CRM PPT
-
Upload
arushirajvanshi -
Category
Documents
-
view
212 -
download
0
description
Transcript of CRM PPT

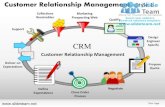
CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT
The Importance of Trust in Procurement Practices and Its Impact on Business
Performance: An Empirical Investigation From the Perspective of the Buyer–
Supplier Dyad
Amartojit Basu (37120)Arushi Rajvanshi (37142)Kashmira Brahmane (37191)

Research ProblemThis research study seeks to investigate how procurement practices influence business survival in a developing economy through analysis of buyer-supplier relationships in the restaurant industry

Research ObjectivesTo find the relationship between firms‘ perceived performance and importance of procurement practices effect on business survival
To find similarities and differences between firms‘ overall perceptions of procurement practices and business survival
To find out the gaps exist within and between firms‘ procurement practices and their effect on business survival in a turbulent environment

Literature ReviewBased on the literature reviewed for the definitions of trust in this study,it can be concluded that the term trust can mean relatively the same thing to parties involved in a relationship or can mean something completelydifferent.
(Currall and Judge, 1995; Simchi-Levi et al., 2002; Tomkins, 2001).
(Dennis and Kambil, 2003; Hines, 2004).
It appears that it is only through trust that stakeholders involved in a procurement arrangements can focus on other issues knowing that those with whom they are involved with will protect their interests and not engage in activities that are harmful to your business Therefore, trust is a belief by one part that the other party will fulfill its obligation in a relationship This suggests that trust is being perceived across procurement practices theoretical paradigms as a critical construct upon which buyer and seller interactions are premised.

When relational exchange partners trust each other, they are more willing to share relevant ideas, clarify goals and problems and communicate efficiently. It also increases satisfaction with the relationship (Anderson and Weitz, 1989, Mohr and Spekman 1994), enhances continuity expectations (Ganesan, 1994; Joshi and Stump, 1999; Smith and Barclay, 1997), and foments cooperation, coordination, collaboration and communication.
Based on the above discussions, the researcher believes that further study of trust as a determinant of buyer – supplier procurement practices covers a reasonable number of dimensions that are common in nearly all the other theories covered in this paper. Trust is therefore perceived throughout this study as the necessary precursor for:
Feeling to be able to rely upon another organization Cooperating with and experiencing to be part of another group Taking thoughtful risks, and Experiencing believable interactions

Dimensions of Trust

Research Methodology
This research was exploratory in nature. Multiple-case study analysis Primary Research –
In depth, structured interviews with 5 eating joints in Baner. 6 Suppliers to these joints. Limitations – Given the exploratory nature of the research,
we have done descriptive anaylsis of the collected data.

Questionnaire


Findings and Observation A total of 22 in-depth interviews were conducted with 11 cases (i.e., 5
buying organizations and 6 supplying organizations) within the restaurant Industry in Pune city.
All interviewees had more than 3 years of relevant experience in the concerned industry and
were directly involved in activities related to procurement practices in their respective
organizations.
The majority of these cases (8 out of 11) had been operating in the industry for at least 5 years
Overall, the findings supported 24 of the 31 dimensions of the trust attributes in buyer–supplier
procurement practices as having an impact on business performance.
All 11 cases supported the dimension of track record/history in the security attribute as an
important influence on business performance.
whereas the least supported dimension (2 out of 11 cases) was identified as the willingness to
disclose trade secrets in the openness attribute.

CLOSENESS
Four dimensions of CLOSENESS and the responses : Joint decision making – 7 out of 11 in support building of joint outcomes – 7 out of 11 in support Social bonding – 6 out of 11 in support sharing of information – 5 out of 11 in support
Interviewees comments :
“It is procurement function’s responsibility to engage with suppliers who show willingness to undertake joint corrective action through
working jointly to align and achieve both parties’ objectives.”
“Information is power, and a strong basis for our company to make informed
decisions as a result of communication is intergral in our company policy.”

OPENNESS Four dimensions of the openness and responses :
internal stakeholder engagement – 7 of 11 cases external stakeholder engagement – 7 of 11 cases working together – 7 of 11 cases willingness to disclose trade secrets - 5 of 11 cases
Interviewee Comment
“We value openness and transparence when forming and developing interorganizational relationships with third parties. Performance is measured by its ability to work collaboratively with key stakeholders to achieve cost efficiencies and cost savings.”
“The procurement function works collaboratively with both internal and external stakeholders in a way influencing [the] decision-making process throughout the procurement process.”
The lack of support for willingness to disclose trade secrets, we speculate is due to the fact that it doesn’t make a difference because it is the functionaing of the two organizationsa re sperate and that they respect the business secrets of theor partners. This helps develop a sense of respect and integrity for the other party.

