Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
Transcript of Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
1/39
Department of Child HealthNephrology Division
FKUI – RSCMJakarta
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
2/39
Hypertensive crisis:
uncommon medical emergency
Hypertension stage 1:2.6%
Hypertension stage 2:0.6%
Diagnosis and rapid treatment preventirreversible brain damage or death
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
3/39
2004The fourth repo rt on the diagnos is, evaluat ion , and
treatment of h igh b lood pressu re in ch i ldren andadolescents:
Hypertension:
• Stage 1 hypertension: BP 95th percentile to 5 mmHg above 99 th percentilesfor gender, age, and height
• Stage 2 hypertension: BP > 5 mmHg above 99 th percentile for gender, age,and height
National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and
Adolescents. The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in
children and adolescents. Pediatrics 2004;114:555-76.
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
4/39
Hypertensive crisis
-SBP > 180 mmHg
-DBP > 120 mmHg-Hypertension (BP < 180/120 mmHg) withencephalopathy, heart failure, retinopathy
(Jo int National comm ittee on Detect ion , Evaluat ion and
Treatment of Hypertensio n, JNC7)
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
5/39
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
6/39
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
7/39
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
8/39
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
9/39
Hypertensive crisis:
Hypertensive urgency Without organ target damage Clinical manifestations: headache, vomiting Possibility progressive to a hypertensive
emergency Perioperative hypertension
Hypertensive emergency:
Severe Hypertension with end-organ injury ofthe brain, heart, kidney
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
10/39
Hypertensive emergency
(organ target damage: +)
Hypertensive encephalopathy
Congestive heart failure
Pulmonary edema
ARF/CRF
Adrenergic crisis
Head trauma Stroke
Myocardial infarction
Dissecting aortic aneurysm
Hypertensive urgency
(organ target damage:-)
Accelerated hypertension
Malignant hypertension
Peri-operative hypertension
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
11/39
Etiology
1. Renal parenchymal disease
a. Glomerulonephritis
b. Systemic vasculitis with renal
involvementc. Hemolytic uremic syndrome
d. Interstitial nephritis (chronicpyelonephritis)
e. Hereditary diseases
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
12/39
2. Renovasculara. Intrinsic renal artery disease:
•Fibromuscular dysplasia• Arteritis (Kawasaki, Takayasu, Moyamoya disease)
•Renal transplant artery stenosis
•Newborn with umbilical vessel catheters
•Renal transplant renal artery or venous thrombosis
•Renal traumab. Extrinsic compression
•Neoplasia: Wilm’s tumor, neuroblastoma,pheochromocytoma, paraganglioma, neurofibroma,lymphoma
•Perirenal hematoma, trauma
•Retroperitoneal fibrosis
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
13/39
3. Cardiovascular
a. Coarctation of aorta
b. Middle aortic syndromec. Williams syndrome
d. Turner syndrome
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
14/39
4. Endocrine abnormalitiesa. Tumor secreting vasoactive substance (cathecholamines, renin)
b. Thyroid disorders
c. Cushing syndromed. Hyperaldosteronism
e. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
f. Hypercalcemia
5. Miscellaneous causesa. Neurologic abnormalities- Elevated intracranial pressure
- Recent seizure, status epilepticus
- Familial dysautonomia
b. Cyclic vomiting syndrome
c. Polycythemia, recombinant erythropoietin therapy
d. Anesthetic drugs : ketamine, naloxone
e. Drug abuse: cocaine, amphetamine, methamphetamine,phencyclidine, methylphenidate
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
15/39
Pathophysiology
• Renin angiotensin system
• Fluid overload• Sympathetic stimulation
• Endothelial dysfunction
• Medication and other substances
Flynn JT, Tullus K. Pediatr Nephrol 2009;24:1101-12
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
16/39
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
17/39
• Heart failure symptoms : Tachypnea,Shortness of breath, edema
• Suggest renal disease: hematuria, flankpain, “cola colored” urine
• Exophtalmos : hyperthyroidism
• Abdomial mass: Wilm’s tumor, polycystickidney, neuroblastoma
• Important !! sign of child abuse with CNS
trauma
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
18/39
Retinopathy hypertension : 27%
Encepalopathy hypertension : 25%
Seizure : 25%
Left Ventrikel hypertrophy : 13%
Facial Palsy : 12%
Vision Changes : 9%
Hemiplegia : 8%
Cranial bruits : 5%
BP >99 without organ damage : 24%
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
19/39
Management
• Antihypertensive drugs
• Evaluation for target organ damage• Investigation of causes
• Supportive management
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
20/39
a. Antihypertensive drugs
• Should be initiated prior to obtaining the results of
laboratory and radiologic
• Preferably in intensive care setting with
continuous cardiac monitor• Goal of therapy: BP to normal or near normal
level as quickly as possible
• Target :
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
21/39
• BP measure:
• @ 5 minute ( First 15 minute)• @ 15 minute ( First hour)
• @ 30 minute until Diastolic BP 100
• @ 1-3 hour
• Intravenous or Oral anti hypertensive
• Lowering BP
• 25-30% in 8-12 hour
• 25-30% in 24-36 hour
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
22/39
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
23/39
b. Investigation of causes
Evaluations: - causes
- co-morbidity
- target organ damage
Evaluation should be individualized
Majority causes: renoparenchym or renovascular screening to this condition
Diagnostic tests:
Urinalysis
BUN,SC
CBC
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
24/39
c. Evaluation for target organ damage
Abnormality of brain, heart, kidney, eyes
d. Supportive management
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
25/39
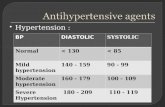
Antihypertensive for hypertensive crisis
• Drug of choice:
• Short acting
• Can be titrated• Indonesia:
• Nifedipine, Na nitroprusside, clonidine,
nicardipine
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
26/39
Nifedipine
• Calcium-channel blockers• Direct vasodilators by inhibiting vascular smooth muscle
contraction by interfering with cellular calcium influx
• Sublingually: start 0,1 mg/kg max 10 mg/dosage or 120
mg/day
• Effective within 10 minutes with peak effect in 30 - 40 min.
