Electrochemistry Oxidation-reduction reactions. Review Ionic bonds : give and take of electrons...
Transcript of Electrochemistry Oxidation-reduction reactions. Review Ionic bonds : give and take of electrons...

ElectrochemistryElectrochemistry
Oxidation-reduction reactionsOxidation-reduction reactions

ReviewReview
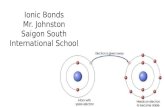
Ionic bonds : give and take of electrons Ionic bonds : give and take of electrons (example NaCl)(example NaCl)
Covalent bonds: electrons shared Covalent bonds: electrons shared (example CO(example CO22))
All elements in the molecule become All elements in the molecule become STABLE (like a noble gas in electron STABLE (like a noble gas in electron configuration) and NEUTRAL (balanced in configuration) and NEUTRAL (balanced in charge)charge)

Oxidation NumbersOxidation Numbers
We can assign a specific charge to We can assign a specific charge to elements involved in bondingelements involved in bonding
For simplicity, we assign full charges to For simplicity, we assign full charges to elements even if they are sharing elements even if they are sharing (example H(example H220…H is considered to be 1+ 0…H is considered to be 1+ and O as 2-)and O as 2-)
(H (H 1+1+) x 2 + O ) x 2 + O 2-2- = H = H220 0 (Oxygen has a tighter hold on the (Oxygen has a tighter hold on the
electrons therefore is “negative”)electrons therefore is “negative”)

Building moleculesBuilding molecules
We can use oxidation numbers to predict We can use oxidation numbers to predict the ratios of elements or elements with the ratios of elements or elements with polyatomic negative ions in a stable and polyatomic negative ions in a stable and neutral molecule.neutral molecule.
Example Pb(SOExample Pb(SO44))
(SO (SO 44) has a 2- charge ,therefore Pb must ) has a 2- charge ,therefore Pb must
be 2+ be 2+ Name = Lead II SulfateName = Lead II Sulfate

Determining Oxidation NumbersDetermining Oxidation Numbers
What about SOWhat about SO44 ? ?Oxygen is given oxidation number 2- Oxygen is given oxidation number 2- 4 oxygen atoms = 8- charge!4 oxygen atoms = 8- charge!What must S’s charge be so that SOWhat must S’s charge be so that SO4 4 has has
a total net charge of 2-?a total net charge of 2-?S must have a 6+ charge S must have a 6+ charge

Practice!Practice!
Determine the oxidation numbers of each Determine the oxidation numbers of each element in the following examples:element in the following examples:
HClHClPbOPbOFeFe22OO33
CuNOCuNO33
NaOHNaOH

OXIDATIONOXIDATION
Process whereby an element becomes Process whereby an element becomes MORE positive by losing electronsMORE positive by losing electrons
REMEMBER that there are protons in the REMEMBER that there are protons in the nucleus that are now unequal to the nucleus that are now unequal to the number of electronsnumber of electrons

REDUCTIONREDUCTION
Process whereby elements become Process whereby elements become MORE negative by gaining electronsMORE negative by gaining electrons
Element now has MORE electrons than it Element now has MORE electrons than it has positive protons in the nucleus and has positive protons in the nucleus and has a net charge that is negative.has a net charge that is negative.

Oxidizing agentOxidizing agent
This would be any element or molecule This would be any element or molecule that TAKES electrons allowing another that TAKES electrons allowing another element to be oxidized (become more element to be oxidized (become more positive by losing electrons)positive by losing electrons)
The oxidizing agent is reduced in the The oxidizing agent is reduced in the processprocess

Reducing agentReducing agent
This would be any element or molecule This would be any element or molecule that GIVES electrons to another element that GIVES electrons to another element allowing it to be reduced- becoming more allowing it to be reduced- becoming more negative by gaining electronsnegative by gaining electrons
The reducing agent is oxidized in the The reducing agent is oxidized in the processprocess

ExampleExample
Sodium reacts with carbon to produce Sodium reacts with carbon to produce sodium carbide sodium carbide
Identify the oxidation number of each Identify the oxidation number of each elementelement
Determine if any of the elements changed Determine if any of the elements changed oxidation numberoxidation number
Determine who is acting as the agents of Determine who is acting as the agents of change!change!

Writing half reactionsWriting half reactions
Once we identify which elements are Once we identify which elements are being oxidized and reduced, we can write being oxidized and reduced, we can write out “half reactions” for the transfer of out “half reactions” for the transfer of electrons involvedelectrons involved
Eg:Eg: Na + CNa + C NaNa44CCSodium is losing an electron= oxidizedSodium is losing an electron= oxidizedCarbon is gaining electrons = reducedCarbon is gaining electrons = reduced

NaNa00 NaNa1+1+ + 1 e- (oxidized) + 1 e- (oxidized)CC00 + 4 e- + 4 e- CC4-4- (reduced) (reduced)We need to make sure that the number of We need to make sure that the number of
electrons given and taken is EQUAL!electrons given and taken is EQUAL!Therefore we will need 4 sodium atoms to Therefore we will need 4 sodium atoms to
donate all of the electrons needed for donate all of the electrons needed for carboncarbon
This is often a good way to help balance This is often a good way to help balance difficult reactions.difficult reactions.

Try this!Try this!
Magnesium solid reacts with oxygen gas to Magnesium solid reacts with oxygen gas to produce magnesium oxideproduce magnesium oxide
STEP #1STEP #1 -write a chemical equation -write a chemical equation STEP #2STEP #2 -assign oxidation numbers-assign oxidation numbers STEP #3STEP #3 -write “half reactions”-write “half reactions” STEP #4STEP #4 -label oxidation/reduction-label oxidation/reduction STEP #5STEP #5 -balance electrons-balance electrons STEP #6 -balance the equation! STEP #6 -balance the equation!

Try these for homework!Try these for homework!
Fe + CuS0Fe + CuS044 Cu + FeS0Cu + FeS044
HH2 2 + 0+ 022 HH2200
Cu + AgN0Cu + AgN033 Cu(N0Cu(N033))22 + Ag + Ag
HNOHNO33 + H + H22SS S + NO + HS + NO + H22OO