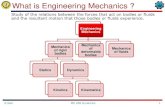
Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
-
Upload
kasun-karunadhara -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
Transcript of Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
1/47
-
Distributed ForcesDistributed Forces
Than Lin, Ph.D.
Instructor, Undergraduate Program
Asian Institute of Technology
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
2/47
Presentation Outline
Introduction
Center of Mass
Centroids (Line, Area, Volume)
Composite Bodies and Figures
Theorem of PappusSpecial Topics
- -
-Beams-Internal Effects
Flexible CablesFluid Statics
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
3/47
Introduction
When forces are applied over a region whose dimensions are not
neg g e compare w t ot er pert nent mens ons, we must
account for the actual manner in which the force is distributed by.
For this purpose, we need to know the intensity of the force at any
location and we will use the integration to find their total effects.
Area Distribution
Line Distribution
Volume Distribution
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
4/47
Centers of Mass & Centroids
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
5/47
Center of Mass
CG: point where the resultant gravitational force W acts
Location of the CG and CM are found by the principle of moment
sum of the moments = moment of the sum
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
6/47
Centers of Mass & Centroids
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
7/47
Centers of Mass & Centroids
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
8/47
Centroids of lines, areas, volumes
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
9/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
10/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
11/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
12/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
13/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
14/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
15/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
16/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
17/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
18/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
19/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
20/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
21/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
22/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
23/47
Composite Bodies and Figures;
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
24/47
Approximation Method
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
25/47
Irregular Volume
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
26/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
27/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
28/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
29/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
30/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
31/47
Locate the center of mass of the bracket and shaft combination. The vertical face is
made from sheet metal which has a mass of 25 kg/m . The material of the horizontal
base has a mass of 40 kg/m2, and the steel shaft has a density of 7.83 Mg/m3.
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
32/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
33/47
Theorem of Pappus
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
34/47
Theorem of Pappus
Several practical objects have their surface or volume created
by revolving the planar curve or the planar area about thenonintersecting line in its plane.
revolved object.
This is done by dividing the object into infinitesimal circular-arc
strips along the axis of revolution. Then the total area or volume
may be determined from integrating the infinitesimal area or
volume of these strips.
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
35/47
Theorem of Pappus
= dLyA 2
LA 2=
dAyV = 2
AyV 2=
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)AyV=
LyA =
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
36/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
37/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
38/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
S i l T i
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
39/47
Special Topics- -
Various Types of Beam Loading and Support
Beam - structural member designed to supportoa s app e at var ous po nts a ong ts engt .
Beam can be subjected to concentrated loads or
distributed loads or combination of both.
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
S i l T i
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
40/47
Special Topics- -
Type of Beams
eams are c ass e accor ng to way n w c t ey are supporte .
Reactions at beam supports are determinate if they involve only three
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
unknowns. Otherwise, they are statically indeterminate.
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
41/47
Distributed Loads
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
42/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
43/47
- -
Beam design is two-step process:
moments produced by applied loads2) select cross-section best suited to resist
shearing forces and bending moments
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
44/47
Wish to determine bending moment and
shearing force at any point in a beam
subjected to concentratedand distributed
loads.
Determine reactions at supports by treating
w o e eam as ree- o y.
u eam a an raw ree- o y
diagrams for AC and CB. By definition,
positive sense for internal force-couple
.
From equilibrium considerations, determine
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
an .
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
45/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
46/47
Shear and Bendin Moment Dia rams
Variation of shear and bending moment along beam may
Determine reactions at supports.
Cut beam at C and consider member AC,
==
Cut beam at E and consider
member EB,
( ) 22 xLPMPV +==
For a beam subjected to concentrated loads, shear is
constant between loadin oints and moment varies
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)
linearly.
-
7/31/2019 Engineering Mechanics DistributedForces
47/47
Engineering Mechanics 3(3-0), AIT-UG (Sept2011)

![Engineering Mechanics - DrChawin.com Engineering Mechanics I [Statics] Lecture 1 Page 1 of 12 Lecture 1: Introduction to Engineering Mechanics Engineering mechanics is the …](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/5aa4d6047f8b9ab4788c63da/engineering-mechanics-engineering-mechanics-i-statics-lecture-1-page-1-of-12.jpg)
![Engineering Mechanics[May2013]](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/55cf8c955503462b138dea30/engineering-mechanicsmay2013.jpg)