Evaluation of the VOLVO Truck Demonstrator - aide-eu.org · Start and end at VTEC Start and finish...
Transcript of Evaluation of the VOLVO Truck Demonstrator - aide-eu.org · Start and end at VTEC Start and finish...
www.aide-eu.org
Experimental design - route
Urban (50km/h) and interurban (70/90 km/h) road – approx 40 minutes driveSame route all drives, location of UC triggering predetermined – same for all cases Rush hours avoidedTraining of in-vehicle systems and tasks preceded the driveStart and end at VTEC Start and
finish
Lundbyleden
Gårdsten
www.aide-eu.org
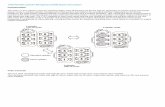
Experimental design – 8 Use Cases
All UC were repeated 2 times – in total 16 tasks/drive
Integrated HBK + SID
Visual + voice
Visual + voice
Visual + voice
Phone call delayed
Message delayed
AIDE
Incoming phone call, out going phone call, MP3
song (UC2,3,4)
High cognitive workload –warning message (UC10)
Intersection driving demand –warning message (UC8)
Reading SMS – warning message (UC9)
Intersection with traffic light –incoming phone call (UC7)
Driver looking for vehicle state information – incoming
message (UC5)
Use Case
Handheld phoneNomadic device integration
Visual + soundOutput form modification to resolve inattention conflict
Visual + soundOutput form modification to resolve workload conflict
Visual + soundOutput form modification to
resolve between channel conflict
Phone call not delayed
Rescheduling to resolve workload conflict
Message not delayed
Rescheduling to resolve channel conflict
Non-AIDEDemonstrator use case group
www.aide-eu.org
Experimental design – triggering and data logging
Supervision of data logging and task annotations
Supervision of DVE state and UC triggering
www.aide-eu.org
Objective data - SWRR
SWRR• Gap size = 3• LPF = 0.6 Hz
Estimated Marginal Means for SWRR
0
5
10
15
20
25
AllUC
UC2 UC3 UC4 UC5 UC7 UC8 UC9 UC10
Use cases
BaseLineAIDENon Aide
• Higher Visual WL for A and NA in total and for all UC except 7,8 and 10• Higher for NA v. A for UC3 (phone out)
www.aide-eu.org
Objective data – Speed Control
Mean speed lower for NA and A vs. BL – total of all UCMean speed was lower for NA vs. BL for all UC (individually) except UC2, 9Mean speed was lower for A vs. BL for UC4
Max speed few significant differences (NA lower vs. BL in UC3,4,5)
Sd speed higher for NA and A vs. BL – total of all UCSd speed higher for NA and A vs. BL in UC4 and 9Sd speed higher for NA vs. A in UC2
Conclusion: Lower speed and higher Sd speed in A and NA vs. BL
www.aide-eu.org
Estimated Marginal Means for Mod SDLP
0
0,02
0,04
0,06
0,08
0,1
0,12
0,14
All UC UC2 UC3 UC4 UC5 UC9 UC10
Use cases
Base LineAIDENon Aide
• Poor lateral data in many cases• MSDLP, LC• Very few differences only MSDLP• TLC not feasible
Objective data - Lateral Control
• A < NA• BL< NA
• UC 3 Making a phone call
www.aide-eu.org
Objective data – Eye Gaze data
• FaceLab – 2 camera system• VDM tool for analysis• Metrics – PRC, GF, TGT• Only UC 2, 3, 4, 5 and 9
• NA < BL for All UC (total), all UC (individually)• A< BL for All UC (total), all UC (individually) except UC5• NA < A for All UC (Total), all UC (individually) except UC4
Percent Road Centre
Aide helped the drivers to keep their eyes on the road
Estimated Marginal Means PRC
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
All UC UC2 UC3 UC4 UC5 UC9
Perc
ent BaseLine
AIDENon Aide
www.aide-eu.org
Objective data – TDT Hit Rate
• Hit rate lower for NA vs. BL• Hit rate lower for A vs. BL except UC 7, 8• Hit rate higher for A vs. NA UC7
• UC7 Delayed phone call• UC8 Message at intersection
Estimated Marginal Means for TDT Hit rate
0
10
20
30
4050
60
70
80
90
All UC
UC2
UC3
UC4
UC5
UC7
UC8
UC9UC10
Use cases
Perc
ent BaseLine
AIDENon Aide
www.aide-eu.org
Estimated Marginal Means for TDT Mean RT
0
0,2
0,4
0,6
0,8
1
1,2
All UC
UC2
UC3
UC4
UC5UC7
UC8
UC9UC10
Use cases
Seco
nds BaseLine
AIDENon Aide
Objective data – TDT Reaction Time
• UC7 Delayed phone call
• RT longer for NA and A vs BL All UC (total)• RT longer for NA and A in most UC (individually)• RT longer for NA vs. A in UC2, 7 and 9
TDT data shows positive effect of Aide in one UC
www.aide-eu.org
Estimated Marginal Means for RSME
05
101520
2530354045
All UC UC2 UC3 UC4 UC5 UC7 UC8 UC9 UC10
Use cases
RSM
E (0
- 15
0)
BaseLineAIDENon Aide
Subjective data - RSME
• RSME was lower for BL compared to A and NA in total and for all UC• RSME was lower for A compared to NA in total and for UC7 (delayed phone call)• A trend that RSME is lower in 5 of 8 UC
• UC7 Delayed phone call
www.aide-eu.org
Subjective data - DALI
0,00
0,50
1,00
1,50
2,00
2,50
3,00
3,50
4,00
4,50
5,00
1 Glob
att d
eman
d2 V
isual
deman
d3 A
udit d
eman
d4 T
actile
deman
d
5 Stre
ss6 T
empo
ral de
mand
7 Inte
rferen
ce
BaseLineAIDENonAIDE
• There were no differences between A and NA• A ratings were higher vs. BL for global, auditory, temporal and interference • NA ratings higher vs. BL for visual, auditory, stress, and interference
www.aide-eu.org
Subjective data – CRF questionnaire driving performance
Four questions were asked with relation to driving performanceGeneral driving performance (Very well – Very bad) - no difference between the three conditionsFeeling of safety – (Very safe – Very unsafe) less safe for NA vs. BLNumber of errors made (e.g. missed to look in the rear view mirror, missed road signs etc.) most errors in NA and least in BL but no sign, differences.Finally, they were asked about the most frequent errors – most frequent, missed to look in the rear view mirrors, missed road signs and misjudging lead vehicle speed.
