Do Now
description
Transcript of Do Now

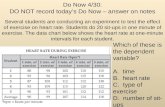
Do Now
• Write the formula or name for the following compounds:1. Cobalt III Chloride2. Nickel II Sulfide3. MnCl4
4. ZnF2
5. V(SO4)2



• Tend to lose electrons easily• Have low ionization energy
(energy needed to remove electrons)
• Have low electronegativity (attraction for electrons)
• Form positive ions when combining with other atoms
• Lustrous - reflect light, shine when they are polished
• Flexibleo malleable –
o ductile –
• Are solids at room temperature
• Good conductors of heat and electricity
(except formercury)
can be rolled or hammered into sheets
can be drawn intowires
WRITEWRITEDOWNDOWN

WRITEWRITEDOWNDOWN
• The metal atoms in a piece of metal lose electrons and become positive ions (cations).
• The cations are attracted to the electrons, but not strongly enough to hold onto them.
• As a result, the electrons are free to move among the cations. They are mobile.
• So, a metallic bond is positive ions in a “sea” of mobile electrons.

The bond between the electrons and The bond between the electrons and the cations is strong.the cations is strong.
The electrons are free to move The electrons are free to move between the cations.between the cations.
The electrons that bond the cations are The electrons that bond the cations are mobile.mobile.
The electrons ,which are held loosely, The electrons ,which are held loosely, jump up to higher energy levels, and jump up to higher energy levels, and fall back down giving off light.fall back down giving off light.

Do Now
• Describe how to name a compound with the stock system.
• Describe how to name a binary covalent compound.


• Iodine monochloride (ICl) is a solid at room temperature.oWhat holds the crystal together?
• Check the electronegativities and the shape of the iodine monochloride molecule.
• The molecule is polar.• Polar molecules are often called dipoles since
they have two poles.
Atom Electronegativity
Chlorine
Iodine
E.N.D.
3.23.22.72.7
0.50.5
I ClI Clδ+ δ−
WRITEWRITEDOWNDOWN

WRITEWRITEDOWNDOWN
• There is an attraction between the oppositely charged ends of the polar iodine monochloride molecules.
• dipole-dipole attraction: The attraction between the oppositely charged ends of polar molecules.
• It accounts for the fact that iodine monochloride is solid.
Cl ICl Iδ+δ−
I ClI Clδ+ δ−

• Consider iodine (I2):o It is a solid at room temperature.o It is a diatomic molecule
with nonpolar bonds.• What holds the iodine crystals together?• Even though iodine consists of nonpolar,
diatomic, neutral molecules, there is still a weak attraction :
• Van der Waals Forces to be caused by temporary dipoles that form as the electrons move, causing temporary dipole-dipole attractions.
WRITEWRITEDOWNDOWN

• Look at the phases of the elementsin the halogen family.
• Under normal conditions (STP),fluorine and chlorine are gases,bromine is a liquid, and iodineand astatine are solids.
• They are all diatomic, nonpolar molecules. What accounts for the differences in boiling points?
As the size of an atom or molecule increases, As the size of an atom or molecule increases, so does the Van der Waals force of attraction.so does the Van der Waals force of attraction.
WRITEWRITEDOWNDOWN

• Consider the following family of compounds:
• The boiling points decreasewith mass as expected.
• You’d expect water to have the lowest boiling point.
• But it doesn’t! Why not!?
Compound Mass (amu)
Boiling Point (°C)
HH22TeTe
HH22SeSe
HH22SS
HH22OO
130
81
34
18
−60.2
−40.1
1
?
−800 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
−60
−40
−20
0
20
40
60
80
100
Mass (amu)
100

• Water’s high boiling point is evidence for intermolecular forces much stronger than Van der Waals forces. . ., but why?
• Determine theelectronegativitydifferences in thefollowing compounds.
• Water is a verypolar molecule.
• Water molecules form a strong dipole-dipole attraction called a hydrogen bond.
CompoundElectronegativity
Metal Nonmetal Difference
HH22TeTe
HH22SeSe
HH22SS
HH22OO
2.12.1
2.12.1
2.12.1
2.12.1
2.12.1
2.62.6
2.62.6
3.43.4
0.00.0
0.50.5
0.50.5
1.31.3

• Hydrogen bonds form between molecules of nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), or fluorine (F), and hydrogen. Hydrogen bonding is FON
• The slightly positive hydrogen is strongly attracted to the slightly negative nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine.
WRITEWRITEDOWNDOWN