Effect dietary supplementation with fish oil lipids mild asthma - Thorax
fish Lipids
-
Upload
kolita-kamal -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of fish Lipids
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
1/31
Lipids
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
2/31
Lipids
(generally soluble in organic solvents
Plant sources
(olive, palm)
No cholesterol
Animal sources
(butter, lard, tallow)
Triacylglycerol
Oils and Fats
SterolsWaxes
(monoesters)
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
3/31
Lipids
Definition of Lipids Naturally occurring biological substances made from C, H
and O of pronounced hydrophobicity that are soluble inorganic solvents but not water Petroleum distillates (e.g. hexane)
Chloroform Ethers Alcohols
Also classified as biological molecules containing fattyacids or the corresponding alcohols or sphingosine bases
Lipids have more C and H than carbohydrates, which is whythey generate more energy when utilized 2.25 timesmore = 9 kcal/g vs. 4 kcal/g.
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
4/31
Lipids
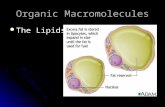
Biological roleA. Structural
- found in membranes
- protective barriers
B. Regulatory
- steroids/prostaglandins
- phospholipids
C. Storage
- triglyceride is
storage for energy
D. Vitamins
- solvent
- precursor
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
5/31
LipidsRole in foods
A. Calories (kcal)
energy
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
6/31
Lipids
Classification of lipids (structure)1) Simple lipids
Mono, Di and Triacylglycerols Waxes
2) Compound lipids Phospholipids Glycolipids Sphingolipids (amide to alcohol)
3) Derived lipids Free fatty acids Sterol esters Tocopherol (Vit-E) -carotene
Triacylglycerol
Glycerol
backbone Fatty acids
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
7/31
Lipids
1) Non-polar lipids
(neutral lipids) Fatty acids
Mono-, di-, & triacylglycerols
Waxes
Sterols
Carotenoids
Tocopherols
2) Polar lipids Glycerophospholipid
Glyceroglycolipid
Sphingophospholipid
Sphingoglycolipid
Classifications of lipids (polarity)Classifications of lipids (polarity)
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
8/31
Lipids
Structure & properties of fatty acids Fatty acid are composed of a hydrocarbon chain with
methyl group (CH3) on one end and a carboxyl group
(COOH) on the other. Basic properties common to most fatty acids
1. Most are even carbon #
2. Most are monocarboxylic acids
3. Most are part of triacylglycerides (triglycerides)
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
9/31
Lipids
NOMENCLATURE
1. Number of carbons C4-C24 most common
E.g. C8 = octa
C12 = dodeca2. Saturation
Saturated
(no double bonds)
Unsaturated
(double bonds) Mono (1 = bond)
Poly (>1 = bond)
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
10/31
Lipids
2. Saturation (cont.) No double bond = Anoic
E.g. C18:0
One double bond = Enoic E.g. C18:1
Two double bonds = Dienoic E.g. C18:2
Three double bonds = Trienoic E.g. C18:3
3. Geometric configuration
of double bonds Cis vs. Trans
Has an influence on
the fatty acid backbone
structure
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
11/31
Lipids
4. Position of double bonds Delta () system - count # of carbons to the = bond from the
COOH end E.g. 9-octadecenoic acid
Means: a) C18 = octadecenoicb) 1 double bond = octadecenoic
c) double bond is 9 carbons from the COOH end
Omega () system - count # of carbons to the = bond from the
CH3 end used for abbreviations of fatty acids
E.g. 9-octadecenoic acid would be C18:19
-3 therefore would mean that the = bond is 3 C from the CH3 end
-3, -6 and -9 the most common
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
12/31
Lipids
What is the name of this fatty acid using the delta & omegasystems?