www.aide-eu.org
Subjective data – CRF Perceived utility
• Most averages on the positive side• Small differences between Aide and Non Aide
Mean values for Precieved Usability Questions 1.2 and 1.3
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
Accurat
ely(+
) / Ina
ccurat
ely(-)
Slowly(
-) / Q
uickly
(+)
Satisfi
ed(+) /
Unsatis
fied(-
)
Amused(+
) / Ann
oyed
(-)
Nervou
s(-) /
Relaxe
d(+)
Displea
sed(-)
/ Plea
sed(+)
Intere
sted(+
) / Unin
terest
ed(-)
AIDENon AIDE
Mean values for Percieved Usability Questions 1.4 - 1.7
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
Made noerrors(+) /
Made lots oferrors(-)
Induced me tomake errors(-)
/ Preventedme frommaking
errors(-)
Helped me torecover from
errors Imade(+) / Did
not help torecover from
errors Imade(-)
Difffcult touse(-) / Easy
to use(+)
Easy tolearn(+) /
Difficult tolearn(-)
It is necessaryto read
instructions /It is not
necessary toread
instructions
Easy toremember /difficult toremember
AIDENon AIDE
www.aide-eu.org
Subjective data – CRF Adequacy of interfaces
• All averages on the positive side• Small differences between Aide and Non Aide
2.1 In general, how do you evaluate the acoustic messages of the system?
-3,00
-2,00
-1,00
0,00
1,00
2,00
3,00
4,00
Com
preh
ensi
ble(
+)/
Inco
mpr
ehen
sibl
e(-
)
Supe
rflo
us(-
) /N
eces
sary
(+)
Inad
equa
te(-
) /A
dequ
ate(
+)
Plea
sant
(+) /
Unp
lesa
nt(-
)
Frig
hten
ing(
-) /
Soot
ing(
+)
Diff
icul
t to
hear
(-)
/ Eas
y to
hea
r(-)
AIDENonAIDE
2.4 How do you evaluate the visual interface of the system?
-3,00
-2,00
-1,00
0,00
1,00
2,00
3,00
Com
preh
ensi
ble(
+)/
Inco
mpr
ehe
nsib
le(-)
Supe
rflou
s(-)
/N
eces
sary
(+)
Inad
equa
te(-)
/A
dequ
ate(
+)
Plea
sant
(+) /
Unp
lesa
nt(-)
Frig
hten
ing(
-) /
Soot
ing(
+)
Perc
eptib
le(+
) /Im
perc
eptib
le(-)
AIDENonAIDE
www.aide-eu.org
Subjective data – CRF Final questionniare
Drivers' final preferences (n=20)
0,0%
10,0%
20,0%
30,0%
40,0%
50,0%
60,0%
70,0%
Non AIDE AIDE
Per
cent
• The final questionnaire consisted of 11 comparative questions• One question concerned possible differences (A/NA) with respect to LKA but most did not feel a difference• However, over 60% preferred the A over the NA condition
www.aide-eu.org
Summary of results
Objective dataSWRR – supports hypothesis partly specific UC3 (phone out)Speed – no clear results (but less speed variation for A UC2 (in phone call))
Lateral pos – no clear results (but MSDLP lower for A in UC3 (out phone))
Eye Gaze – supports hypothesis (driver’s eyes on the road)TDT – supports hypothesis for UC7 (delayed phone call)
Subjective dataRSME - supports hypothesis (total and UC7)DALI - indifferentCRF – Driving performance - indifferentCRF – Perceived utility – indifferentCRF – Adequacy of interfaces – indifferentCRF – Final comparison – supports hypothesis
www.aide-eu.org
Transferring to risk
Risk factor All Use Cases Individual Use Cases
Average speed A & NA ↓ vs. BL UC2 NA ↑ vs A
Speed variability A & NA ↑ vs. BL UC2 NA ↑ vs A
Driver workload
- SWRR A & NA ↑ vs. BL UC3 NA ↑ vs. A
- TDT A & NA ↓ vs. BL UC7 NA ↓ vs. A
- RSME NA ↑ vs. A↑ vs. BL UC7 NA ↑ vs. A
- DALI A & NA ↑ vs. BL ----
Driver distraction
- PRC NA ↓ vs. A↓ vs. BL UC2,3,5,9 NA ↓ vs. A
www.aide-eu.org
Conclusions
Objective data provided useful information for the evaluationThe UC affected workload, performance, and safety – A/NAAide contributed to improve in some cases e.g. eyes on the road
Subjective data did not contribute much to the evaluationExcept subjective workload and general preferenceDifficult to relate questions to specific phenomena
No difference detected in risk between A and NA
However,Difficult for the drivers to perceive the difference between A and NAThe difference between A and NA was not always very distinct e.g. UC8, 9 and 10 –presentation of messages (display/voice vs. display/sound)Too many UC in one drive?Lack of some critical data e.g. headway and improved lateral data