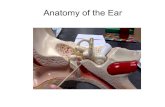
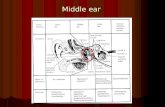
HEARING CONSERVATION. Parts of the Ear Outer Ear Middle Ear Inner Ear.
Ear
-
Upload
ashraf-al-hamshary -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
627 -
download
1
Transcript of Ear
• This mirror is concave
• It reflects the light beam coming from a fixed source behind and above the left shoulder of the patient
• It is placed just in front of the examiner’s right eye
The Head Mirror
The head Lamp
• Easy to use• Allows movement of
the examiner• Portable so allows
bed side examination
Examination of infant
The assistant sits on theexamination chair
The infant is lying on the lapof the assistant
The infant head is held byone of the assistant hand The body is held by theother assistant hand
• Examination of child patient The assistant sits on the examination chair The child sits on the lap of the assistantThe child hands are grasped against the abdomen by oneassistant handThe child head is grasped against the assistant chest by the otherhand
• Examination of child patient The assistant sits on the examination chair The child sits on the lap of the assistantThe child hands are grasped against the abdomen by oneassistant handThe child head is grasped against the assistant chest by the otherhand
• The auricle is pulled upwards and backwards, Why?
Answer: this will straighten the outer cartilagenous part because:
• The outer cartilagenous part is directed upwards, backwards and medially
• The inner bony part is directed downwards, forwards and medially
Hand Held Speculum
• It is held by examiner’s hand
• The speculum is placed in the cartilagenous part
• The largest speculum that is comfortable is used to provide the best vision
Otoscopic Examination
Advantage of Otoscope
1-Easy to use2-Provides magnified view3-Allows free movement of the examiner4-portable
Pneumatic examination
Left : Seigle’s SpeculumRight : Pneumatic Otoscope
To assess Mobility of DrumTo perform Fistula test
ValvelessRubber Pump
Examination under Microscope
• Mention 2 advantages
1- provides magnified view with good illumination
2-allows the use of both hands
Enumerate2 tests done bythis instrument
Mention the principle ofevery test
Mention the results ofeach test in normal caseand in conductive andsensorineural hearingloss
Tunning fork
•Pure Tone Audiometry
•Value :
Usefull for diagnosis of:1- Degree of Hearing
Loss ( mild, moderate severe or profound)
2-Type of Hearing loss, ( CD, SNHL Or Mixed)
• An example of a mixed deafness in the right ear. Both the bone conduction and air conduction tests show that there is a hearing loss and Air Bone Gap is also seen
35 years old male patient C/O diminished hearing & tinnitus in Rt. Ear + vertigo
250 500 1000 2000 4000 8000 Hz
Speech Discrimination Scores = Rt. Ear: 84% Lt. Ear: 100%
250 500 1000 2000 4000 8000 Hz
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
dB
Q1- Comment on the type hearing loss.
Q2- Give one possible etiology.
dB
AnswerRight Sensorineural Hearing loss affecting the lower tonesLeft Normal HearingOne possible etiology is Meniere’s Disease
Tympanometry
This graph is knownas……… type…….. and is diagnosticof………….
NormalTympanogram
Type Ad
Type B
Type C
Secretory otitis media
ET dysfunction
Ossicular discontinuity
Ossicular fixation
e.g Otosclerosis
30 years old female patient
Q1 – Comment on the type of tympanograms.Q2 – Give one possible etiology.
