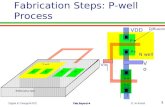
Fabrication Process 1
-
Upload
mahabub-hossain -
Category
Documents
-
view
227 -
download
0
Transcript of Fabrication Process 1
-
8/12/2019 Fabrication Process 1
1/7
Semiconductor FabricationMd Mahabub Hossain
-
8/12/2019 Fabrication Process 1
2/7
Oxidation
Lithography &Etching
Ion Implantation Annealing &Diffusion
Introduction
Silicon Growth
& Wafer
-
8/12/2019 Fabrication Process 1
3/7
Quartz, or silica, consists of silicon dioxideSand contains many tiny grains of quartzSilicon can be artificially produced by combining silica and carbon in electric furnaceGives polycrystalline silicon (multitude of crystals)Practical integrated circuits can only be fabricated from single-crystal material
Silicon Crystal & Growth
Growth
A solid seed crystal is rotated andslowly extracted from a pool ofmolten Si.Requires careful control to givecrystals desired purity anddimensions.
Czochralski processis a technique in making single-crystal silicon.
-
8/12/2019 Fabrication Process 1
4/7
Wafer Manufacturing
The silicon crystal is sliced in ingot by using a diamond-tipped saw into thin wafersSorted by thicknessDamaged wafers removed during lappingEtch wafers in chemical to remove any remaining crystal damagePolishing smoothes uneven surface left by sawing process
-
8/12/2019 Fabrication Process 1
5/7
Oxidation of SiliconSiO2 growth is a key process step inmanufacturing all Si devices
- Thick (~1m) oxides are used for fieldoxides (isolate devices from one another )- Thin gate oxides (~100 ) control MOS
devices- Sacrificial layers are grown and removed to
clean up surfacesThe stability and ease of SiO2 formation is one
of the reasons that Si replaces Ge as thesemiconductor of choice.
The simplest method ofproducing an oxide layerconsists of heating a silicon
wafer in an oxidizingatmosphere.
-
8/12/2019 Fabrication Process 1
6/7
Dry oxide - Pure dry oxygen is employedSi + O2 SiO2
Disadvantage- Dry oxide grows very slowly.
Advantage- Oxide layers are very uniform.- Relatively few defects exist at the oxide-silicon interface.- It has especially low surface state charges andthus make ideal dielectrics.
Wet oxide - Same way as dry oxides, butsteam is injected
Si +2H2O SiO2 + 2H2Disadvantage
-Hydrogen atoms liberated by thedecomposition of the water moleculesproduce imperfections that may degrade theoxide quality.
Advantage -Wet oxide grows fast.-Useful to grow a thick layer of field oxide.
Oxidation of Silicon
Si Wafers
O 2 N 2H 2O or TCE(trichloroethylene)
Quartz tube
Resistance-heated furnace
Flowcontroller
-
8/12/2019 Fabrication Process 1
7/7
Oxidation of Silicon
Estimation
(a) How long does it take to grow0.1 m of dry oxide at 1000 oC ?
(b) How long will it take to grow0.2 m of oxide at 900 oC in a wetambient ?
Solution :
(a) From the 1000 oC dry curve, ittakes 2.5 hr to grow 0.1 m of oxide.
(b) Use the 900 oC wet curve only. Itwould have taken 0.7hr to grow the0.1 m oxide and 2.4hr to grow 0.3
m oxide from bare silicon. Theanswer is 2.4hr 0.7hr = 1.7hr.