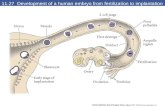
11.27 Development of a human embryo from fertilization to implantation
Fertilization &Implantation
description
Transcript of Fertilization &Implantation

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki
FertilizationFertilization Definition:Definition: It is the fusion of It is the fusion of
the male & female the male & female gametes (union of gametes (union of a a spermsperm and an and an ovum)ovum) to form to form zygote.zygote.
Normal site:Normal site: Ampulla Ampulla or lateral or lateral
third of the uterine third of the uterine (fallopian) tube.(fallopian) tube.
Time:Time: Within Within 24 hours24 hours
from from ovulationovulation.. 2ry 2ry oocyte is viable for oocyte is viable for only 24 hours.only 24 hours.

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki
Steps of fertilization:Steps of fertilization:1-Transport of gametes:1-Transport of gametes: Ovum:Ovum: during ovulation during ovulation
the fimbriated end of the the fimbriated end of the uterine tube becomes uterine tube becomes closely applied to the closely applied to the ovary. ovary.
Sweeping action of tubal Sweeping action of tubal fimbriae carries the oocyte fimbriae carries the oocyte into the uterine tube.into the uterine tube.
The oocyte then passes The oocyte then passes into the ampulla of the into the ampulla of the tube by beating of the cilia tube by beating of the cilia and peristaltic contraction.and peristaltic contraction.
Sperm:Sperm: of the of the 200-300 200-300 millions sperms deposited millions sperms deposited in the vagina, onlyin the vagina, only 300-500 300-500 reach the site of reach the site of fertilization only fertilization only one one spermsperm is capable of is capable of fertilizing the ovum & is fertilizing the ovum & is called the (fertilizing called the (fertilizing sperm)sperm)

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki
Ii. Sperm ConditioningIi. Sperm Conditioning
Sperms deposited in the female genital tract must undergo two Sperms deposited in the female genital tract must undergo two changes before they can fertilize an ovum:changes before they can fertilize an ovum:
1. Capacitation:1. Capacitation: Sperms Sperms cannotcannot fertilize oocytes when they are fertilize oocytes when they are newly newly
ejaculated.ejaculated. The process of capacitation takes 5-7 hours.The process of capacitation takes 5-7 hours. Capacitated sperms are more Capacitated sperms are more activeactive.. Location: capacitation occurs in the uterus and oviducts.Location: capacitation occurs in the uterus and oviducts. The acrosomal reaction cannot occur until capacitation has The acrosomal reaction cannot occur until capacitation has
occurred.occurred. The The glycoprotein coatglycoprotein coat removed from the cell membrane removed from the cell membrane
covering the acrosomal cap.covering the acrosomal cap.

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki
2. Acrosome reaction:2. Acrosome reaction: Fusion occurs between the Fusion occurs between the
outer acrosomal membrane outer acrosomal membrane and the cell membrane of and the cell membrane of the corona radiata with the the corona radiata with the release of acrosomal release of acrosomal enzymes (enzymes (acrosin)acrosin)..
a) Hyaluronidase results in a) Hyaluronidase results in digestion of the corona digestion of the corona radiata.radiata.
b) Trypsin-like substance & b) Trypsin-like substance & zona lysin lead to zona lysin lead to penetration of the zona penetration of the zona pellucida.pellucida.
During fertilization, the sperm During fertilization, the sperm must penetrate:must penetrate:A-A-the corona radiata. the corona radiata. B-B-the zona pellucida. the zona pellucida. C.C.the oocyte cell membrane.the oocyte cell membrane.

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki
Phases of fertilization:Phases of fertilization: Phase 1:Phase 1:
penetration of corona penetration of corona radiata:radiata:
many sperms penetrate many sperms penetrate the corona radiata with the the corona radiata with the aid of acrosomal enzymes aid of acrosomal enzymes (hyaluronidase)(hyaluronidase)
Phase 2:Phase 2: penetration of zona penetration of zona pellucida: pellucida:
Only Only one spermone sperm penetrates penetrates the zona and once the the zona and once the sperm is inside, the sperm is inside, the properties of zona properties of zona pellucida will change to pellucida will change to prevent other sperm to prevent other sperm to enter.enter.

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki
Phase 3Phase 3:: fusion of the oocyte and sperm fusion of the oocyte and sperm cell membranes.cell membranes.
After fertilization, as soon as the sperm has After fertilization, as soon as the sperm has entered the oocyte: a)entered the oocyte: a) the oocyte finishes its the oocyte finishes its 22ndnd meiotic meiotic division & forms the division & forms the female female pronucleus;pronucleus; b) b) the zona pellucida becomes the zona pellucida becomes impermeable to other sperms;& impermeable to other sperms;& c) c) The head The head of the sperm separates from the tail, swells of the sperm separates from the tail, swells & forms & forms the male pronucleus.the male pronucleus.
The female pronucleus The female pronucleus comes into close contactcomes into close contactwith male pronucleus.with male pronucleus. The nuclear membranes The nuclear membranes of the 2 pronuclei of the 2 pronuclei disappear and theirdisappear and theirchromosomes becomechromosomes become around the equatoraround the equatorthus the zygote isthus the zygote is formed.formed.

