Copyright ©2003 Brooks/Cole A division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Definitions variableA variable is...
-
date post
20-Dec-2015 -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
1
Transcript of Copyright ©2003 Brooks/Cole A division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Definitions variableA variable is...

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
DefinitionsDefinitions• A variablevariable is a characteristic that
changes or varies over time and/or for different individuals or objects under consideration.
• Examples:Examples: Hair color, white blood cell count, time to failure of a computer component.

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
DefinitionsDefinitions• An experimental unitexperimental unit is the
individual or object on which a variable is measured.
• A set of measurements, called data,data, can be either a samplesample or a population.population.

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
DefinitionsDefinitions• PopuationPopuation is collection of all items we
are interested in.• SampleSample is subset of population that we
observe.

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
Types of VariablesTypes of Variables
Qualitative Quantitative
Discrete Continuous

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
Types of VariablesTypes of Variables•Qualitative variablesQualitative variables measure a quality or characteristic on each experimental unit.
•Examples:Examples:•Hair color (black, brown, blonde…)•Make of car (Dodge, Honda, Ford…)•Gender (male, female)•State of birth (California, Arizona,….)

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
Types of VariablesTypes of Variables•Quantitative variablesQuantitative variables measure a numerical quantity on each experimental unit.
Discrete Discrete if it can assume only a finite or countable number of values.
Continuous Continuous if it can assume the infinitely many values corresponding to the points on a line interval.

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
ExamplesExamples
• For each orange tree in a grove, the number of oranges is measured. – Quantitative discrete
• For a particular day, the number of cars entering a college campus is measured.– Quantitative discrete
• Time until a light bulb burns out– Quantitative continuous

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
2.1 Describing Qualitative Data2.1 Describing Qualitative Data• Use a data distributiondata distribution to describe:
– What valuesWhat values of the variable have been measured
– How oftenHow often each value has occurred• “How often” can be measured 3 ways:
– Frequency– Relative frequency = Frequency/n– Percent = 100 x Relative frequency

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
ExampleExample• A bag of M&M®s contains 25 candies:• Raw Data:Raw Data:
• Statistical Table:Statistical Table:Color Tally Frequency Relative
FrequencyPercent
Red 5 5/25 = .20 20%
Blue 3 3/25 = .12 12%
Green 2 2/25 = .08 8%
Orange 3 3/25 = .12 12%
Brown 8 8/25 = .32 32%
Yellow 4 4/25 = .16 16%
m
m
m
mm
mm
m
m m
m
m
mm m
m
m m
mmmm
mmm
m
m
m
m
m
m
mmmm
mm
m
m m
m mm m m mm
m m m

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
GraphsGraphs
Bar Chart
Pie Chart

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
2.2 Describing Quantitative Data2.2 Describing Quantitative Data
• Dot plot• Stem and leaf plot• Histogram.

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
DotplotsDotplots• The simplest graph for quantitative data• Plots the measurements as points on a
horizontal axis, stacking the points that duplicate existing points.
• Example:Example: The set 4, 5, 5, 7, 6
4 5 6 7

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
Stem and Leaf plotStem and Leaf plot
The ages of the CEOs of 30 top ranked small companies in Americain 1993.
33 38 40 43 43 44 45 45 46 46 47 47 47 48 48 50 50 51 52 53 55 55 56 57 57 58 60 61 63 69.
3|38
4|0334556677788
5|00123556778
6|01369

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
Relative Frequency HistogramsRelative Frequency Histograms
• A relative frequency histogramrelative frequency histogram for a quantitative data set is a bar graph in which the height of the bar shows “how often” (measured as a proportion or relative frequency) measurements fall in a particular class or subinterval.
Create intervals
Stack and draw bars

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
Relative Frequency HistogramsRelative Frequency Histograms• Divide the range of the data into 5-125-12
subintervalssubintervals of equal length. • Calculate the approximate widthapproximate width of the
subinterval as Range/number of subintervals.• Round the approximate width up to a
convenient value.• Use the method of left inclusionleft inclusion, including the
left endpoint, but not the right in your tally.• Create a statistical tablestatistical table including the
subintervals, their frequencies and relative frequencies.

