Control and coordination, Brain and its functions
-
Upload
kendriya-vidyalaya-fort-william -
Category
Education
-
view
1.269 -
download
2
description
Transcript of Control and coordination, Brain and its functions

Control & Coordination

CONTROL AND COORDINATION
The Nervous SystemNeuronsCentral Nervous System
•Brain•Spinal Cord
Peripheral Nervous SystemThe Senses

Organization in the Body
Several organs working together; each system has one major role
A distinct body part that carries out one or more main functions
A group of similar cells that carry out a specialized job
The basic building block of all living things, plant or animal
Specialized structures inside a cell that have specific functions
A collection of systemsOO
ORGANELLE
CELL
TISSUE
SYSTEM
BODY
ORGAN

The Nervous
System
Helps the body adjust to changes in your environment

FUNCTIONSStimulus
Any change inside or outside your body that brings about a response
HomeostasisRegulation of steady conditions inside the body

Neurons
Building blocks of the nervous system
100 billion neurons in your brain alone30,000 on a pinheadThey communicate with each other
thousands of times a second.Bundles of neurons make up nerves

The Nervous System
Central Nervous System =Brain + Spinal Cord
Peripheral Nervous System =Nerves to rest of body

3 Types of Nerve Cells
Sensory NeuronsReceive information form a sensory receptor and send impulses to the CNS
InterneuronsRelay impulses from sensory neurons to motor neurons
Motor NeuronsCarry impulse from the CNS to muscles and glands through out the body

Parts of a Neuron
3 MAIN PARTSDendrites - receive
messages from other neurons
Cell Body – nucleus is found here
Axon - sends messages to other neurons

Parts of a Neuron
Dendrites
Cell Body
Axon


Synapse
Space between each neuronNeurotransmitters are the messengers that
travel across each synapseThey are chemical signals that neurons use to
talk to each other, which is what makes your brain work. They help determine how you feel, think and act.

NeurotransmittersSerotonin - involved in mood (such as helping you
to feel happy), sleep, mental health, blood pressure and heartbeat.
Dopamine - important in helping to regulate physical movement, pleasure, and thought.Missing in patients with Parkinson's Disease.

Neurotransmitters
• Acetylcholine - involved in regulating muscles, memory, mood, sleep, and organs (like the heart).– Lowered amounts associated with
Alzheimer’s Disease

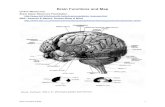
Central Nervous System(C.N.S.)
BRAIN
SPINALCORD

Cerebrum Largest part of the brain Interprets impulses from
the senses
Responsible for: thinking and learningcreativity five sensesmemory and emotionproblem-solvingdecisions

Cerebellum
Coordinates voluntary muscle movement
Helps maintain balance
When a ball is thrown to you, the cerebellum coordinates the proper response to prevent injury

Brainstem Controls involuntary
actions Connects the brain to the
spinal cord Regulates heart rate,
breathing, swallowing, blinking, and more
Made up of:the midbrainPonsmedulla

Spinal CordMade up of bundles of
neuronsCarries impulses to and
from the brainTogether, the brain and
spinal cord make up the Central Nervous System (C.N.S.)
Fun fact:The spinal cord is about
45 cm long in men and 43 cm long in women.

Peripheral Nervous System(P.N.S.)
Connects the C.N.S. with the rest of the body
• sensory nerves take impulse from stimulus (sensory receptors) to the CNS
• motor nerves take impulse from the CNS to the muscles and glands that take action.

ReflexREFLEX
An involuntary, automatic response to a stimulus controlled by the spinal cord
Like when the doctor uses the rubber mallet on your tendon below your knee
Movement when someone unexpectedly throws something at you

Reflex ArcWhen the body receives a painful stimulus (stepping
on a nail, touching a hot surface, etc), the body responds super-fast.
Path of reflex arc:
STIMULUS sensory receptor sensory nerve spinal cord (interneuron) motor nerve muscle RESPONSEAn impulse continues up to the brain to be interpreted by the cerebrum, BUT, meanwhile the affected area has already produced a response!

Senses
VisionSensory Receptors
Rods sense brightnessCones sense color
The retina, in the back of your eye, has cells that are sensitive to light. They connect directly to your
brain.

Senses
Hearing Sound waves make your
eardrum vibrate. Small bones in your ear
vibrate (hammer, anvil, stirrup)
Vibrations go through the snail-like cochlea, which turns them into nerve impulses to your brain.

SensesTaste10,000 taste buds in your
mouthYour tongue picks up four
types of taste:• sweet• sour• bitter• salty
Sweet and salty are least sensitive
Bitter ones are most sensitive

Senses
SmellOdor particles drift into your noseStimulate sensory receptors –
olfactory cells – in nasal passagesSensory receptors send impulses
to your brain to be interpreted.

Senses
There are at least six types of touch receptors
in your skin:• Hot• Cold• Pain
• Pressure• Touch
• Fine touch
TOUCH