Digestion: Process of breaking down food molecules so nutrients can be absorbed.
-
Upload
hilary-mcdonald -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
Transcript of Digestion: Process of breaking down food molecules so nutrients can be absorbed.

Digestion: Process of breaking down food molecules so
nutrients can be absorbed

Mechanical Digestion: *teeth chewing breaks ↓ food into
smaller pieces (prepares for chemical
digestion by ↑ing SA for enzymes to work
in chemical digestion)
*churning of stomach (sm muscles)

Chemical Digestion: Enzymes further break ↓ food particles
so nutrients can be absorbed

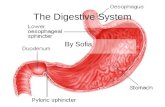
4 Layers of Digestive Tract


*Frenulum: attaches tongue to floor of mouth




Epiglottis: closes off trachea and bolus passed into
esophagus (behind trachea) when you swallow


Salivary Glands: In mouth start chemical digestion of carbs


Pharynx (throat)

Esophagus
and Cardiac Sphincter
cardiac sphincter

Stomach
*
*




Small Intestine: ABSORPTION of
nutrients
Duodenum
1st part of sm intestine is where most digestion takes place
Rest of sm intestine
absorption

Villi/Microvilli
Of Sm Intestine
↑ SA for absorption of nutrients



Liver and Gall Bladder





Lg Intestine:
Fx Absorption of H2O




jejunum

Peritoneum: Serous moist membrane lines abdominal cavity
& covers organs
(remember Epi membranes serous, cutaneous, mucous
connective tissue membranes synovial
no Epi component
Shiny surface of the organs is the visceral peritoneum; shiny lining the abdominal wall is the parietal peritoneum

Mesentary: Extension of Parietal Peritoneum
Anchors Sm Intestine to abdominal wall

Greater Omentum: Extension of parietal peritoneum
Envelopes inflamed appendix
CAT
M
E
O
W

Digestion of Carbs: major source of energy
Starts in mouth w/salivary amylase
Sm Intestine: pancreatic & intestinal juices digest starch & sugars
____________ase (enzyme for what it works on)
Amylase breaks ↓starch & sugars
Maltase breaks ↓maltose (gal + gal)
Sucrase breaks ↓ sucrose (glu + fru)
Lactase breaks ↓ lactose (glu + gal)
* Starches polysaccharides disaccharides monosaccharides

Carbs: preferred energy food
Glycolysis: glucose metabolism (catabolic)
CR: w/ O2 = lots of ATP
Glycogenolysis: glu glycogen for storage (an anabolic)
Pancreas: Alpha Cells glucagon hormone
glycogen glucose ↑’s BS
Beta Cells insulin hormone
carries glucose across CM ↓BS
Antagonists
Hypoglycemia: low BS vs Hyperglycemia: high BS
Diabetics metabolize fats vs glucose byproduct ketones
Ketoacidosis affects blood pH diabetic coma

Proteins: Growth & development, repair, enzymes (catalysts)
Can be broken ↓ for energy
Starts in stomach
Enzymes Renin & Pepsin in gastric juice
Sm Intestine: Trypsin in pancreatic juice
Pepsidase in intestinal juice

Fats: store energy (2x more than carbs) impt in cm’s
Saturated, Unsaturated, Polyunsaturated
No C=C 1 C=C >1 C=C bond
Animals Plants
Solid @ RT Liquid @ RT
Gastric lipase in gastric juice digests some fat in stomach
Most fat undigested until of sm Intestine
Bile salts (aid enzyme Fx) made in liver stored in gall bladder, released into duodenum to emulsify fats (mechanical)
Pancreatic enzymes splits fats into glycerol & 3 fa’s

Food Undergoes: Digestion, Absorption (↑ SA) Metabolism
*Metabolism = anabolic + catabolic Rx’s (dehy synth & hydro)
H2O = most of body wt (blood plasma >90% H2O
Minerals: Inorganic & req’d by body
(to make Hgb, DNA, RNA, ATP)
Ca: teeth, bones, nerve, muscle fx
Vitamins: Help enzymes fx
K & some B complex made in liver
D made in skin (w/ sunlight)
A, D, E, K, fat soluble & stored in fatty tissue
C & B H2O soluble, need daily