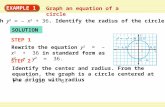
EXAMPLE 1
-
Upload
ramona-chapman -
Category
Documents
-
view
18 -
download
1
description
Transcript of EXAMPLE 1

EXAMPLE 1 Use the SAS Congruence Postulate
Write a proof.
GIVEN
PROVE
STATEMENTS REASONS
BC DA, BC AD
ABC CDA
1. Given1. BC DAS
Given2. 2. BC AD
3. BCA DAC 3. Alternate Interior Angles Theorem
A
4. 4. AC CA Reflexive Property of Congruence
S

EXAMPLE 1 Use the SAS Congruence Postulate
STATEMENTS REASONS
5. ABC CDA SAS Congruence Postulate
5.

EXAMPLE 2 Use SAS and properties of shapes
In the diagram, QS and RP pass through the center M of the circle. What can you conclude about MRS and MPQ?
SOLUTION
Because they are vertical angles, PMQ RMS. All points on a circle are the same distance from the center, so MP, MQ, MR, and MS are all equal.
MRS and MPQ are congruent by the SAS Congruence Postulate.
ANSWER

GUIDED PRACTICE for Examples 1 and 2
In the diagram, ABCD is a square with four congruent sides and four right angles. R, S, T, and U are the midpoints of the sides of ABCD. Also, RT SU and .SU VU
1. Prove that SVR UVR
STATEMENTS REASONS
1. SV VU 1. Given
3. 3. RV VR Reflexive Property of Congruence
2. 2. SVR RVU Definition of line
4. 4. SVR UVR SAS Congruence Postulate

GUIDED PRACTICE for Examples 1 and 2
2. Prove that BSR DUT
STATEMENTS REASONS
1. 1. GivenBS DU
2. 2. RBS TDU Definition of line
3. 3. RS UT Given
4. 4. BSR DUT SAS Congruence Postulate