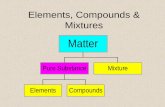
Elements Elements – pure substance that cannot be broken down by physical or chemical means Pure...
-
Upload
liliana-ward -
Category
Documents
-
view
238 -
download
1
Transcript of Elements Elements – pure substance that cannot be broken down by physical or chemical means Pure...
Elements
• Elements – pure substance that cannot be broken down by physical or chemical means
• Pure substance – a substance that contains only one type of particle.
• Elements have characteristic properties that do not depend on amount of material present
• Most elements are combined in nature
– Examples
• H2O (water)
• CaF2 - fluorite
Atoms
• HaveProtons – positive
charged particles
Neutrons – neutral charged particles
Protons and neutrons are found in center of atom, called a nucleus
Atoms
• Surrounding nucleus are
Electrons – negative charge particles
This region is called the electron cloud or energy levels
Atoms
• Atomic number- number of protons in the nucleus
• Mass number (atomic mass)- number of protons plus neutrons
Isotopes
• The number of protons in an element never changes.
• The number of neutrons in an element may change.
• Isotope- a variation of an element that differs only in the number of neutrons.
• Examples (hydrogen):– protons neutrons
1 0 (hydrogen) 1 1 (deuterium- heavy water) 1 2 (tritium- radioactive)
Metals
• Shiny• Good conductors of
heat and electricity• Malleable – flattened
into thin shapes• Ductile – drawn into
thin wires• Can be solid or liquid• Copper, lead and tin
are examples
Nonmetals
• Dull (not shiny)• Poor conductors of
heat and electricity• Brittle• Can be solid,
liquid or gas• Bromine, sulfur and
neon are examples
Metalloids
• Have properties of metals and nonmetals
• Many are called semiconductors
• Dull or shiny• Some can be
malleable or ductile• Examples include
antimony, silicon, boron
Dmitri Mendeléev
• In 1869, Dmitri Mendeléev created the first version of the periodic table.
• Grouped elements based on atomic mass
• Found elements in same group had similar chemical properties.
• Blank spaces were left open to add the new elements
• Just over 50 elements were known then.
The Periodic Table
Rows = Periods
-no similar properties
-1st element = reactive metal
-last element = non reactive gas
Columns = Groups/Families
-have similar properties
-have same number of valence electrons
- examples lithium, sodium and potassium
Hydrogen
-single element with its own classification
-sits atop Group IA
-1 electron in its only energy level
IA
Alkali Metals
-Group IA elements, excluding hydrogen (all metals)
-always combined with other elements in nature
-1 electron in its outer energy shell
IA
Alkaline Earth Metals
-Group IIA elements (all metals)
-always found combined with other elements in nature
-2 electrons in its outer energy shell
IIA
Transition Elements
-Group B elements (all metals)
-many found combined with other elements in nature, some found in their elemental state (gold and silver)
-varying numbers of electrons in outer energy shell
B
Boron Family
-Group IIIA elements (boron = metalloid, rest are metals)
-always found combined with other elements in nature
-3 electrons in its outer energy shell
IIIA
Carbon Family
-Group IVA elements (nonmetal, metalloids and metals)
-mostly found combined with other elements in nature but may be found in its elemental state (e.g. diamond and graphite)
-4 electrons in its outer energy shell
IVA
Nitrogen Family
-Group VA elements (nonmetals, metalloids and a metal)
-mostly found combined with other elements in nature
–5 electrons in its outer energy shell
VA
Oxygen Family
-Group VIA elements (nonmetals, metalloids and a metal)
-mostly found combined in nature but may be found in its elemental state (e.g. sulfur)
-6 electrons in its outer energy shell
VIA
Halogens
-Group VIIA elements (nonmetals and a metal)
-mostly found combined with other elements in nature
-7 electrons in its outer energy shell
VIIA
Noble Gases
-Group VIIIA elements (nonmetals)
-never found combined with other elements in nature
-contain a full set of electrons in its outer energy shell
VIIIA