H3C-(CH2)4-CH=CH-CH2-CH=CH-(CH2)7-COOH
Delta: ___________________________
Omega: __________________________
Common name is Linoleic acid (C18:2)
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
13/31
Lipids
Major fatty acids in foods Saturated
Palmitic (16:0) Stearic (18:0)
Monoenoic Oleic (18:19)
Dienoic Linoleic (18:26) 9, 12 - common in plants; some in animal
Trienoic Linolenic (18:33) 9, 12, 15
Tetraenoic Arachadonic (20:46) - 5, 8, 11, 14 - part of membrane phospholipids
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
14/31
Lipids
Factors affecting the properties of fatty acids1.Length of fatty acids
Longer chain length leads to increase in melting point and gives
more stable fatcrystals
Classes: C4 C8 - liquid @ room temperature (20-25)
These are water soluble good emulsifiers
C10 - C14 - viscous @ room temperature
C16 - C26 - solid @ room temperature
For example: C6:0 MP = -2C
C10:0 MP = 31.5C
C16:0 MP = 63C
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
15/31
Lipids
Factors affecting the properties of fatty acids2. Double bonds
An increase in double bonds decreases melting point
Example:
18:0 = 70C18:1 = 15C
18:2 = -5C
18:3 = -11C
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
16/31
Lipids
Factors affecting the properties of fatty acids
3. Cis vs. Trans Cis has lower melting point than Trans
Cis produces a kink in the fatty acid chain which creates a more
open fatty crystal structure
Kink
Melting Point
18:1c 15C
18:1t 44 C
18:2c -5 C
18:2t 29 C
18:3c -11 C18:3t 71 C
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
17/31
Lipids
Arrangement of fatty acids on triacylglycerides1. Not random (usually)
2. Specificity controlled
3. General pattern
The arrangement can significantly affect physical properties of fat
LC : Long chain; SC: Short chain
Position Plant Mammal Milk Bird Fish
1 S S S S S-LC
2 U U S U U
3 U LC U or SC S or U LC
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
18/31
Lipids
% 16:1
Consistency
SSS
SSU
SUS
SUU
USU
UUS
Cocoa Butter
62.00
hard sharp mp
0.03
0.01
0.81
0.15
0.01
0.01
Tallow
64.00
greasy broad mp
0.28
0.16
0.32
0.18
0.02
0.03
High mp
Low mp
Importance of sn position; Cocoa butter vs. Tallow
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
19/31
Lipids
Important Compound Lipids1. Phospholipids Make up cellular membranes Lipid molecules that contain a phosphate
group attached to a functional group Have both hydrophobic
(fatty acids) and hydrophilic
(phosphate and functional
group) portions
Good emulsifiers May have a protective effect
against ulcers (milk PL)
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
20/31
Lipids
2. Glycolipids Contain at a minimum one sugar
Some may also have a phosphate group (glycosphingolipids)
Found in all tissues of animals
Have same solubility characteristics as regular lipids
3. Sterols Made of four fused hydrophobic rings with a hydrophilic OH group
Not so important as a food ingredient but important for dietary reasons Cholesterol in animal foods
Can contribute to coronary heartdisease (arteriosclerosis)
300 mg/day the recommended intake limit
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
21/31
Lipids
4. Fat substitutes Sucrose fatty acid polyesters
Olestra (Procter and Gamble Co.) 6-8 fatty acids (>C12) esterified to sucrose
Caloric free due to its bulky structure and because lipases cannot
hydrolyze it
May lead to loss of fat soluble vitamins and can give diarrhea
Approved for use in frying oils (snacks)
Sucrose and polyol fatty acid esters
1-3 fatty acids esterified to sucrose or a polyol (e.g. sorbitol) Have caloric value (polyol fatty acid esters only about 1.5 kcal/g)
Used as emulsifiers and stabilizers
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
22/31
Triacylglycerol
Sterols
Wax
(bees wax)
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
23/31
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
24/31
Compound Lipids
Phospholipid
Glycolipid
Sugar unitPhosphategroup
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
25/31
Derived Lipids
Sterols Carotene
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
26/31
Peptide based liquid
Tube or oral feeding Efficient energy utilization
MCT OIL (Novartis nutrition) unable to digest or absorb
conventional fats Less enzymes and bile acids
for digestion
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
27/31
Fish Lipids
Fish are classified as lean, semi-fatty or fatty. Fish that store lipids only in the liver as lean and fish
storing lipids in fat cells distributed in other body tissues as
fatty.
Typical lean species are bottom-dwelling ground fish likecod, and hake.
Fatty species include pelagic such as herring, mackerel
and sprat.
Some species store lipids in limited parts of their bodytissues only, or in lower quantities than typical fatty
species, and are consequently termed semi- fatty species
(e.g. barracuda, mullet and shark).
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
28/31
Type of lipids in fish
The lipids present in teleost fish species may be
divided into two major groups: Phospholipids
The phospholipids make up the integral structure of the unit
membranes in the cells; thus, they are often called structural
lipids.
Triglycerides The triglycerides are lipids used for energy storage in fat
depots, usually within special fat cells surrounded by a
phospholipid membrane and a rather weak collagen network. The triglycerides are often termed depot fat. A few fish
have wax esters as part of their depot fats.
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
29/31
Fish & Mammals lipids
Fish and mammalian lipids differ mainly in that
fish lipids include up to 40 percent of long-chain
fatty acids (14-22 carbon atoms) which are highly
unsaturated. Mammalian fat rarely contains more than two
double bonds per fatty acid molecule while the
depot fats of fish contain several fatty acids withfive or six double bonds.
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
30/31
Lipids: marine & freshwater fish
The percentage of polyunsaturated fatty acids
with four, five or six double bonds is slightly lower
in the polyunsaturated fatty acids of lipids from
freshwater fish (approximately 70 percent) Lipids from marine fish (approximately 88
percent).
However, the composition of the lipids is not completelyfixed but can vary with the feed intake and season
-
8/14/2019 fish Lipids
31/31
THANK YOU!!!!