Dna and rna
-
Upload
eruder -
Category
Technology
-
view
740 -
download
4
Transcript of Dna and rna

DNA and RNA
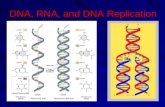
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
“the double helix” and
Ribonucleic Acid

The Double Helix
• The structure of DNA was discovered in 1953 by scientists James Watson and Francis Crick.
• Double Helix = “twisted ladder”

Nucleotide
• Basic building block of DNA or RNA
• DNA sugar is Deoxyribose, bases A,T,C,G
• RNA sugar is Ribose, bases A,U,C,G

DNA Base Pairing Rules
• Adenine – Thymine
• Cytosine – Guanine

DNA Replication
• DNA Helicase “unwinds” the helix.
• DNA Polymerase lays down new nucleotides (base pair rules).
• Resulting in two new strands identical with one old and one new backbone each.

Oops! Remember?
• If a mistake is made in replication a MUTATION results.
• Most are caught and repaired during proofreading (CDK and Cyclin “supervisors”).
• Remember: DNA replication takes place during the S phase of the cell cycle (interphase) and has to happen before Cell Division can take place.

RNA Bases Pairing Rules
• Adenine – Uracil
• Cytosine – Guanine

Transcription = making RNA
Copies info from DNA.

3 types of RNA
mRNA= Messenger RNA codon = 3 nucleotides carries “message” from DNA tRNA = Transfer RNA anticodon = 3 nucleotides that pair with codon
rRNA = Ribosomal RNA associates with proteins to form ribosomes.

Comparing DNA to RNA
• DNA• NEVER leaves nucleus• Double Strand• A-T, C-G• Deoxyribose Sugar• ONE KIND• Mistake = MUTATION!• “original blueprints”
• RNA• Made in Nucleolus• Can leave Nucleus• Single Strand• A-U, C-G• Ribose Sugar• 3 KINDS• Codons/anitcodons• “copy for work site”

Practice: ATTCGCCTTACG
• What would the complimentary strand be?
• Is this DNA or RNA?
• What would the transcribed RNA be?