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
Relative Frequency HistogramsRelative Frequency Histograms• Draw the relative frequency histogramrelative frequency histogram,
plotting the subintervals on the horizontal axis and the relative frequencies on the vertical axis.
• The height of the bar represents– The proportionproportion of measurements falling in
that class or subinterval.– The probabilityprobability that a single measurement,
drawn at random from the set, will belong to that class or subinterval.

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
ExampleExampleThe ages of 50 tenured faculty at a state university.• 34 48 70 63 52 52 35 50 37 43 53 43 52 44
• 42 31 36 48 43 26 58 62 49 34 48 53 39 45
• 34 59 34 66 40 59 36 41 35 36 62 34 38 28
• 43 50 30 43 32 44 58 53
• We choose to use 6 6 intervals.
• Minimum class width == (70 – 26)/6 = 7.33(70 – 26)/6 = 7.33
• Convenient class width = 8= 8
• Use 66 classes of length 88, starting at 25.25.

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
Age Tally Frequency Relative Frequency
Percent
25 to < 33 1111 5 5/50 = .10 10%
33 to < 41 1111 1111 1111 14 14/50 = .28 28%
41 to < 49 1111 1111 111 13 13/50 = .26 26%
49 to < 57 1111 1111 9 9/50 = .18 18%
57 to < 65 1111 11 7 7/50 = .14 14%
65 to < 73 11 2 2/50 = .04 4%

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
2.4 Numerical Measures of Center
Skewed left: Mean < Median
Skewed right: Mean > Median
Symmetric: Mean = Median

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
20
2.6: Interpreting the Standard Deviation
• Chebyshev’s Rule
• The Empirical Rule
Both tell us something about where Both tell us something about where
the data will be relative to the meanthe data will be relative to the mean..

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
Chebyshev’s Theorem
Given a number k greater than or equal to 1 and a set of n measurements, at least 1-(1/k2) of the measurement will lie within k standard deviations of the mean.
Given a number k greater than or equal to 1 and a set of n measurements, at least 1-(1/k2) of the measurement will lie within k standard deviations of the mean.
Can be used for either samples ( and s) or for a population ( and ). Valid for any dataset.Important results: Important results:
If k = 2, at least 1 – 1/22 = 3/4= 75% of the measurements are within 2 standard deviations of the mean.If k = 3, at least 1 – 1/32 = 8/9=89% of the measurements are within 3 standard deviations of the mean.
x

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
Using Measures of Center and Spread: The Empirical Rule
Given a distribution of measurements that is approximately mound-shaped:
The interval contains approximately 68% of the measurements.
The interval 2 contains approximately 95% of the measurements.
The interval 3 contains approximately 99.7% of the measurements.
Given a distribution of measurements that is approximately mound-shaped:
The interval contains approximately 68% of the measurements.
The interval 2 contains approximately 95% of the measurements.
The interval 3 contains approximately 99.7% of the measurements.

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
Empirical Rule Example• Hummingbirds beat their wings
in flight an average of 55 times per second.
• Assume the standard deviation is 10, and that the distribution is symmetrical and mounded.– Approximately what
percentage of hummingbirds beat their wings between 45 and 65 times per second?
– Between 55 and 65?– Less than 45?

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
24
Since 45 and 65 are exactly one standard deviation below and above the mean, the empirical rule says that about 68% of the hummingbirds will be in this range.
• Hummingbirds beat their wings in flight an average of 55 times per second.
• Assume the standard deviation is 10, and that the distribution is symmetrical and mounded.– Approximately what
percentage of hummingbirds beat their wings between 45 and 65 times per second?
– Between 55 and 65?– Less than 45?
Empirical Rule Example

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
25
This range of numbers is from the mean to one standard deviation above it, or one-half of the range in the previous question. So, about one-half of 68%, or 34%, of the hummingbirds will be in this range.
• Hummingbirds beat their wings in flight an average of 55 times per second.
• Assume the standard deviation is 10, and that the distribution is symmetrical and mounded.– Approximately what
percentage of hummingbirds beat their wings between 45 and 65 times per second?
– Between 55 and 65?– Less than 45?
Empirical Rule Example

