Emily Vance Ferris State University. What is Dementia? Treatments Medications/Side Effects...
-
Upload
caitlin-harrington -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
1
Transcript of Emily Vance Ferris State University. What is Dementia? Treatments Medications/Side Effects...

DementiaEmily Vance
Ferris State University

Introduction What is Dementia? Treatments
• Medications/Side Effects• Non-pharmacological
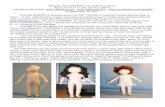
Doll Therapy
The purpose of this assignment is to “practice collaborative leadership to advocate for quality nursing practice using evidence based knowledge”

Evidence for CareDoll Therapy
Nursing Problem Is this therapy effective in treating
distress in dementia patients? Is it ethical to use?

Evidence of Care Nursing Theory
• Katharine Kolcaba – Comfort Theory• John Bowlby – Attachment Theory

Evaluation of the Evidence
1st study• Mixed methods design to
collect observational data• Used Likert Scale • 14 residents
2nd study • 66 residents• Examined case notes
3rd study Bradford Dementia Group Wellbeing
Profiling too
4th study• Questionnaires to 46 care staff• 37 residents
Results• All showed some decrease in
agitation and wandering• However, some caregivers found it
“demeaning…patronising…babish”
Methods

Evaluation of the Evidence
Article Critique Nursing Research
• British Journal of Nursing• Authors’ are nurses
Qualitative Study• Mainly anecdotes from other studies
Limitations• Sample sizes• Studies only done in UK and Japan• Not enough research!• Ethical concerns

Patient Care Design Nurse Leader
• Nursing staff In-services and other training options
• Family Counseling, support groups
• Social Worker• Behavioral Therapists• Physical/Speech Therapy

TRUEPICSituation: Mrs. T is a 78 year old dementia patient that is newly admitted to a locked dementia unit of a nursing home. She is accompanied by her daughter who is having a hard time coping with her mother’s illness. After the daughter leaves, Mrs. T. is seen pacing the halls and entering other patient rooms. Mrs. T is easily agitated when staff try to redirect her. She is confused and keeps asking how her daughter will find her.
The nurse is a 26 year old BSN prepared RN with 1 year experience working on a ortho med-surg unit. She has no experience dealing with patients with moderate to severe dementia.
1.Identify…
78 year old female
Dementia/confused
New admit
Easily agitated
Wandering
Looking for young daughter
3. Understand…
Proposition: “If the pt’s agitation is not controlled she could injure herself or others.”
Significance of Assumptions: “If pt is unaware of why she is here and doesn’t socialize then she can become depressed.”
Possible Confounding Variables: “If pt is unable to be redirected then she will be unwilling to take medication to help with other health issues.”
2. Relate…
Primary Proposition: “Pt is agitated because family left her in a nursing home.”
Possible Assumptions:“Pt doesn’t participate in regular social activities.”
Possible Confounding Variables: “Pt has moderate dementia and is difficult to redirect.”

TRUEPIC4.Explain…
Proposition: In a meaningful way , explain where her family is and why she is here.
Assumptions:. Explain to her the importance of social activies
Confounding Variables: Explain to family how dementia works.
5. Predict…Proposition: if agitation continues the pt will hurt herself, staff, or other pts.
Assumptions: if she does not participate she could get depression and her dementia could worsen
Confounding Variables: if pt is unable to be redirected she could injure herself
6. Influence…
Proposition: Make sure staff knows how to deal with her agitation.
Assumptions: Make sure staff provides activities she likes
Confounding Variables: Make sure to educate staff and family about dementia.
7. Control…- Nurses will calm pt with the use of nonpharmacologic methods such as reality orientation, aromatherapy, music therapy, or doll therapy (if allowed)
Nursing DiagnosisRisk for injury: Risk Factors: confusion, agitation.

Advocate Role Educate Staff/family/patients Treat patients with dignity More Research Significance to Nursing Practice
• Better patient compliance• Holistic nursing

References Colley, S. (2014). NURS 441 Nursing theory 3 [spring 2014 course
syllabus]. Retrieved from https://fsulearn.ferris.edu/webapps/portal/fram eset.jsp?tab_group=courses&url=%2Fwebapps %2Fblackboard%2Fexecute%2Fcontent%2Ffile %3Fcmd%3Dview%26content_id%3D_510231_1 %26course_id%3D_8632_1%26framesetWrappe d%3Dtrue
Comfort Theory by Katharine Kolcaba. (n.d.). Comfort Theory by Katharine Kolcaba. Retrieved January 26, 2014, from
http://currentnursing.com/nursing_theory/comfort_theory_Kathy_Kolcaba.html
Mitchell, G. & O’Donnell, H. (2013). The therapeutic use of doll therapy in dementia. British Journal of Nursing, 22(6), 329-334.
Videbeck, S.L. (2014). Psychiatric-mental health nursing (6th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
![The Inventory of the John Holbrook Vance [Jack Vance ...archives.bu.edu/finding-aid/finding_aid_122912.pdf · Vance.JR Box 1 Box 2 Box 3 VANCE, JOHN HOLBROOK, 1916 - [Jack Vance]](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/5e776f55989f9014e425e4a0/the-inventory-of-the-john-holbrook-vance-jack-vance-vancejr-box-1-box-2-box.jpg)