• Sublingual more rapid than oral for 10 to 15 minutes
• Side effects: headache, flushing, dizziness, tachycardia
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
27/39
Scheme: Treatment of crisis/encephalopathy hypertension
with nifedipine
Nifedipine sublingually 0.1 mg/kgbw
Increased 0.1 mg/kgbw/dose every 30 minutes
Max. dose: 10 mg/dose
+ Furosemide 1 mg/kgbw/dose, 2 x per day i.v.
(Orally: in good condition)
If blood pressure is not decreased,
+ Captopril 0.3 mg/kgbw/dose 2-3 x per day
(max. 2 mg/kgbw/dose)
Diastolic90 – 100 mmHg
STABILE
MAINTENANCE NIFEDIPINE
0.2 mg – 1 mg/kgbw/day, 3-4 x
Alatas H. Naskah simposium dan workshop sehari: Kegawatan pada penyakit ginjal anak.
Makasar, 27-28 Mei, 2006,17-28.
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
28/39
Nitroprusside
• Nitric oxide donor vasodilatory effect on venous and
arteriolar
• renal blood flow
• Continuous infusion• Dose: begin at 0.3 g/kg/min,
and titrated to a max. dose of 8 g/kg/min
• Requires continuous BP monitoring
• Toxic metabolites: cyanide, thiocyanate
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
29/39
Nitroprusside ● ● ● ● ● • Side effects: Cyanide/thiocyanate toxicity:
- anxiety, headache, dizziness, confusion, jaw stiffness,seizures,- metabolic acidosis and hypoxemia
Hypotension, methemoglobinemia, hypothyroidism, tinnitus,visual disturbances, tachyphylaxis
• > 72 hours or renal failure:- monitor cyanide levels
- co-administer with Na-thiosulfate(infusion of nitroprusside to thiosulfate: 10 : 1)
• Contraindicated:- intracranial pressure- caution in aorta coarctation
• Solution should be protected from light
Rust RS, Chun RWM. IPediatric Neurology, Principles & Practice, 4th ed., Philadelphia, Mosby Elsevier,
2006,p.2233-83
Vogt BA, Davis ID. Pediatric Nephrology, 5th edition, Philadelphia, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins,.2004;p.1199-1220
Li SPS, Wong SN. Practical Paediatric Nephrology, 1st ed., Hong Kong, Medcom Limited, 2005;p.89-95
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
30/39
2. Clonidine
• Central agonist
• Useful when intensive care monitoring facilities are not available
• Side effects:- drowsiness
- decreased alertness
- elevations in liver enzymes
- muscle or joint pain, weight gain, and rash.
• Clonidine difficult to follow the course of hypertensiveencephalopathy
• Cause rebound hypertension if suddenly withdrawn
Brazy PC. Primer on Kideny Diseases, 1st ed, San Diego, Academic Press, 1994;p. 355-61
Alatas H. Naskah simposium dan workshop sehari: Kegawatan pada penyakit ginjal anak, Makasar, 27-28 Mei, 2006,17-28.
Vogt BA, Davis ID. Pediatric Nephrology, 5th edition, Philadelphia, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins,.2004;p.1199-1220.
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
31/39
Scheme. Treatment of crisis/encephalopathy hypertension
with clonidine
Clonidine drip 0.002 mg/kgbw/8 hoursin 100 cc dextrose 5% (12 drops micro)
Inceased every 30 minutes until max. dose
0.006 mg/kgbw/8 hours
+ Furosemide 1 mg/kgbw/dose IV
Captopril orally 0.3 mg/kgbw/dose
(max. 2 mg/kgbw/dose), 2-3 times/day
Diastolic 90-100 mmHg
STABILE
Clonidine stop
Captopril continue
Alatas H. Naskah simposium dan workshop sehari: Kegawatan pada penyakit ginjal anak.
