D.Deeprasert1 Sentence Study Week 5. D.Deeprasert2 Outline Passive voice Clause Adjective Clause...
-
Upload
frederica-hawkins -
Category
Documents
-
view
225 -
download
3
Transcript of D.Deeprasert1 Sentence Study Week 5. D.Deeprasert2 Outline Passive voice Clause Adjective Clause...

D.Deeprasert 1
Sentence Study
Week 5

D.Deeprasert 2
Outline
Passive voice Clause
Adjective Clause Adverb Clause Noun Clause
Changing clauses to modifying phrases

D.Deeprasert 3
Objective
The students are expected to be able to read and comprehend complicated
sentences by answering questions correctly.

D.Deeprasert 4
1. Reviews of Types of dependent Clauses Adjective Clause Adverbial Clause Noun Clause
2. Passive Voice
3. Sentence Transformation Changing Clauses modifying phrases
3. Understanding Complicated sentences

D.Deeprasert 5
Types of Dependent Clauses
1. Adjective Clause
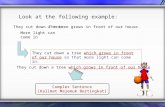
An adjective clause is used to describe a noun:
Ex. The car, which was red, belonged to Mr. Peterson.

D.Deeprasert 6
A relative pronoun is usually used to introduce an adjective clause:
Hans, who is an architect, lives in Berlin.
Mike, whom Hans knows well, is an interior decorator.
Judy has a dog which follows her everywhere.
Mike is decorating a house that Hans designed.

D.Deeprasert 7
More Practice on adjective clauses at:
http://web2.uvcs.uvic.ca/elc/studyzone/410/grammar/adj1.htm

D.Deeprasert 8
2. Adverb clause
An adverb clause is a dependent clause which takes the place of an adverb in another clause or phrase.
An adverb clause answers questions such as "when?", "where?", "why?", "with what goal/result?", and "under what conditions?".

D.Deeprasert 9
Type Question answered
Example
Place Where? Wherever there are computers, there is Microsoft software.
Time When?After the fruit is harvested, it is
sold at the market.
Cause Why? (What
caused this?) I didn't call her because I'm shy.
PurposeWhy? (What was
the reason for doing this?)
She took a computer course so that she could get a better job.
ConcessionWhy is this
unexpected?
Although Jay has a Master's degree, he works as a store
clerk.
ConditionUnder what conditions?
If you save your money, you will be able to go to college.

D.Deeprasert 10
More Practice on adverb clauses at:
http://web2.uvcs.uvic.ca/elc/studyzone/410/grammar/advcls1.htm

D.Deeprasert 11
3. Noun Clause
A noun clause is a clause which does the work of a noun in a sentence. It is a group of words containing a subject and a finite verb of its own.
Usually noun clauses begin with that, what, where, when, who, whom, which, whose, how, why, whether, etc.

D.Deeprasert 12
Uses of Noun Clauses
A. As the subject of a verb
Why she kept on crying puzzled every one.
B. As the direct object
Nobody knows how he got involved in
gangland activities
verb noun clause
noun clause main verb

D.Deeprasert 13
c.As the complement of the verb "to be"
What we are worried about is that he may have another heart attack.
The question is why they could escape through the front door when there were so many guards there.

D.Deeprasert 14
More Examples He said that he would not come. We were all curious to know what he had done. Nobody knows when the registration will begin. We all wanted to find out who the winner was. Whom they were in contact with on the day of the
robbery is of great interest to the police. Jane is not sure which university she should apply for. The judges had a hard time deciding whose painting
was the best. How the baby fell from the window is a mystery. They asked the boy why he had hit his classmate. Whether you like it or not is not the issue.

D.Deeprasert 15
Passive Voice
There are two special forms for verbs called voice: Active voice Passive voice
Passive voice makes sense when the agent performing the action is obvious, unimportant, or unknown.
The passive voice is effective in such circumstances because it highlights the action and what is acted upon rather than the agent performing the action.

D.Deeprasert 16
To create a passive sentence, you must know:
Who is the person (the "agent") of the action? (the "doer")
Who is the object (the "receiver) of the action?

