Fitzroy catchment water quality targets · Noosa Cooroy Bundaberg Maryborough Gympie Rosedale...
Transcript of Fitzroy catchment water quality targets · Noosa Cooroy Bundaberg Maryborough Gympie Rosedale...

FITZROY REGIONFitzroy catchment water quality targets
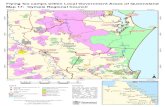
Catchment profileUnder the Reef 2050 Water Quality Improvement Plan, water quality targets have been set for each catchment that drains to the Great Barrier Reef. These targets (given over the page) consider land use and pollutant loads from each catchment.
The Fitzroy catchment covers 142,552 km2 (92% of the Fitzroy region). Rainfall averages 646 mm a year, which results in river discharges to the coast of about 6018 GL each year.
The Fitzroy catchment covers the majority of the Fitzroy region. Lying inland of the region’s smaller coastal catchments, it is the largest catchment draining to the Great Barrier Reef lagoon. The Fitzroy River forms the main channel transporting run-off from the whole catchment, which comprises an extensive network of tributaries. Some of these are an extensive area in their own right. There are five main tributaries: the Connors and Isaac rivers in the north of the catchment; the Nogoa River in the western reaches of the catchment, which joins the Mackenzie; and the Dawson River in the south of the catchment, which also joins the Mackenzie to form the Fitzroy River. Agriculture is the major land use in the catchment; this is mostly grazing but also includes large areas of cropping, forestry and horticulture. The Fitzroy catchment also contains a diverse array of wetlands, waterways, floodplains and lagoon systems. It includes a number of urban centres, including Rockhampton and Emerald, and the area is known for mining.
20 40 60 80 100
Grazing ForestryNature
conservationDryland cropping
OtherIrrigated cropping
WaterUrban
Horticulture
0%
Land uses in the Fitzroy catchmentThe main land uses are grazing (80%), forestry (6%), and nature conservation (6%).
Belyando Sub-catchment
B o w e n B o g i eS u b - c a t c h m e n t
B u r d e k i n S u b - c a t c h m e n t
C o m e t S u b - c a t c h m e n t
D a w s o n S u b - c a t c h m e n t
Fitzroy Sub-catchment
I s a a c S u b - c a t c h m e n t
M a c k e n z i e S u b - c a t c h m e n t
Nogoa Sub-catchment
T h e r e s a C r e e kS u b - c a t c h m e n t
PaulReef
HeronReef
MangroveIsland (No 1)
LongIsland(No 1)
South Island
Middle Island
TurkeyIsland
RosewoodIsland
Quail Island
TownshendIsland
Curtis Island
HummockHill Island
FraserIsland
Facing Island
Great Keppel(Wop-pa)Island
LeicesterIsland
BoyneIsland
BalaclavaIsland (No 2)
Casuarina Island
Frigate Cay
Mystery Cay
TwinCays
(North)
SnakeCays
CapeCapricorn
Cape Clinton
CapeKeppel
CapePalmerston
Cape Manifold
CapeTownshend
S W A I NR E E F S
H e r v e y B a y
Ke ppe lBa y
B r o a dS o u n d
ShoalwaterBay
GinGin
Childers
Mundubbera
TinCanBay
Biggenden
ProstonMurgon
WondaiCherbourg
Kilkivan
Gladstone
Yeppoon
Emu Park
Tannum Sands
Miriam ValeBororen
Calliope
Mackay
Mount Morgan
Gayndah
Monto
Nambour
Kingaroy
NanangoKumbia
Yandina
NoosaCooroy
Bundaberg
Maryborough
Gympie
RosedaleAvondale
Burnett HeadsBargara
Imbil
Eidsvold
HerveyBay
Augathella
Walkerston
Nebo
SarinaSarina Beach
Alpha
Emerald
Springsure
Rockhampton
Clermont
St Lawrence
Marlborough
Moranbah
Dysart
Middlemount
Capella
BlackwaterDingoBluff
Woorabinda
Banana
Biloela
Thangool
MorvenMitchell
Injune
Miles
Taroom
Wandoan
Theodore
Roma
Moura
KeppelSands
MountLarcom
Boyne Island
Carmila
Tieri
Duaringa
Baralaba
Gracemere
FitzroyCatchment
Bur
nett River
Eagle fi eld
Creek
R olf C reek
Roper Cr eek
ClaudeRi ver
De
