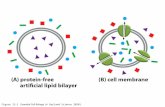
Figure 16.45a The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007)
-
date post
20-Dec-2015 -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
4
Transcript of Figure 16.45a The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007)
EGF-R
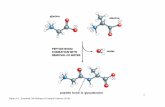
Molecular Evaluation of Biopsy Samples Can Provide Indications of Drug Delivery and Efficacy I
EGF-R
pEGF-R
????
Molecular Evaluation of Biopsy Samples Can Provide Indications of Drug Delivery and Efficacy II
Reversal of Tumor Growth by Induction of Redifferentiation
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia reverted to Neutrophils
(stem-like)
(ATRA)
Possible Mechanism: Proteosome-mediated destruction of PML-RAR protein
Also note: 13-cis-retinoic acid delays progression of premalignant mouth & throat to frank head-and-neck cancers.
Creation by 15:17 translocation
Shutting Down Instigating Oncogene Sometimes But Not Always Achieves Permanent Regression of the Tumor
Failure
Figure 16.11a The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007)
Blockade of Key Protein – Protein Interactions Case 1: MDM2/P53
A Component of Green Tea Blocks Key Hydrophobic pockets of the Apototic Inhibitory Proteins Bcl-XL & Bcl-2
Figure 16.12 The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007)
A Family Tree of The 518 Members of the Set of Human Protein Kinases
Figure 16.16a The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007)
An Ingenious Approach to Screenng Candidate Compunds for Kinase Activity
Figure 16.10a The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007)
Gleevec – The Poster Child of Rationale Anti-Cancer Drug Design
Figure 16.25b The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007)
Molecular & Cellular Demonstrations of Gleevec’s Efficacy
Molecular
Cytological
Figure 16.31a The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007)
EGF-Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Receptor Inhibitors Iressa & Tarceva
Figure 16.33b The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007)
Resistance to EGF-Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Figure 16.37 The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007)
Velcade Interferes With the NF-Kb Pathway
Figure 16.38b The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007)
EMSA Shows Importance of NF-Kb Signalling in MM and Dramatic Reduction of NF-Kb Levels by Velcade
Gel Shift
Proof with DN
Figure 16.40a The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007)
The Hedgehogs (Sonic, indian & Desert) are Involved in the Many Cancers esp. Pancreatic Cancer, Gliomas
and Basal Cell Carcinoma
Figure 16.40d The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007)
Expression of Patched and Hedgehog – an Autocrine Loop
Effect of HH Neutralizing Antibody
Figure 16.42b The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007)
A Inhibitor of Smoothened, HhAntag, Shows Promise in a Mouse Medulloblastoma Model