Type As Tympanogram( decreases compliance and normal pressure)
One etiology: Otosclerosis
• On application of a loud sound to an infant (below 6 month) the infant responds by a reflex movement
• This movement may be a jerk of the whole body called Moro or Startle reflex
The Moro reflex
• This test is known as Positional Test• One disease diagnosed by this test is
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)
1- The Handel of Malleus
2-The Cone of Light
3-lateral process of Malleus
4-Pars Tensa
5-Pars Flaccida
Normal Tympanic membrane
1
2
3
4
5
• The bone number…… is that one included in otosclerosis
• The handle of the bone number…….. is foreshortened when the drum is retracted
1 2 3
• The bone number 3 is that one included in otosclerosis
• The handle of the bone number 1 is foreshortened when the drum is retracted
• Microtia with atresia of the External Auditory Canal
Investigations• CT scan of Temporal
bone• Audiological
evaluationTreamentPlastic surgery
• Infected Preauricular sinus• Infection is clear (left)
Investigations:• Culture and
sensitivity of the discharge
Treatment:- Systemic antibiotic- Analgesic
antipyretic- Incision for drainage
of pus- Later on: excision
Foreign body (FB)in the external auditory canal
- On the left side it is animate FB (insect), the treatment is to kill the insect by alcohol or oil before removal
- On the left side it is animate FB (insect), the treatment is to kill the insect by alcohol or oil before removal
Cerumen impaction
• Treatment- Removal by ear wash or instruments- If wax is hard, it should be softened by glycrine
bicarbonate or hydrogen peroxide before ear wash
A brownish mass in the external canal
• Hearing loss & Tinnitus
Wax accumulationQ- Symptoms inthis patient are:1-…………..2-…………..
• Diagnosis :………..• It is a complication of
1- ………….. 2-……………
• Diagnosis
Cauliflower ear• It is a complication of
1- hematoma auris• 2- perichondrtitis
• Painless, slowly growing, solid tumor that distorts the auricle and changes the normal architecture. It resembles a cauliflower ear, but it is much harder and cannot be compressed by squeezing it with the fingers
Chondroma of the Auricle
• A 64-year-old man presented with a 7-day history of pain and increased swelling behind his left ear. This 2-cm fluctuant, mass represented ………………………….., that required incision and drainage
Infected sebaceous cyst
• Squamous cell carcinoma (left) • Basal cell carcinoma (right)• Describe the character of each ulcer seen
Everted edge Inverted beaded
edge
Necrotic floor
Otomycosis
• Right: whitish massa filling the external canal ( Candida Albicans)• Left: black mass with hyphae and spores (asprigillus Niger)What is the main symptom that patient in patient ? • Itching
Traumatic drum perforation Central perforation in the pars tensa elliptical in shape with irregular hyperaemic sharp edge
• In this pateint:1-surgical treatment is
mandatory2- conservative treatment is not
successful in most cases 3- The use of antibiotic ear
drops is helpful4- surgical treatment is indicated
when the perforation fails to heal after 3 months
Answer: 4
•Retracted Tympanic Membrane
• What are the signs of Retracted Drum seen in this case?
• Prominent lateral process of malleus
• Fore-shortened handel of malleus
• Distorted cone of light
• Bulging Tympanic Membrane• Treatment of this patient : Myringotomy
In infants, the tympanic membrane is thicker than in adults, so it does not bulge easilyDon’ t wait for bulging drum and MYRINGOTOMY is done if there is persistent pain & fever for 48 hours
Schirmer test • Principle:…………………………………………….• It is significant when…………………and this is
seen if the lesion of ………….nerve is ………….
A B
Moderate central perforation
• Thickened Hyperaemic middle ear mucosa
• Yellowish discharge is seen
Before myringoplasty
control of infection is
needed
Grommet tube in the antero-inferior part of the tympanic membrane
• The arrow points to ………….. which is situated in the…………quadrant of the ………..
• This patient is suffering from ………….
• The arrow points to Grommet tube which is situated in the anteroinferior quadrant of the tympanic membrane
• This patient is suffering from secretory otitis media
• A patient on the operating table for mastoidectomy and drainage of Bezold abscess
- Positive Kernig sign inability to extend theknee completely whenthe hip is flexedThis sign is positive inMENINGITIS
Poaitive Brudzniski signReflex flexion of thehip and knees whenthe neck is flexed
This sign is positive inMENINGITIS