Makasar, 27-28 Mei, 2006,17-28.
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
32/39
Nicardipine
• Calcium channel blockers• Direct vasodilators by inhibiting vascular smooth muscle contraction by
interfering with cellular calcium influx
• Rapid, safe, effective
• Continuous infusion: 0,5 to 5,0 g/kg/min (max. = 5 mg/hour)
• Cause tachycardia, headache, flushing, dizziness
• Contraindicated: head trauma, intracranial haemorrhage
• Alternative to nitroprusside or intravenous labetalol
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
33/39
Diazoxide
• Nondiuretic thiazide
• Potent arteriole vasodilator• Dose: 1 to 3 mg/kg per dose
• IV infusion over 5 to 10 minutes and may be given every 10 to 15 minutes
• Max. dose: 10 mg/kg or 150 mg
• Causes sodium retention and requires diuretic: furosemide
• Side effects: = other systemic vasodilators- hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia, nausea, vomiting, constipation,
- hypertrichosis, skin rash, fever, leucopenia, thrombocytopenia
• Contraindicated: -intracerebral hemorrhage
-dissecting aortic aneurysm
-acute myocardial infarction-coarctation of the aorta
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
34/39
Labetalol
•
-blocker or
-adrenergic antagonist with peripheral
-adrenergic
antagonismvasodilatation of peripheral vasculature
antihypertensive effect
• blood pressure by reducing heart rate and myocardial contractility,
and reduce cardiac output
• Is not cardioselective and does not have intrinsic symphatomimetic
activity
• Dose: 0,2-1,0 mg/kg/dose IV push over 2 minutes
• If no response, may redose q5-10 minutes incrementally to max. dose
= 60 mg, or 0,25-2,0 mg/kg/hour IV continuous infusion
Vogt BA, Davis ID. Pediatric Nephrology, 5th edition, Philadelphia, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins,.2004;p.1199-
1220.
Rust RS, Chun RWM. Pediatric Neurology, Principles & Practice, 4th ed., Philadelphia, Mosby Elsevier,
2006,p.2233-83Flynn JT, Tullus K. Pediatr Nephrol 2009;24:1101-12
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
35/39
Hydralazine
• Induces relaxation of vascular smooth muscles arteriolarvasodilatation
• Short half-life
• Tachycardia, plasma renin activity, sodium retention
• Best used with diuretic and -blocker
• IV bolus or IM: 0,2-0,5 mg/kg/dose q4-6 hr
(max. 3,5 mg/kg/day)
• Side effects: headache, palpitation, sweating, nausea,
dizziness.
• Hydralazine (> 200 mg/day) lupus-like syndrome
Vogt BA, Davis ID. Pediatric Nephrology, 5th edition, Philadelphia, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins,.2004;p.1199-1220.
Brazy PC. Primer on Kideny Diseases, 1st ed, San Diego, Academic Press, 1994;p. 355-61Flynn JT, Tullus K. Pediatr Nephrol 2009;24:1101-12
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
36/39
Fenoldopam
• Dopamine-1 receptor agonist
• 0,5-2 g/kg/min
• Contraindicated: glaucoma
• Cause headaches, tachycardia
Li SPS, Wong SN. Practical Paediatric Nephrology, 1st ed., Hong Kong, Medcom Limited, 2005;p.89-95Flynn JT, Tullus K. Pediatr Nephrol 2009;24:1101-12
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
37/39
Esmolol, Enalaprilat
• Rare used in children• Esmolol:
● Cardioselective adrenoreceptive -blocker
● IV bolus: 100-500 g/kg over 1-2 min,
then 50-500 g/kg/min
• Enalaprilat:
● ACE inhibitor
● IV: 0,005-0,01 mg/kg/dose q8-24hr
up to 1,25 mg/dose
Vogt BA, Davis ID. Pediatric Nephrology, 5th edition, Philadelphia, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins,.2004;p.1199-1220.Flynn JT, Tullus K. Pediatr Nephrol 2009;24:1101-12
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
38/39
Summary
• Hypertensive crisis may lead to encephalopahty, heartfailure, and retinopathy
• Secondary hypertension is commonest causes and
investigations is necessary to identify the etiology
• Management consisted of antihypertensive agents,
evaluation for target organ damage, investigation of
causes, and supportive management
-
8/18/2019 Dr. GAP Nilawati Sp. a (K), MARS - Reducing Blood Pressure in Hypertension Crisis
39/39











![dts.sunykorea.ac.krdts.sunykorea.ac.kr/sites/default/files/EST 559_professor Mark Whitaker... · Web viewOptional: [Reducing Risk in Agriculture] Mars, Russ. 2016. The Permaculture](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/5d3ca67788c993d64f8d86d9/dts-559professor-mark-whitaker-web-viewoptional-reducing-risk-in-agriculture.jpg)