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
26
Half of the entire data set lies above the mean, and ~34% lie between 45 and 55 (between one standard deviation below the mean and the mean), so ~84% (~34% + 50%) are above 45, which means ~16% are below 45.
• Hummingbirds beat their wings in flight an average of 55 times per second.
• Assume the standard deviation is 10, and that the distribution is symmetrical and mounded.– Approximately what
percentage of hummingbirds beat their wings between 45 and 65 times per second?
– Between 55 and 65?– Less than 45?
Empirical Rule Example

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
27
• Since ~95% of all the measurements will be within 2 standard deviations of the mean, only ~5% will be more than 2 standard deviations from the mean.
• About half of this 5% will be far below the mean, leaving only about 2.5% of the measurements at least 2 standard deviations above the mean.
Empirical Rule

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
28
2.7: Numerical Measures of Relative Standing
• Percentiles: for any (large) set of n measurements (arranged in ascending or descending order), the pth percentile is a number such that p% of the measurements fall below that number and (100 – p)% fall above it.
• K-tk Quartile: k quarters lie below it.

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
29
Percentiles• Finding percentiles is similar to finding the
median – the median is the 50th percentile.
– If you are in the 50th percentile for the GRE, half of the test-takers scored better and half scored worse than you.
– If you are in the 75th percentile, you scored better than three-quarters of the test-takers.

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
30
Z-scores
• The z-score tells us how many standard deviations above or below the mean a particular measurement is.
• Sample z-score
• Population z-score
x xz
s
x
z

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
31
Z-Scores• Z scores are related to the empirical rule:
For a perfectly symmetrical and mound-shaped distribution, – ~68 % will have z-scores between -1 and 1– ~95 % will have z-scores between -2 and 2– ~99.7% will have z-scores between -3 and 3

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
32
2.8: Methods for Determining Outliers
• An outlier is a measurement that is unusually large or small relative to the other values.
• Three possible causes:
– Observation, recording or data entry error
– Item is from a different population
– A rare, chance event

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
33
Box plot
• The box plot is a graph representing information about certain percentiles for a data set and can be used to identify outliers

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
34
BoxPlot
30 35 40 45 50 55
Wins by Team at the 2007 MLB All-Star Break
Minimum Value
Lower Quartile(QL)
Median Upper Quartile(QU)
Maximum Value

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
35
BoxPlot
30 35 40 45 50 55
Wins by Team at the 2007 MLB All-Star Break
Interquartile Range (IQR) = QU - QL

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
36
BoxPlot
20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110
Wins by Team at the 2007 MLB All-Star Break(One team had its total wins for 2006 recorded)
Inner Fence at QU + 1.5(IQR)Outer Fence at QU + 3(IQR)

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
37
• Outliers and z-scores
– The chance that a z-score is between -3 and +3 is over 99%.
– Any measurement with |z| > 3 is considered an outlier.
Outliers and Z-scores

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
38
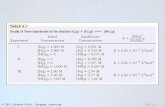
• Outliers and z-scoresHere are the descriptive
statistics for the games won at the All-Star break, except one team had its total wins for 2006 recorded.
That team, with 104 wins recorded, had a z-score of (104-45.68)/12.11 = 4.82.
That’s a very unlikely result, which isn’t surprising given what we know about the observation.
#Wins n = 30
Mean 45.68
Sample Variance
146.69
Sample Standard Deviation
12.11
Minimum 25
Maximum 104

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
39
2.9: Graphing Bivariate Relationships
• Scattergram (or scatterplot) shows the relationship between two quantitative variables
Positive Relationship
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
0 2000 4000 6000 8000 10000 12000 14000
Gross domestic product
Im
ports
Negative Relationship
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
1000
1100
0 2 4 6 8 10 12
Year
Pre
sent
Val
ue (
i = 1
0%)

Copyright ©2003 Brooks/ColeA division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
40
• If there is no linear relationship between the variables, the scatterplot may look like a cloud, a horizontal line or a more complex curve Source: Quantitative Environmental Learning Project
http://www.seattlecentral.org/qelp/index.html