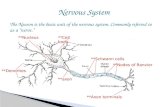
Dendrites Axon Nucleus Cell Myelin Sheath Axon Terminals.
-
Upload
brianna-owens -
Category
Documents
-
view
262 -
download
2
description
Transcript of Dendrites Axon Nucleus Cell Myelin Sheath Axon Terminals.

You Have Some Nerve

Dendrites
Cell
Axon
Axon Terminals
Myelin Sheath
Nucleus

Neuron – long, thin cells of nerve tissue that transfer messages to and from the brain
Axon – aka “nerve fiber,” transfer the electrical impulses away from cell body
Dendrite – short, branch-like extension of the nerve cell that receive impulses from other cells
Myelin sheath – Casing of electrically insulated protection around the axon
Axon Terminal – small projection from the nerve cell that sends out information to other cells

Synapse
Synapse – a small gap between one cell’s axon terminal and another cell’s dendrite through which the electrical impulses that pass through the brain are passed

SynapsesConsist of 3 Parts: 1. Presynaptic ending – made up of neurotransmitters
at the Axon Terminal that transmit information2. Postsynaptic ending – made up of receptor sites
that receive the information in the Dendrites3. Synaptic Gap – small gap between the Axon
Terminal and the Dendrite through which the electrical impulses are transmitted

Presynaptic Neuron
Lots of chemical activity
Post Synaptic Neuron

NeurotransmittersKind of boring, but it will help this make a little bit more sense
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p5zFgT4aofA

Th Action Potential

Action PotentialAction Potential – the explosion of electrical impulse that fires down the axon away from the cell body and to the neurotransmitters

Th Action Potential

Th Action Potential

Th Action Potential

Th Action Potential

Axon Terminals
Dendrites

Axon Terminals
DendritesNeurotransmitter
Receptor

TerminalButtons
Dendrites
Neurotransmitter
Receptor

TerminalButtons
DendritesExcitatory: Continue the action potential

AxonTerminals
Dendrites
Inhibitory: End the action potential

A Good Explanation of Neurotransmittershttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ukFjH9odsXw

Both kinds received at once
Excitatory has to pass a certain threshold to create an Action potential
Excitatory or Inhibitory?


Neurotransmitters
AcetylcholinePresent in the synapses in the nerves at our muscles.
More Acetycholine in the synapse: Binds with receptors at the dendrite to effect an action potential, and thus, create muscle movement
Less acetylcholine in the synapse: no action potentials...no muscle movement

Neurotransmitters
BOTOX

BOTOX
Inhibits
Acetylcholine

Acetylcholine is the
neurotransmitter, which, when
abundant in our muscle synapses,
control muscle movement
BOTOX
keeps acetylcholine out of the synapse
So the muscles that cause
wrinkles are temporarily paralyzed