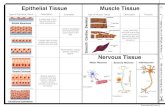
Epithelial Tissue Chapter 4.1 (Human Anatomy). Histology is the branch of anatomy that studies the...
-
Upload
amber-anderson -
Category
Documents
-
view
220 -
download
0
Transcript of Epithelial Tissue Chapter 4.1 (Human Anatomy). Histology is the branch of anatomy that studies the...

Epithelial TissueEpithelial Tissue
Chapter 4.1 (Human Chapter 4.1 (Human Anatomy)Anatomy)

HistologyHistology is the is the branch of anatomy branch of anatomy
that that studies the studies the structure of animal structure of animal
tissue on a tissue on a microscopic levelmicroscopic level..

WhatWhat is a tissue?is a tissue?►A group of cells A group of cells
that all perform that all perform the the samesame specific functionspecific function
►Example: Example: cardiac, muscle, cardiac, muscle, or nervesor nerves

4 Types of Tissues4 Types of Tissues►1) 1) Epithelial TissueEpithelial Tissue – covers body – covers body
surfaces and organs, lines body surfaces and organs, lines body cavitiescavities
►2) 2) Connective TissueConnective Tissue – binds and – binds and supports body partssupports body parts

►3) 3) Muscular TissueMuscular Tissue – contracts – contracts producing movementproducing movement
►4) 4) Nervous TissueNervous Tissue – responds to – responds to stimuli and transmits nerve stimuli and transmits nerve impulsesimpulses

Epithelial TissueEpithelial Tissue►Tightly packed cellsTightly packed cells►Readily divides (mitosis) Readily divides (mitosis)
producing new cells to replace producing new cells to replace old or damaged cellsold or damaged cells
►Lacks blood vesselsLacks blood vessels►Exists on the skin and on the Exists on the skin and on the
surface of organs, blood vessels, surface of organs, blood vessels, and body cavitiesand body cavities

►Function:Function:
- - ExternallyExternally – – protectsprotects body body from from drying out, injury, and drying out, injury, and bacterial invasionbacterial invasion
- - InternallyInternally – – protectsprotects, sweeps , sweeps up impurities, up impurities, secretessecretes mucus, mucus, absorbsabsorbs

►Covers surfaces and Covers surfaces and lines cavitieslines cavities Has a free surfaceHas a free surface Other surface attached Other surface attached
to underlying tissue by to underlying tissue by the the basement basement membranemembrane
Basement membrane
Nucleus
Free Surface
Free SurfaceNucleu
s
Basement membrane
Cytoplasm

►SimpleSimple Epithelial Tissue – composed Epithelial Tissue – composed of a of a single layer of cellssingle layer of cells
►StratifiedStratified Epithelial Tissue – Epithelial Tissue – composed of composed of 2 or more layers of cell2 or more layers of cell

Types of Epithelial TissuesTypes of Epithelial Tissues
1] Squamous Epithelium: simple 1] Squamous Epithelium: simple and stratifiedand stratified
2] Cuboidal Epithelium2] Cuboidal Epithelium
3] Columnar Epithelium3] Columnar Epithelium
4] Pseudostratified Epithelium4] Pseudostratified Epithelium
5] Transitional Epithelium5] Transitional Epithelium



Squamous EpitheliumSquamous Epithelium
►2 types of squamous 2 types of squamous epithelium:epithelium:
* * Simple Simple Squamous Squamous EpitheliumEpithelium
* * Stratified Stratified Squamous Squamous EpitheliumEpithelium

►SIMPLE SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM:SIMPLE SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM:
– – Single layer of flattened cellsSingle layer of flattened cells
– – FunctionFunction: : secretion, absorption, and secretion, absorption, and filtrationfiltration
– – LocationLocation: : lines the lungs, blood lines the lungs, blood vessels and heartvessels and heart

Simple Squamous EpitheliumSimple Squamous Epithelium
Nucleus Cytoplasm

►STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUMEPITHELIUM– – Many layers of Many layers of flattened cellsflattened cells– – Function: Function: protectionprotection– – Location: Location: outer layer outer layer of skin, lining the of skin, lining the various orifices of the various orifices of the bodybody

Stratified Squamous EpitleliumStratified Squamous Epitlelium

Cuboidal EpitheliumCuboidal Epithelium► SimpleSimple Cuboidal Cuboidal
Epithelium:Epithelium:
- - single layer of cube-single layer of cube-shaped cells attached to a shaped cells attached to a basement membranebasement membrane
► StratifiedStratified Cubiodal Cubiodal Epithelum: Epithelum: two or more two or more layers of cube-shaped cellslayers of cube-shaped cells
LocationLocation FunctionFunction
GlandsGlands secretionsecretion
Kidney Kidney tubulestubules
Secretion & Secretion & absorptionabsorption

Simple Cuboidal EpitheliumSimple Cuboidal Epithelium
Basement membrane
Nucleus
Free Surface

Simple Columnar EpitheliumSimple Columnar Epithelium►Composed of Composed of
cells that are cells that are longer than longer than widerwider
►Nucleus found in Nucleus found in the lower half of the lower half of the cellthe cell
LocationLocation FunctionFunction
Digestive organDigestive organ AbsorptionAbsorption
Uterine tubesUterine tubes Propel egg to Propel egg to uterusuterus

Basement membrane
Nucleus
Free Surface

Pseudostratified EpitheliumPseudostratified Epithelium►Cells appear to be Cells appear to be
layered due to layered due to irregularly placed nucleiirregularly placed nuclei but each cell touches the but each cell touches the basement membranebasement membrane
►May contain May contain ciliacilia – aids – aids in movement of particlesin movement of particles
►Function: Function: protection, protection, secretion, movement of secretion, movement of mucus and sex cellsmucus and sex cells
►Location:Location: respiratory respiratory tract, reproductive tracttract, reproductive tract

Pseudostratified EpitheliumPseudostratified Epithelium
Basement membrane
NucleusCilia

Transitional EpitheliumTransitional Epithelium
►Tissue that changes Tissue that changes in response to in response to tensiontension
►Found in organs that Found in organs that need to stretchneed to stretch
►Location: urinary Location: urinary bladder, ureters, bladder, ureters, urethraurethra

Transitional EpitheliumTransitional Epithelium
Basement membrane
NucleusFree Surface