Effect of Urbanization on Runoff in the Whiteoak Bayou Watershed in Houston, Texas
description
Transcript of Effect of Urbanization on Runoff in the Whiteoak Bayou Watershed in Houston, Texas

Effect of Urbanization on Runoff in the Whiteoak
Bayou Watershed in Houston, Texas
Effect of Urbanization on Runoff in the Whiteoak
Bayou Watershed in Houston, Texas
Francisco OliveraTexas A&M UniversityDepartment of Civil Engineering
Burren DeFeeUniversity of Arkansas at MonticelloSchool of Forest Resources
AWRA GIS in Water ResourcesHouston, May 8-10, 2006

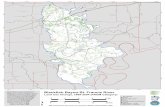
Whiteoak Bayou WatershedWhiteoak Bayou Watershed
The watershed is located in northwest Houston in Texas.Area = 223 km2.

Whiteoak Bayou WatershedWhiteoak Bayou Watershed
Precipitation and flow have increased significantly over time.
0
250
500
750
1000
1250
1500
1750
2000
1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010
Year
An
nu
al R
un
off
an
d P
reci
pit
atio
n D
epth
(m
m)
Annual Precipitation
Annual Runoff

Whiteoak Bayou WatershedWhiteoak Bayou Watershed
Cumulative annual runoff.
0
5,000
10,000
15,000
20,000
25,000
1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010
Year
Cu
mu
lati
ve A
nn
ual
Ru
no
ff (
mm
)
Year ≤ 1972: 245 mm/yr
Year ≥ 1973: 603 mm/yr
Break point in 1972 - 1973

Whiteoak Bayou WatershedWhiteoak Bayou Watershed
Peak 12-hour precipitation depths and peak flows have significantly increased over time.
0
200
400
600
800
1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010
Year
Pea
k F
low
(m
3/s)
0
50
100
150
200
12-H
ou
r P
reci
pit
atio
n D
epth
(m
m)
Peak Flows
12-Hour Precipitation Depths

Whiteoak Bayou WatershedWhiteoak Bayou Watershed
Cumulative annual peak flow.
0
2,500
5,000
7,500
10,000
12,500
1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010
Year
Cu
mu
lati
ve P
eak
Flo
w (
m3 /s
)
Year = 1967: 113 m3/s
Year = 1968: 293 m3/s
Break point in 1967 - 1968

Whiteoak Bayou WatershedWhiteoak Bayou Watershed
Parcel data was obtained from the Harris County Appraisal District.
Data included: parcel digital map, parcel area, building square footage, number of floors and year of construction.

Whiteoak Bayou WatershedWhiteoak Bayou Watershed
Developed parcels and roads.

Whiteoak Bayou WatershedWhiteoak Bayou Watershed
One point per developed parcel.
19501960
2000
197019801990

Whiteoak Bayou WatershedWhiteoak Bayou Watershed
Percent developed area and percent impervious cover
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
1949
1951
1953
1955
1957
1959
1961
1963
1965
1967
1969
1971
1973
1975
1977
1979
1981
1983
1985
1987
1989
1991
1993
1995
1997
1999
Year
Per
cen
t
Watershed Impervious Cover Total Developed Area

Whiteoak Bayou WatershedWhiteoak Bayou Watershed
Developing new parcels can change the spatial configuration of the developed areas.

Whiteoak Bayou WatershedWhiteoak Bayou Watershed
Edge density and mean shape index.
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010
Ed
ge
de
ns
ity
(m
/Ha
)
1.5
1.6
1.7
1.8
1.9
2.0
Me
an
sh
ap
e in
de
x
Edge density
Mean shape index

Whiteoak Bayou WatershedWhiteoak Bayou Watershed
Number and mean area of the developed patches.
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010
Nu
mb
er o
f p
atch
es
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
180
200
Mea
n p
atch
siz
e (H
as)
Number of patches
Mean patch size

Whiteoak Bayou WatershedWhiteoak Bayou Watershed
Observed and predicted annual runoff values.Break point: 1972 – 1973.
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010
Year
An
nu
al R
un
off
Dep
th (
mm
)
Observed
Predicted e = 54 mm
S i iR 0.458 P 255
S i i iR 0.593 P 2.05 DA 414

Whiteoak Bayou WatershedWhiteoak Bayou Watershed
Annual runoff assuming pre-1972 conditions.
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010
Year
An
nu
al R
un
off
Dep
th (
mm
)
Observed
No adjustment

Whiteoak Bayou WatershedWhiteoak Bayou Watershed
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010
Year
Pea
k F
low
(m
3/s
)
Observed
Estimated e = 81 m3/s
Observed and predicted annual peak flows.
S i (12)i i iQ 1.57 P 0.149 P 1.27 DA 169

Whiteoak Bayou WatershedWhiteoak Bayou Watershed
Peak flows assuming impervious remains lower than 10%.
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010
Year
Pea
k F
low
(m
3/s
)
Observed
Estimated IC < 10%

Whiteoak Bayou WatershedWhiteoak Bayou Watershed
Annual runoff depth for the period 1973 – 2000:
Accounting for increasing urbanization level• Average: 603 mm. Range: 310 mm – 1030 mm
Assuming 1972 urbanization level (i.e., 10% impervious cover)• Average: 340 mm. Range: 50 mm – 600 mm
Annual runoff increment because of urbanization is 77%.Total annual runoff increment is 146%.

Whiteoak Bayou WatershedWhiteoak Bayou Watershed
Peak flows for the period 1973 – 2000:
Accounting for increasing urbanization level• Average: 299 m3/s. Range: 108 m3/s – 711 m3/s
Assuming 1972 urbanization level (i.e., 10% impervious cover)• Average: 226 m3/s. Range: 57 m3/s – 434 m3/s
Peak flow increment because of urbanization is 32%.Total peak flow increment is 159%

Whiteoak Bayou WatershedWhiteoak Bayou Watershed
Peak flows tend to increase less than annual runoff depths because a significant part of the additional flow takes place during small events.
It was observed that the 12-hour precipitation increased much more over time than the annual precipitation.
Urbanization below a critical threshold value appears not to affect annual rainfall depth, after which it increases proportional to the developed area. That threshold value took place in 1972-1973 in the Whiteoak Bayou watershed, when the watershed reached a 10% impervious cover.
The variation in the number of developed patches can be interpreted as a measure of the connectivity of the impervious cover and of its capacity to convey flow. The number of patches reached a maximum value in 1972.

Whiteoak Bayou WatershedWhiteoak Bayou Watershed
Future work:Apply same methodology to other cities in the world:
• Portland, Oregon, an example of a “planned” city as opposed to Houston, Texas.
• Madrid, in collaboration with the Castilla – La Mancha University in Spain.
Consider non-linear regressions.