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki
Results Of FertilizationResults Of Fertilization RestorationRestoration of the of the diploiddiploid number of number of chromosome chromosome
(46).(46). Determination Determination of the sexof the sex of the embryo. An X- of the embryo. An X-
carrying sperm produces a female embryo, and a carrying sperm produces a female embryo, and a Y- carrying sperm produces a male embryo.Y- carrying sperm produces a male embryo.
Completion of the Completion of the 22ndnd maturation (meiotic) maturation (meiotic) divisiondivision with formation of the mature ovum and with formation of the mature ovum and 22ndnd polar body. polar body.
Initiation of Initiation of cleavagecleavage or cell division of the or cell division of the zygote .zygote .
The The zona & cortical reactions occurzona & cortical reactions occur to prevent to prevent fertilization of the same ovum by more than one fertilization of the same ovum by more than one sperm.sperm.

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki
In- Vitro Fertilization (IVF)In- Vitro Fertilization (IVF) A method of treatment of A method of treatment of
infertility, if there is occlusion of infertility, if there is occlusion of fallopian tube.fallopian tube.
The female is given gonadotropin The female is given gonadotropin to stimulate multiple ovulations.to stimulate multiple ovulations.
The ova are collected with The ova are collected with aspirator during laparoscopy & aspirator during laparoscopy & are put in a glass plate.are put in a glass plate.
Sperms collected from the Sperms collected from the husband are added immediately.husband are added immediately.
After fertilization, the eggs are After fertilization, the eggs are monitored to 8- cell stage then monitored to 8- cell stage then placed in the uterus to develop to placed in the uterus to develop to termterm..


Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki
CLEAVAGECLEAVAGE
Definition:Definition: Is a series of Is a series of
mitotic mitotic divisionsdivisions of of the zygote the zygote results in an results in an increase in increase in cellscells number number without without increase in increase in total size.total size.
Site:Site: uterine tube.uterine tube.

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki
Stages Of CleavageStages Of Cleavage The zygote divides by mitosis into two-cell stage. The zygote divides by mitosis into two-cell stage.
Each cell is named blastomere.Each cell is named blastomere. Repeated mitosis giving 4 cells, 8 cells& so on Repeated mitosis giving 4 cells, 8 cells& so on
until a until a MorulaMorula of of 12-12-1616 compacted cellscompacted cells is is formed after 3 days after fertilization & enters formed after 3 days after fertilization & enters the uterus. The morula is differentiated into an the uterus. The morula is differentiated into an inner cell mass & an outer cell mass.inner cell mass & an outer cell mass.
Blastocyst stage:Blastocyst stage: fluid from the uterine cavity fluid from the uterine cavity accumulates between the blastomeres dividing accumulates between the blastomeres dividing them into 2 groups, one group of cells in the them into 2 groups, one group of cells in the center center ((inner cell mass)inner cell mass) which will which will give the give the embryoembryo so it is called so it is called ((embryoblast)&embryoblast)& 2 2ndnd group group of cells at the periphery, forming the wall of of cells at the periphery, forming the wall of blastocyst blastocyst (outer cell mass)(outer cell mass) which will forms which will forms the the foetal membranesfoetal membranes,, it is called it is called trophoblast.trophoblast.

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki
BlastocystBlastocyst Consists of: Inner cell mass: Consists of: Inner cell mass: 1-1-embryoblast :embryoblast : large cells on large cells on
the embryonic pole of the blastocyst. These cells form the the embryonic pole of the blastocyst. These cells form the embryo (embryo proper)embryo (embryo proper)
2-2-Outer cell mass: trophoblast :Outer cell mass: trophoblast : small cells forming the small cells forming the wall of blastocyst. They forms the foetal membranes and wall of blastocyst. They forms the foetal membranes and placenta.placenta.3-3-Blastocoele:Blastocoele: a cavity. a cavity.
The zona pellucida has The zona pellucida has disappeared,disappeared, allowing implantation allowing implantation to begin.to begin.

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki

Implantation Implantation
Events during the first week of human Events during the first week of human developmentdevelopment
Definition:Definition: It isIt is the the embedding of embedding of the the blastocystblastocyst into the into the compact layer compact layer of the of the endometriumendometrium..Time: It begins about the 6th day after fertilization.It is completed by the 11th or 12th day.

