Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 4 From Cells to Organ Systems Tissues Anatomical...
-
Upload
raymond-parsons -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
Transcript of Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 4 From Cells to Organ Systems Tissues Anatomical...

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Chapter 4From Cells to Organ Systems
Tissues
Anatomical terms
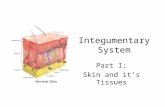
Integumentary system- Skin

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Tissues
Groups of cells with a common function
Four primary tissues Epithelia
Connective tissues
Muscle
Nervous

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Epithelial Tissues
Line body cavities and cover surfaces

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Epithelial Tissues: Classification
Shape Squamous: flattened cells; line vessels, part
of lungs, body surface
Cuboidal: cube shaped; form lining of tubules, glandular tissue
Columnar: column shaped; line respiratory, digestive, reproductive tracts

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Epithelial Tissues: Classification
Number of layers Simple/single–layered: adapted for diffusion
across cell barriers; line glands, and respiratory, digestive, reproductive systems
Stratified/multiple–layered: provide protection, as in the skin surface

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Connective Tissue Supports and Connects Body Parts: Basement Membrane
Fibrous connective tissue Loose: surrounds many organs, lines
cavities around blood vessels
Dense: forms tendons, ligaments, deeper layers of skin

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Connective Tissue Supports and Connects Body Parts (cont.)
Special connective tissue Cartilage: produced by chondroblasts; found
in lacunae; no blood vessels; high collagen content
Bone: inorganic matrix with calcium salts for hardness
Blood: fluid matrix of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets
Adipose tissue: fat cells; function in insulation, protection, and energy storage

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Fibrous Connective Tissue (cont.)
Figure 4.3

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Muscle Tissue: Contracts for Movement
Skeletal muscle Moves body parts
Voluntary, multinucleated
Cardiac muscle Functions in the heart
Involuntary, single nucleus
Smooth muscle Surrounds hollow structures
Involuntary, single nucleus

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Nervous Tissue: Transmits Impulses
Neuron: specialized nervous system cell Structural components: cell body, dendrites,
axon
Glial cells support neurons

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Organs and Organ Systems Perform Complex Functions
Organ systems Groups of organs that perform a common
function
Examples
Digestive system: mouth, throat, stomach, intestines, and liver
Lymphatic system: lymph nodes, tonsils, and spleen

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Body Cavities
Figure 4.8

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Anatomical Position or Direction
Figure 4.9
Superior(closer to the head or upper part of a structure)
Proximal(nearer to the trunk)
Posterior(at or near the back)
Distal(farther away from the trunk)
Frontalplane
Transverseplane
Midsagittalplane
Inferior(farther from the head or toward the lower part of a structure)
Anterior(at or near the front)

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Skin: Integumentary System
Figure 4.10

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Skin: Integumentary System
Functions: prevents dehydration, protects from injury, serves as defense against microorganisms, regulates body temperature, makes vitamin D, provides sensation
Structure Epidermis: outer layer, stratified squamous
epithelial cells, no blood vessels, specialized keratinocytes and melanocytes
Dermis: deeper layer, support tissues, fibers

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Accessory Structures of Dermis
Hair: shaft, follicle
Smooth muscle: attached to hair follicle, raises hair to upright position
Oil glands/sebaceous glands: secretion moistens and softens skin

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Accessory Structures of Dermis (cont.)
Sweat glands: secrete sweat, help in temperature regulation
Blood vessels: supply nutrients, remove waste, assist in temperature regulation
Sensory nerve endings: detect heat, cold, touch, deep pressure, vibration

Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Homeostasis
Maintenance of relative constancy of the conditions of the internal environment
Mechanisms Negative feedback: deviations from normal
detected and counteracted
Components: controlled variable, sensor, control center, effector
Positive feedback: amplifies original change:
Rarely found in organisms