Electron Configuration · arrangement of electrons in an atom. OOrbital notation shows how the...
Transcript of Electron Configuration · arrangement of electrons in an atom. OOrbital notation shows how the...
Essential Question
O What is electron configuration, and why is it
important?
O What is orbital notation, and why is it
important?
Where Are the Electrons?
O Electron Configuration represents the
arrangement of electrons in an atom.
O Orbital notation shows how the electrons
fill the sublevels.
O Uses boxes or lines as orbitals and arrows to
represent electrons.
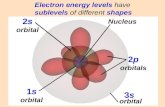
Orbital shapesO There are 4 different orbit shapes
s - Sphere
p - Dumbbell
d - Flower
f - is way more complicated than you have to know.
S P D F & the Periodic TableO The period # on the periodic table is equal to the
number of energy levels (n) in an atom.
O Within each energy level there are sublevels.
O The periodic table is divided into blocks to represent
each sublevel, with each orbital holding only 2 electrons.
s -Block
p -Block
d -Block
f -Block
1s
Energy Level Sub-levels Total Orbitals Total Electrons Total Electrons
per Level
n = 1 s 1 (1s orbital) ____ ____
n = 2 s
p
1 (2s orbital)
3 (2p orbitals)
2
____
____
n = 3 s
p
d
1 (3s orbital)
3 (3p orbitals)
5 (3d orbitals)
2
6
____
____
n = 4 s
p
d
f
1 (4s orbital)
3 (4p orbitals)
5 (4d orbitals)
7 (4f orbitals)
2
6
10
____
____
The RulesAs you learn E-CON & Orbital
Notation, there are 3 rules you
need to remember.
OHund’s Rule
OPauli’s Exclusion Principle
OAufbau Principle
Hund’s RuleO States electrons must occupy orbitals of a given
sublevel singly before pairing.
O The electrons must have parallel spins
Pauli’s Exclusion Principle
O States that electrons occupying the SAME
orbital must have opposite spins.
Aufbau PrincipleO States that electrons will fill the lowest energy level
before moving on to the next.
O In other words, an energy level must be completely
filled before moving on to the next.
Electron Configuration(E-Con)
There are 3 parts to the electron configuration
This is the electron configuration
for Helium!
Energy
When & What to WriteO Read the periodic table like you read a
book – LEFT TO RIGHT – until you get to
the element that you want
O What energy level are you in?
O What orbital (s, p, d, f)?
O How many electrons?
Essential Question
O What is shorthand notation, how is it
different from ‘normal’ electron
configuration?
Short cut!O Tired of writing out all of the 1 and 2 and s
and p? We’ve got a shortcut!
O It has two names
O Shorthand electron configuration
O Noble Gas configuration
O The reason it is known as noble gas
configuration is because you use the
last passed Noble gas as a starting
point.
O If you think of regular electron configuration as giving specific directions, Noble Gas configuration gives much more general directions
O For example, if someone is trying to get to Lake Ridge from Fort Worth, you can give them turn by turn directions. This would be normal electron configuration
O BUT if the person knows how to get to the Chicken Express, you can give them much less direction and that would be noble gas configuration.
Well how do you do it?!?
O Step 1: Find the element you are writing the
e-con for.
O Step 2: Find the Noble Gas that came before
it
O Step 3: Put the Noble Gas symbol in
brackets [He]
O Step 4: Write out the electron configuration
like you would, just starting at the noble
gas!!