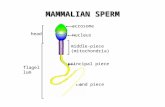
Fertilization Sperm reaches secondary oocyte and the acrosome helps the sperm to penetrate oocyte...
36
Fertilization • Sperm reaches secondary oocyte and the acrosome helps the sperm to penetrate • • oocyte cell membrane _
-
Upload
elisabeth-horn -
Category
Documents
-
view
231 -
download
5
Transcript of Fertilization Sperm reaches secondary oocyte and the acrosome helps the sperm to penetrate oocyte...
- Slide 1
- Fertilization Sperm reaches secondary oocyte and the acrosome helps the sperm to penetrate oocyte cell membrane _
- Slide 2
- Fertilization Once sperm within oocyte nucleus of the sperm head swells forms _ Female meiosis completes only after the sperm enters the egg. Nuclei unite, chromosomes mingle. Zygote is oocyte and sperm, has 46 chromosomes.
- Slide 3
- Morula Travel time to uterus: solid ball of about 16 cells called the _____________________. Remains ________________________ in the uterine cavity for three days.
- Slide 4
- Blastocyst Structure becomes _ Implants in the uterus by _
- Slide 5
- Organization Blastocysts organizes into gives rise to the _ Outer cells become embryonic portion of _ Embryo until _ Fetus until _
- Slide 6
- Placenta Placenta develops attaches the embryo to uterine wall exchanges _ wastes between maternal blood and embryonic blood. Placenta also _
- Slide 7
- Hormone changes In non pregnant female, the corpus luteum degenerates uterine lining sloughs off In pregnant female, need to _
- Slide 8
- HCG HCG: human chorionic gonadotropin. prevents _ HCG and some of the embryonic cells continues to _ inhibits _
- Slide 9
- HCG HCG secretion is high for ____________________________ and then declines. Corpus luteum ________________________________, but is most important in the first few months before the _
- Slide 10
- More hormones Placental lactogen stimulates __________________________________ and prepares the mammary glands for milk secretion. hormone from _ Inhibits the ________________________________ in the myometrium, ___________________________________ until birth. ______________________________________ of the symphysis pubis and SI joints aids passage of fetus through birth canal.
- Slide 11
- More hormones Increased secretion of _______________________________ and of parathyroid hormone Aldosterone from adrenal cortex promotes renal _ . PTH helps to maintain high concentrations of calcium.
- Slide 12
- Parturition Pregnancy continues for about ____________________________ and ends with ______________________ or birth.
- Slide 13
- Hormonal changes with birth no longer preventing uterine contractions __________________________ stimulate ______________________ to contract.
- Slide 14
- Labor Contractions start at the ________________________________ and travel downward, forcing the contents toward the cervix. Labor contractions force the fetal head against the cervix elicits a reflex _
- Slide 15
- Dilation of cervix Dilation of cervix stimulates increased release of oxytocin more contractions.
- Slide 16
- Involution After the birth, the _ expelled by the remaining uterine contractions, stimulated by _
- Slide 17
- Involution For _________________________ the uterus undergoes _ which is the _ For several weeks will pass a _ then a _ until the ______________________________ and returns to a non-pregnant state.
- Slide 18
- Mammary glands Mammary glands: ______________________________ specialized to secrete milk following pregnancy. composed irregularly shaped lobes Each lobe contains _______________________________________ that leads to the nipple and opens to the outside.
- Slide 19
- More hormones (breast) During pregnancy, placental estrogen and progesterone stimulate mammary development. Estrogen: Progesterone
- Slide 20
- More hormones (breast) Prolactin, released in _________________ and present throughout pregnancy. Prolactin causes _
- Slide 21
- Milk production and secretion The _____________________________________. No longer will inhibit prolactin. Prolactin stimulates the mammary glands to secrete large quantities of milk not until two or three days following birth Until then, there is _
- Slide 22
- Milk ejection Milk must be _ When the breast is _ release of _ causes the muscles to contract and eject the milk.
- Slide 23
- Milk production Prolactin is released as long as milk is removed from the breasts. If milk not removed regularly, prolactin is inhibited
- Slide 24
- Birth Control: the ______________________________ of the number of offspring produced and _ Contraception: method designed to _____________________________ of an egg following intercourse or _
- Slide 25
- Withdrawing the penis from the vagina before ejaculation Natural family planning. Requires _ More effective when coupled with _ Wake up in the morning, without getting out of bed, take temperature. Body temp rises degree following ovulation. Dips just a bit before
- Slide 26
- Cervical mucus Cervical mucus will become When the mucus is stretchy, it _____________________ through which the sperm can travel to reach the egg
- Slide 27
- Mechanical barriers Condom _ Female condom: inserted into the vagina. Blocks semen from reaching the cervix. __________________________: Cup shaped structure with a flexible ring forming the rim. inserted into the vaginal canal and _ Prevent entry of sperm into cervix. Must be properly fitted. Best used with a _
- Slide 28
- Mechanical barriers ________________________: smaller than diaphragm. Inserted before intercourse. Have been made from _
- Slide 29
- Chemical barriers Includes _ Will create an environment that is unfavorable for sperm cells. Have ______________________________. Most effective when coupled with the barrier methods.
- Slide 30
- Contraceptives Oral contraceptives: contains _ Disrupts the gonadotropin secretion and ________________________________________ that would normally trigger ovulation interfere with _ May cause nausea, water retention, increased pigmentation of skin, breast tenderness. Also liver damage, and some controversy surrounding breast cancer.
- Slide 31
- IUD Intrauterine devices: physician places IUD within _ IUD may be expelled, produce pain, excessive bleeding. May _
- Slide 32
- Vaginal Ring releases a continuous _ The ring is inserted into the vagina _ A new ring is used with each cycle.
- Slide 33
- Vaginal Ring Disadvantages increased _ vaginal _ cannot use a diaphragm or cervical cap for a backup method of birth control
- Slide 34
- Patches place a thin plastic _________________________________ of the buttocks, stomach, upper outer arm, or upper torso once a week for _ releases combined hormones that protect against pregnancy for one month
- Slide 35
- Patches Disadvantages ______________________ at the site of application for wearers of contact lenses, a change in vision or the inability to wear the lenses may not be as effective for women who weigh more than 198 pounds
- Slide 36
- Surgical methods Physician removes a small _______________________________ near the epididymis and _ May result in pain for a week or so. Sperm cannot leave the epididymis, and are therefore _ Tubal ligation: __________________________________________ so that sperm cells cannot reach an egg cell.