COMMITMENT Eight dimensions of the commitment attribute and responses senior management support – 7 of 11 cases long-term relationship - 7 of 11 cases coordinated arrangements - 7 of 11 cases structured organization – 9 of 11 cases willingness to make idiosyncratic investment – 4 of 11 cases leadership and accountability – 6 of 11 cases Visibility – 7 of 11 cases Willingness to take risk - 7 of 11 cases
Interviewees comments
“The firm’s procurement practices are perceived as providing leadership and advice to business through forging relationships with trusted suppliers, cooperat[ing] with other
functions, and striv[ing] for joint and collaborative relations with supply partners to assist both firms maximize shareholders value”
“The company prefers long-term contracts with strategic suppliers, so that they can be integrated in the development of strategically important products and for the improvement of
the existing ones.”

SECURITY
Five dimensions and customer responses Track record – 11 of 11 cases credibility – 10 of 11 cases character endorsement – 9 of 11 casesacceptance of duty to protect the – 10 of 11 cases rights of partners acknowledgment of duty to protect the interests of
partners – 10 of 11 cases
Interviewee comments
“To keep our business going, we have to be sensitive to certain levels of exposure.”
“We do not indulge in any form of business relationship deals; we
even decline being involved in high-risk, low-returns kind of business.”

HONESTY Three dimensions of the honesty and customer responses
ethical conduct -9 of 11 casesTransparency - 7 of 11 casesopen intentions/motives - 6 of 11 cases
Interviewee comments :
“We distance ourselves from any form of practices that seek to compromise our integrity, as this affects our reputation in the industry.”

COMPETENCE
The three dimensions of the competence and customer responses were capability – 10 of 11 cases character endorsement - 10 of 11 cases traceable reference - 9 of 11 cases
interviewee comments :
“This is an area we have managed to keep our organization ahead of competition and we also accredit our partners on the
same basis.”
“Better skills and high competence levels across the supply chain is what enable us to offer and deliver value for money,
goods, and services.”

DEPENDABLITY
Four dimensions and customer responses
Reliable – 9 of 11 cases deliver on promises - 9 of 11 cases walk the talk – 8 of 11 cases flexibility - 7 of 11 cases
Interviewee comments
“Being reliable is our cause for existence; otherwise, we risk losing our reputation, and without it we have no business.”
“If we anticipate or experience any challenges regarding meeting our promises to our customers and any other stakeholders, our policy is that
we should communicate with all those affected well in advance; we ensure that our customers are kept informed.”

Average Scores

CONCLUSIONS, IMPLICATIONS, AND LIMITATIONS• In conclusion, this study has explored the impact of trust between buyers and suppliers in procurement practices on business performance.
• A total of 11 in-depth interviews were conducted with representatives of 11 organizationsIn Indian restaurant industry, and the findings support 14 of the 15 dimensions of the trust attributes presented in the preliminary framework as having an effect on an organization’s business performance.
• Although the findings revealed endorsement for the majority of the dimensions of the trust attributes as influential on business performance, two dimensions (i.e., willingness to disclose trade secrets in the openness attribute and willingness to make idiosyncratic investment in the commitment attribute) were highlighted as not having a similar effect.
• It should also be noted that there were some variations in attitudes based on buying versus supplying organizations’ viewpoints relating to the impact of 11 dimensions of trust attributes on business performance.
• Furthermore, organizations also acknowledged that the extent of the effect of their procurement practices on business performance was dependent on the level of interconnection between performance and the importance of trust attributes in the respective organizations.
• The findings of this research add new knowledge and insights to the existing literature on business-to-business relationships, procurement, supply chain management, and business performance with the identification of a list of 29 dimensions of trust attributes (existing in buyer–supplier procurement practices) that could impact on business performance.

The results provide organizations in Pune’s restaurant industry with a comprehensive list of dimensions of trust attributes they could consider in their procurement practices to enhance their business performance.
Constraints This study investigated the initial development of a list of dimensions of trust attributes
that exist in buyer–supplier procurement practices that could have an impact on business performance.
The study was conducted within the context of the Indian restaurant industry , and this therefore constrains the applicability of the findings to other industries and country markets.
This study is exploratory in nature, and therefore a more representative sampling population should be sought and tested to generalize the findings.
The list of dimensions of the trust attributes developed in this study should be replicated and tested in other industry and country settings.
This could further contribute to theory and practice when comparisons to the findings could be made to determine whether any significance exists between these industries and countries on the impact of trust in buyer–supplier procurement practices on business performance.





![[PPT]CRM Customer Resource Managementlacity/evecrm02.ppt · Web viewCRM Customer Relationship Management Rich DuBose, ... Different companies in different market sectors have varying](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/5abea1907f8b9ab02d8d2f7a/pptcrm-customer-resource-lacityevecrm02pptweb-viewcrm-customer-relationship.jpg)