e Rive
r
Don R
iv e r
Nogo River
Cad
ar
gaC
reek
VandykeC
reek
Diam
ond Creek
Fun
nel Cre
ek
Baffl e Cre ek
Fox
Cr
eek
Kroombit C reek
Co
nnor
s Rive
r
TinanaCreek
Zam
ia
Cree
k
Hutton Creek
BeeCre ek
Juandah
C
reek
Logan Creek
Thre e MoonC
ree
k
Robinson Creek
S
tuartR
iverAlpha
Creek
Ca
l lideCreek
Eurom b ah Creek
Pla
netC
reek
Barambah
C reek
Mim
os aC
r eek
Comet
Ri ver
Kolan
River
Mis
take
Cree
k
BelyandoRiver
Ther es
a Cr
ee k
Native
Com
panion
Creek
BoyneRiver
Auburn River
Isaac River
Sutto
rR
iv er
Mary
Rive
r
Fitzr
oy Riv erMackenzie Rive
r
N ogoa
Ri ve
r
DawsonR iver
0 30 60 90 120 150
Kilometres
C:\WORKING\3_WORK\Nyssa\GBR catchments map_A4P_v03_Jeremy_Edit_Fitzroy.mxd23 August 2017
Page of
LanduseNature conservationForestry
GrazingIrrigated croppingDryland croppingSugarcaneHorticultureBananaDairyUrban and other intensive usesMiningStream/water inc. damsOther
Legend
!(T
MangroveSeagrass
Sewage treatment plant (STP)[
Ý
Z Dams and weirs
GBR WHA boundary
CatchmentHighwaysSecondary roads

Modelled water quality pollutant loadsThe Fitzroy has minimal anthropogenic loads of dissolved inorganic nitrogen.
The Fitzroy catchment contributes the largest loads of anthropogenic fine sediment in the region, and is the second biggest contributor of the 35 catchments that drain to the Great Barrier Reef. Most of the sediment comes from grazing lands, and includes gully and streambank erosion.
reefplan.qld.gov.au
2025 water quality targets and priorities
End-of-catchment anthropogenic load reductions required from 2013 baseline
Pesticides
Dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN)
Fine sediment Particulate phosphorus (PP)
Particulate nitrogen (PN)
maintain current load
30% 390 kilotonnes
30% 380 tonnes
30% 640 tonnes
To protect at least
99% of aquatic species at the end of catchment
The 2025 targets aim to reduce the amounts of fine sediments, nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus) and pesticides flowing to the reef. Where there are minimal anthropogenic pollutant loads, the aim is to maintain current water quality so there are no increases in loads. Each target for sediment and nutrients is expressed as: (a) the percentage load reduction required compared with the 2013 estimated load of each pollutant from the catchment; and (b) the load reductions required in tonnes. Progress made since 2013 will count towards these targets. Previously reported progress between 2009 and 2013 has already been accounted for when setting the targets. The pesticide target aims to ensure that concentrations of pesticides at the end of each catchment are low enough that 99% of aquatic species are protected. The targets are ecologically relevant for the Great Barrier Reef, and are necessary to ensure that broadscale land uses have no detrimental effect on the reef’s health and resilience.
A high percentage reduction target may not necessarily mean it is the highest priority. The priorities (ranked by colour) reflect the relative risk assessment priorities for water quality improvement, based on an independent report, the 2017 Scientific Consensus Statement. The priorities reflect scientific assessment of the likely risks of pollutants damaging coastal and marine ecosystems.
Water quality relative priority
Very high
High
Moderate
Low
Minimal
Not assessed
Most anthropogenic fine sediment loads come from streambank erosion, grazing and dryland cropping areas.
Fine sediment
Streambankerosion
Grazing Dryland cropping
OtherUrban
Horticulture
Forestry
Most sediment erosion comes from streambanks and gullies in the Fitzroy catchment.
Types of sediment erosion
Streambank Gully Hillslope
0% 100