5. Canning
6. Cold Temperatures

Food Preservation Methods
Drying is the food preservation process that consists of removing the food’s water, which effectively inhibits the growth of microorganisms. Like: Sun Drying

Food Preservation Methods
Commercial Drying The most important types of commercial
drying are: Conventional: heat.Vacuum: pulls the water out.Osmotic: water drawn out by osmosis.Freeze-drying: ice crystals vaporize.

Food Preservation Methods
Sublimation: The process in which a solid changes directly to a vapor without passing through the liquid phase.

Food Preservation Methods
Cure: To preserve food through the use of salt and drying. Sugar, spices, or nitrates may also be added.
Fermentation Pickling uses vinegar to preserve foods. Edible coating: Thin layer of edible material
such as natural wax, oil, petroleum-based wax, etc. that serves as a barrier to gas and moisture.

Food Preservation Methods
Canning is a two-step process: First the food is prepared by being packed into
containers, which are then sealed.
Then the containers are “canned,” or heated to ensure that all microorganisms are destroyed.
Sterilization: The elimination of all microorganisms
through extended boiling/heating to temperatures much higher than boiling or through the use of certain chemicals.

Cold Preservation
Refrigeration slows down the biological, chemical, and physical reactions that shorten the shelf life of food.
For safety purposes, refrigerators should be kept between just above freezing to no more than 40°F (4°C).
All perishable foods should be refrigerated as soon as possible, preferably during transport, to prevent bacteria from multiplying.

Cold Preservation
Freezing makes water unavailable to microorganisms.
The chemical and physical reactions leading to deterioration are slowed by freezing.
Rancid: The breakdown of the polyunsaturated fatty acids in fats that results in disagreeable odors and flavors.
Freezer burn: White or grayish patches on frozen food caused by water evaporating into the package’s air spaces.

Heat Preservation
Pasteurization: A food preservation process that heats liquids to 160°F (71°C) for 15 seconds, or 143°F (62°C) for 30 minutes, in order to kill bacteria, yeasts, and molds.

Thank youThank you
presented by saurabh bansal B.tech ECE 3rd sem 04/25/15