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki
StepsSteps On the On the 55thth day after fertilization, the day after fertilization, the zona zona
pellucidapellucida disappears.disappears. TheThe blastocystblastocyst increases increases rapidly in size.rapidly in size.
On theOn the 6th6th day, theday, the trophoblast cells covering trophoblast cells covering the embryonic pole adhere to the endometrium the embryonic pole adhere to the endometrium & starts to proliferate rapidly. & starts to proliferate rapidly.

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki
It differentiates into It differentiates into 2 layers: 2 layers:
an an inner cytotrophoblastinner cytotrophoblast anan outer outer syncytiotrophoblast syncytiotrophoblast ((cells lose its cellcells lose its cell boundaries) boundaries) - It extends finger-like processes, - It extends finger-like processes,
which secrete proteolytic which secrete proteolytic enzymes that erode the enzymes that erode the endometrium, creating a hole endometrium, creating a hole through which the blastocyst through which the blastocyst is gradually buried in the is gradually buried in the endometrium.endometrium.

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki
3. By the 3. By the 99thth -10 -10thth day, the day, the
hole in the endometrium hole in the endometrium is is closed by a fibrin plug.closed by a fibrin plug. The endometrium The endometrium regenerates by the regenerates by the 1212thth day.day.
Normal site of implantation:Normal site of implantation: PosteriorPosterior wall of the wall of the upper upper part of the uterus near thepart of the uterus near the fundus, in the midline.fundus, in the midline. Time:Time: from 7 from 7thth to 12 to 12thth
day after fertilizationday after fertilization..

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki
Intrauterine Intrauterine ImplantationImplantation The normal site of implantation is the posterior wall of uterus near The normal site of implantation is the posterior wall of uterus near
the fundus.the fundus.

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki
Uterus At Time Of Uterus At Time Of ImplantationImplantation
The endometrium is in the The endometrium is in the secretorysecretory phase. phase.

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki
The deciduaThe decidua It is the It is the endometrium after endometrium after implantation.implantation.After implantation After implantation the decidua the decidua becomes becomes differentiated into:differentiated into: Decidua basalis:Decidua basalis: under the site of under the site of implantation.implantation.Decidua capsularis: Decidua capsularis: covering the covering the blastocyst.blastocyst.Decidua parietalis :Decidua parietalis : lining the rest of the lining the rest of the uterine cavity.uterine cavity.

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki
Ectopic pregnancy( abnormal site of Ectopic pregnancy( abnormal site of implantation)implantation)

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki
Abnormal Site of ImplantationAbnormal Site of Implantation1.Intra- uterine:1.Intra- uterine: Placenta praevia:Placenta praevia:
Implantation in theImplantation in the lower uterine segment lower uterine segment (cervix).(cervix).
3 types: 3 types: lateral, lateral, marginal and central. marginal and central. Cause severeCause severe bleeding bleeding before deliverybefore delivery..
2.2. Extra-uterine:Extra-uterine:(Ectopic(Ectopic pregnancy): pregnancy):
Outside the uterus:Outside the uterus: TubalTubal ovarian ovarian abdominal.abdominal.

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki
Cervical pregnancy Cervical pregnancy (Placenta Previa)(Placenta Previa)Implantation in theImplantation in the lower uterine lower uterine
segment (cervix).segment (cervix). Types of placenta previa:Types of placenta previa: Placenta previa centralis:Placenta previa centralis: the the
placenta completely covers placenta completely covers the internal os.the internal os.
Placenta previa marginalis:Placenta previa marginalis: the the margin of the placenta margin of the placenta reaches the internal os.reaches the internal os.
Placenta previa lateralis:Placenta previa lateralis: the margin the margin of the placenta does not reach of the placenta does not reach the internal os.the internal os.
The placenta previa leads to The placenta previa leads to antepartum haemorrhageantepartum haemorrhage due to early separation of the due to early separation of the placenta from the lower ½ of placenta from the lower ½ of the uterus.the uterus.

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki
Ectopic ImplantationEctopic ImplantationThe most common site of ectopic pregnancy is tubal pregnancy.

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki
a)a) Tubal pregnancy (95%): Tubal pregnancy (95%): Implantation in the Implantation in the fallopian tube causing its fallopian tube causing its rupture.rupture.
It usually ruptures leading It usually ruptures leading to to painpain that is commonly that is commonly confused with appendicitis confused with appendicitis if on the right side.if on the right side.
Rupture usually occurs in Rupture usually occurs in the 2the 2ndnd month causing month causing internal haemorrhage internal haemorrhage which endanger life of the which endanger life of the mother.mother.
b) Ovarian pregnancy b) Ovarian pregnancy c)c) Abdominal pregnancy: Abdominal pregnancy:
Implantation in the Implantation in the peritoneal cavity (Douglas peritoneal cavity (Douglas pouch or mesentery.pouch or mesentery.

Dr: Azza ZakiDr: Azza Zaki