FEDERALISM. Federalism What is it? Confederacy v. Unitary v. Federal.
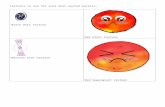
FEDERALISM Chapter 3 How does this cartoon reflect the concept of federalism?
-
Upload
alexis-maxwell -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of FEDERALISM Chapter 3 How does this cartoon reflect the concept of federalism?
The national government and state governments derive all authority from the people.
Local and regional governments derive all authority from a strong national government.
National government derives power from states; weak national government.
• Two or more levels of government have formal authority over the same area and people…another system of checks & balances!
• There is a decentralization or DEVOLUTION of government power; a “sharing of the wealth” and gov’t power.
FEDERALISM:FEDERALISM:
• Do state gov’ts influence the federal gov’t?• Does the federal gov’t influence state gov’ts?• What obligation does the federal gov’t have to states?
– protect the states against violence & invasion
Why was federalism the only real choice for the framers?
• Citizens too spread out to have a unitary gov’t• No other practical choice since transportation &
communication systems too primitive to allow governing from a central location
• The Confederation had clearly failed.• American’s loyalty to state gov’ts was stronger
than it was to the U.S. government• If they tried to abolish state governments, the
Constitution would not have been ratified.
National/Federal Powers under the Constitution
• ENUMERATED• A/k/a Delegated or Expressed powers• 17 specific powers granted to Congress by
Art. I, Sec. 8 of the U.S. Constitution including:– Taxation– Coinage of money– Regulation of interstate commerce– National defense / Declare War
• May also be referred to as exclusive powers.
Implied Powers• Additional powers of federal gov’t
that are implied to make Congress’ expressed powers work
• Source: Elastic Clause– Congress may pass any law “necessary and
proper” for carrying out its expressed powers– IRS is a good example– Explain – Congress’ power to set up the IRS is
implied from what expressed power Congress has?
Article I, Section. 8.
The Congress shall have Power 1-To lay and collect Taxes, Duties, Imposts and Excises, to pay the Debts and provide for the common Defence and general Welfare of the United States; but all Duties, Imposts and Excises shall be uniform throughout the United States; 2-To borrow Money on the credit of the United States; 3-To regulate Commerce with foreign Nations, and among the several States, and with the Indian Tribes; 4-To establish an uniform Rule of Naturalization, and uniform Laws on the subject of Bankruptcies throughout the United States; 5- To coin Money, regulate the Value thereof, and of foreign Coin, and fix the Standard of Weights and Measures; 6- To provide for the Punishment of counterfeiting the Securities and current Coin of the United States; 7-To establish Post Offices and post Roads; 8-To promote the Progress of Science and useful Arts, by securing for limited Times to Authors and Inventors the exclusive Right to their respective Writings and Discoveries;9-To constitute Tribunals inferior to the supreme Court;10--To define and punish Piracies and Felonies committed on the high Seas, and Offences against the Law of Nations; 11-To declare War, grant Letters of Marque and Reprisal, and make Rules concerning Captures on Land and Water; 12-To raise and support Armies, but no Appropriation of Money to that Use shall be for a longer Term than two Years; 13-To provide and maintain a Navy; 14- To make Rules for the Government and Regulation of the land and naval Forces; 15-To provide for calling forth the Militia to execute the Laws of the Union, suppress Insurrections and repel Invasions; 16-To provide for organizing, arming, and disciplining, the Militia, and for governing such Part of them as may be employed in the Service of the United States, reserving to the States respectively, the Appointment of the Officers, and the Authority of training the Militia according to the discipline prescribed by Congress; 17-To exercise exclusive Legislation in all Cases whatsoever, over such District (not exceeding ten Miles square) as may, by Cession of particular States, and the Acceptance of Congress, become the Seat of the Government of the United States, and to exercise like Authority over all Places purchased by the Consent of the Legislature of the State in which the Same shall be, for the Erection of Forts, Magazines, Arsenals, dock-Yards, and other needful Buildings;--And
18-To make all Laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into Execution the foregoing Powers, and all other Powers vested by this Constitution in the Government of the United States, or in any Department or Officer thereof.
Enumerated Powers of Congress
Inherent Powers• Not listed; powers a
sovereign gov’t has just because it is a gov’t
• Examples would be power to control nation’s borders, acquire new territories, determine citizenship laws, defend the nation, etc.
Reserved Powersof the States
• 10TH AMENDMENT– Powers not delegated to federal
government in Constitution nor prohibited to the states are reserved to the states
• STATES HAVE POWER TO:– regulate intrastate commerce, provide
for the public safety, establish local governments, conduct and establish rules for elections, and originally even determined voter qualifications
Concurrent Powers
• Powers that are shared by both federal and state governments– Tax– Borrow Money– Create Banks– Establish courts– Education?
Identify whether the activities below are powers of the federal gov’t, state governments, or both and explain your rationale for each choice.
• Issue driver’s licenses• Determine length of the school year• Maintain the Air Force & Coast Guard• Clean up water pollution in rivers & lakes• Tax individual & corporate income• Set up the process early voting in
presidential elections• Establish a lottery system
Denied Powers
• States cannot– Enter into treaties– Coin money– No ex post facto laws –
meaning?– Impair obligation of contracts– Cannot enter into compacts
with other states without congressional approval
– Denied the authority to take arbitrary actions affecting constitutional rights and liberties
– Cannot pass a bill of attainder
• Congress cannot• Favor one state over
another in regulating commerce
• Cannot charge duties on items exported from any state
• Cannot pass a bill of attainder
• No ex post facto laws
SupremacyWho rules in a conflict –
federal or state?
• Art VI- Supremacy Clause• Provides that supreme law
of the land is made up of:1.THE CONSTITUTION2.Laws of the federal government
3.Treaties of the U.S.
Four historical events have settled the issue of federal/state supremacy:
1. Doctrine of implied powers (McCulloch)
2. Definition of the commerce clause (Gibbons)
3. The Civil War4. The Civil Rights Movement
Federalism and the Marshall Court
• 3 rulings in the early 1800s had a major impact on the balance of power between national & state governments.– McCulloch v. Maryland (1819)
• Upheld power of national government and denied the right of a state to tax the national bank
– Gibbons v. Ogden (1824)• Upheld broad congressional power to regulate
interstate commerce– Barron V Baltimore (1833)
• 5th Amendment (due process) doesn’t apply to actions by states, limited Bill of Rights actions to Congress
McCulloch v. Maryland, 1819
• Supremacy clause & implied powers of national government upheld!
• State of Maryland tried to tax the Baltimore branch of the national Bank of the U.S.
• McCulloch (officer at Bank) refused to pay the tax
• Marshall’s ruling:– States may not tax a federal agency
(due to Art. VI-supremacy clase)
– “Elastic clause” gives Congress the Necessary and Proper powers (implied powers) to enact policies to run the country (the Bank!)
“The power to tax is the power to destroy.”
Watch the Medical Marijuana Federal vs. State power video (4 min.) at the following link:http://www.pbs.org/tpt/constitution-usa-peter-sagal/classroom/episode-1-federalism/
Make sure that you understand the McCulloch v. Maryland case. You will need to explain it in your own words in tomorrow’s class activity.
Find a Venn Diagram showing National Powers State Powers and the overlapping Concurrent Powers and copy and paste it. Make sure you can identify some of each type of power.