D.Deeprasert 17
ACTIVE
He flipped a coin to decide who would go first.
(He is unimportant.)
PASSIVE
A coin was flipped to decide who would
go first. (Focus on the coin flip.)
RECEIVER(coin)
AGENT(person doing
the flip)

D.Deeprasert 18
ACTIVE
John was shaking his little brother, Jimmy.
(Focus on aggressor .)
PASSIVE
Jimmy was being shaken by John. (Focus on victim.)
RECEIVER(victim)
AGENT(aggressor)

D.Deeprasert 19
The Passive is formed:
It is often used in business and in other areas where the object of the action is more important than those who perform the action.
Only verbs that take an object can be used in the passive.
Passive Subject + To Be + Past Participle

D.Deeprasert 20
The object of the active verb becomes the subject of the passive verb:
Activesubject Verb Object
Cats eat fish.
Passivesubject Verb Object
Fishare
eatenby cats

D.Deeprasert 21
For Example: We have produced over 20 different models in the past two years.
Changes to: Over 20 different models have been produced in the past two years.

D.Deeprasert 22
For Example:
Tim Wilson wrote "The Flight to Brunnswick" in 1987.
Changes to:
"The Flight to Brunnswick" was written in 1987 by Tim Wilson.
If the agent (the performer of the action) is important, use "by“.

D.Deeprasert 23
Active Passive Time Reference
They make Fords in Cologne.
Susan is cooking dinner.
James Joyce wrote "Dubliners".
They were painting the house when I arrived.
They have produced over 20 models in the past two years.
They are going to build a new factory in Portland.
I will finish it tomorrow.
Fords are made in Cologne. Present Simple
Dinner is being cooked by Susan
"Dubliners" was written by James Joyces.
The house was being painted when I arrived.
Over 20 models have been produced in the past two years.
A new factory is going to be built in Portland.
It will be finished tomorrow.
Present Continuous
Past Simple
Past Continuous
Present Perfect
Future Intention with Going to
Future Simple

D.Deeprasert 24
More practice on Passive voice at:
http://esl.about.com/library/quiz/blgrquiz_passive1.htm
http://esl.about.com/library/quiz/blgrquiz_passive2.htm
http://www.englishclub.com/grammar/verbs-voice_passive.htm

D.Deeprasert 25
Changing an Adjective Clause to an Adjective Phrase
1.The subject pronoun is omitted and the be form of the verb is omitted.
Clause : The actions which are taken by the government are helpful.
Phrase : The actions taken by the government are helpful.
Clause : John is the man who is responsible for the project.
Phrase : John is the man responsible for the project.

D.Deeprasert 26
2. If there is no “be” form of a verb in the adjective clause, it is sometimes possible to omit the subject pronoun and change the verb to its_ ing form.
Clause : A copyright, which assures an author the sole right to publish, is a right that is
granted by government.Phrase : A copyright, assuring an author the sole right
to publish, is a right granted by government. Clause : Anyone who has a salary of 20,000 bath
or more can apply. Phrase : Anyone having a salary of 20,000 bath
or more can apply.

D.Deeprasert 27
Clause: Large cities provide additional
services which include parks.
Phrase: Large cities provide additional
services including parks.

D.Deeprasert 28
Reducing Adverb Clauses to Modifying Phrases
Sentences with the same subject can reduced after adverb- before, after, while, when, since
1. Omit the subject of the dependent clause and the be form of the verb.
Adverb clause : While she was typing on the computer, she was listening to the radio.
Modifying Phrase: While typing on the computer, she was listening to the radio.

D.Deeprasert 29
2. If there is no “be” form of a verb, omit the subject and change the verb -ing
Adverb clause: Before she left the office, she shut down the computer.
Modifying Phrase: Before leaving the office, she shut down the computer.

D.Deeprasert 30
While I was reading the newspaper, I saw a story about an old friend.
While reading the newspaper, I saw a story about an old friend.
Before I left home, I checked to see that all of the doors were locked.
Before leaving home, I checked to see that all of the doors were locked

D.Deeprasert 31
BUT NOT:
An adverb clause can be changed to a modifying phrase only when the subject of the adverb clause and the subject of the main clause are the same.
No change is possible if the subjects of the adverb clause and the main clause are different.
EX.
Before I took a driving course, my father warned me to be cautious.
Modifying Phrase
* no change (because the subject of the second clause is different.)