Fiber Optics Ieee
-
Upload
sahil-abbas -
Category
Documents
-
view
11 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Fiber Optics Ieee
Fiber Optics
Optical FiberNaveed AbbasRoll # TC-41M.Engg. TelecommunicationNED University of Engineering and Technology1
2What is Optical Fiber?AnOptical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of high quality glass (silica) or plastic, slightly thicker than a human hair.Functions as a waveguide or light pipe that transmits light between two ends of the fiber Optical fibers are widely used infiber-optic communications, which permits transmission over longer distances and at higherbandwidths(data rates) than other forms of communicationFibers are used instead ofmetalwires because signals travel along them with less lossand are also safe toelectromagnetic interference.3Total internal reflectionFiber optic communication works on the principal of total internal reflectionThe phenomenon in which light ray, after a particular critical angle , refelects back into the same medium as of incident ray4
5
Uses of optical fiberOptical fiber can be used as a medium for telecommunication andcomputer networkingbecause it is flexible and can be bundled as cables. It is especially advantageous for long-distance communications, because light propagates through the fiber with little attenuation compared to electrical cables. In June 2013, researchers demonstrated transmission of 400 Gbit/s over a single channel.6Benefits of Optical FiberMuch higher bandwidths than conventional copper cablesFiber is also immune to electrical interference; there is no cross-talk between signals in different cables, and no pickup of environmental noise. Fiber cables do not conduct electricity, which makes fiber a good solution for protecting communications equipment inhigh voltageenvironments, such aspower generationfacilities, or metal communication structures prone tolightningstrikes. They can also be used in environments where explosive fumes are present, without danger of ignition.7Modes of propagation8Single mode there is only one path for light to take down the cable
Multimode if there is more than one path
CladdingCladding
9
Structure of single-mode fiber1. Core: 8m diameter2. Cladding: 125m dia.3. Buffer: 250m dia.4. Jacket: 400m dia.Loss in Optical Fiber10
Losses vary greatly depending upon the type of fiberPlastic fiber may have losses of several hundred dB per kilometerGraded-index multimode glass fiber has a loss of about 24 dB per kilometerSingle-mode fiber has a loss of 0.4 dB/km or less11Fiber Connectors
Did you know?A small optical fiber can carry more data than a large copper cable.
12
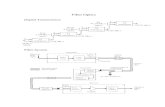
System13ElectricalConnectorElectricalConnectorTransceiverTransceiverFiber Optic CableOpticalConnectorOpticalConnectorOpticalPortOpticalPortA failure anywhere along this link will cause the entire link to failOptical Fiber in Sea
14Thank You 15