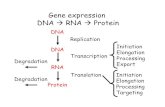
DNA (Gene) Mutations. What is a gene mutation? Often times, parts of DNA will have a base (or more)...
-
Upload
richard-ford -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
description
Transcript of DNA (Gene) Mutations. What is a gene mutation? Often times, parts of DNA will have a base (or more)...

DNA (Gene) Mutations

What is a gene mutation?
Often times, parts of DNA will have a base (or more) missing, added, or incorrect

How common are mutations?
Mutation occurs at a frequency of about 1 in every 1 billion base pairs
Everybody has about 6 mutations in each cell in their body!

If I have that many mutations, why don’t I
look weird? Mutations are not always seen.
Every part of your DNA doesn’t make a protein or trait.

The most common types of gene mutations are:
SubstitutionInsertionDeletion

DNA (Gene) Mutation
Normal DNA: CGA – TGC – ATC
Mutated DNA: CGA – TGC - TTC
What has happened to the normal DNA?

DNA (Gene) Mutation
Normal DNA: CGA – TGC – ATC
Mutated DNA: CGA – TGC - TTC
*Adenine was accidentally replaced with thymine
*What is this mutation called?

Substitution
Normal DNA: CGA – TGC – ATC
Mutated DNA: CGA – TGC - TTC
What will happen to the amino acids?

DNA (Gene) Mutation
Normal DNA: CGA – TGC – ATC
Mutated DNA: CGA – TAG – CAT - C
What has happened to the normal DNA?

DNA (Gene) Mutations
Normal DNA: CGA – TGC – ATC
Mutated DNA: CGA – TAG – CAT - C
*Adenine was inserted,causing the remaining DNA to shift to the right
*What is this mutation called?

Insertion (frameshift)
Normal DNA: CGA – TGC – ATC
Mutated DNA: CGA – TAG – CAT - C
What will happen to the amino acids?

DNA (Gene) Mutation
Normal DNA: CGA – TGC – ATC
Mutated DNA: CGA – TCA- TC
What has happened to the normal DNA?

DNA (Gene) Mutation
Normal DNA: CGA – TGC – ATC
Mutated DNA: CGA – TCA- TC
*Guanine was removed, causing the remaining DNA to shift to the left
*What is this mutation called?

Normal DNA: CGA – TGC – ATC
Mutated DNA: CGA – TCA- TC
Deletion (Frameshift)
What will happen to the amino acids?

• What causes mutations?
has a mutation?• What happens to a person who
Review
Many mutations occur naturally (during DNA replication)Many mutations are caused by mutagens (UV light, exposure to chemicals, radiation, etc.)
The mutation may be harmless (if it’s in junk DNA)Some mutations can cause disorders

• Which mutation would have the least effect on an organism?
• When would a mutation have the most effect on an organism?
Review
Substitution mutations have the least effect, because they only affect ONE amino acid.
Insertion and deletion mutations affect ALL proteins after the mutation. Also, mutations in egg and sperm can cause problems in offspring, whereas mutations in body cells only causes problems for that individual.

• Do mutations get passed on to offspring?
Review
Only if the mutation ends up in the egg or sperm. Mutations in body cells only affect the individual- not his/her children.

Review- Chromosomal Mutations
Any change in the DNA sequence is known as a mutation
Point mutations are changes in a single base pair in DNA
Frameshift mutations are the insertion or deletion of a single base causing the sequence to shift one way or the other

Review- Chromosomal Mutations

Great Websites
http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/aso/tryit/dna/index.html
http://www.dnaftb.org/dnaftb/22/animation/animation.html
http://www.biology.clc.uc.edu/courses/bio104/dna.htm
http://www.johnkyrk.com/DNAanatomy.html