EARTHQUAKES. Earthquakes & Plate Tectonics It is a vibration in the crust due to the release of...
-
Upload
danielle-holten -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
5
Transcript of EARTHQUAKES. Earthquakes & Plate Tectonics It is a vibration in the crust due to the release of...

EARTHQUAKES

Earthquakes & Plate Tectonics
• It is a vibration in the crust due to the release of stress
• Causes a shift in the rocks along a fault or plate boundary
• Explained by the Elastic Rebound Theory“Locked” rocks build up stress,
fracture, & slip back to original position• Slipping causes release of energy =
seismic waves

• Focus is the location (within the earth) along the fault where slippage occurs
• Epicenter (what you hear on the news) is the point, on the surface, directly above the focus– Where most damage occurs

• Approximately 90 % of all earthquake foci are at depths of less than 100 km (62 miles)

3 Major Earthquake Zones
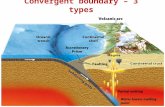
• Pacific Ring of Fire• Mid-oceanic ridges• Eurasian-Melanesian mountain belt
EQ occur along plate boundaries

Recording Earthquakes
• Seismographs detect motion of the crust
• Creates series of wavy lines called seismogram

3 Types of Seismic Waves• BODY= a. Primary waves-
move together & apart like accordion (fastest)
b. Secondary waves- move at right angles to direction of wave travel like a snake
• SURFACE= Love & Rayleigh waves- move up & down like ocean waves (slowest) w/ side-to-side component
These cause most damage Earthquakes seismic waves animation

Locating an Earthquake
• To find epicenter of an earthquake, analyze difference between arrival of P & S waves
• P waves travel 1.7 X faster than S waves
If S waves arrive shortly after P waves = close If S waves arrive long after P waves = far away

Locating an Earthquake
• Need seismographic data from 3 different locations
• Distances to epicenter plotted on map & their intersection determines epicenter

Earthquake Measurement• Magnitude expressed by Richter ScaleMeasures energy released by EQ as
measured by the amplitude (height) of the seismic wave increase by 1 = 31.7 times more energy
Ex. EQ = 7 had 31.7 X more energy released than an EQ = 6
• Largest EQ = 9.5, Chile, 1960

Earthquake Measurement
• Mercalli scale expresses intensity or amount of damage done
• Indicated by Roman numerals I to XII
• Ex. II = low intensity described as “Felt only by a few persons at rest, especially on upper floors of buildings”

Earthquake Damage
• Determined by type of ground that building is located on
Loose soil & rock = more damage
• Most injuries from collapsing buildings & flying debris
• May cause landslides, fires, & explosions

EQ occur along plate borders, little “tears” in the crust create faults
One of the world’s
most active = San Andreas Fault System (made of 100s of faults) in California, it separates the N Am. & Pacific plates
800 mi long
10 mi deep

Seismic Activity in the U.S.
Red/orange = areas of high seismic activity
Yellow = medium seismic activity
Blue/white= low seismic activity

Tsunami
• Created when an the epicenter of the earthquake is on the ocean floor
• Displaces (and pushes) a huge volume of water
• Creates massive “tidal waves” of moving water

As a tsunami approaches the shore
Wavelength decreased & wave height increase

December 2004 Tsunami Disaster





Earthquake Detection
• Scientists try to detect changes in the crust by:
instruments used to detect movementimmobile area = seismic gaps(fault is locked)– Future earthquake
locations

Evidence of Pending Earthquake
Slight tilting of ground just prior to EQIncrease in strain in rocks
• may inject water in cracks to reduce strain
Change in electrical & magnetic propertiesIncreased natural gas seepageDecrease in speed of P waves from
distant earthquakes

• 10 things you didin't know about earthquakes