Company law chap 1
-
Upload
shwetha-girish -
Category
Business
-
view
787 -
download
4
description
Transcript of Company law chap 1

Company LawCompany Law

What is a company?What is a company? A Company is a A Company is a voluntary association voluntary association
of personsof persons formed for the purpose of formed for the purpose of doing business, having a distinct name doing business, having a distinct name and limited liability.and limited liability.
They can be incorporated under the They can be incorporated under the Companies Act (it may be any type of Companies Act (it may be any type of company) company)
Corporations Corporations enacted under special enacted under special enactments ( Even those which are enactments ( Even those which are incorporated outside India)incorporated outside India)
Corporate soleCorporate sole Any Any other body corporateother body corporate notified by notified by
the central governmentthe central government

Features of a companyFeatures of a company
A company is considered as a A company is considered as a separate legal entityseparate legal entity from its from its members, which can conduct members, which can conduct business with all powers to contract.business with all powers to contract.
Independent corporate entityIndependent corporate entity (Saloman V. Saloman) It is (Saloman V. Saloman) It is independent of its members and independent of its members and shareholdersshareholders

Other featuresOther features
Limited LiabilityLimited Liability ( either by share or ( either by share or guaranteeguarantee) )
ItIt can own property, separate from its can own property, separate from its membersmembers. The property is vested with . The property is vested with the company, as it is a body corporate.the company, as it is a body corporate.
The The income of the members are income of the members are different from the income of the different from the income of the companycompany ( Income received by the ( Income received by the members as dividends cannot be members as dividends cannot be same as that of the company)same as that of the company)
cont….cont….

Features continued..Features continued..
Perpetual successionPerpetual succession: Death of the : Death of the members is not the death of the members is not the death of the company until it is wound upcompany until it is wound up
As it is a legal entity or a As it is a legal entity or a juristic juristic person or artificial person it can person or artificial person it can sue sue and be suedand be sued
The company enjoys The company enjoys rights and rights and liabilitiesliabilities which are not as that of the which are not as that of the members of the companymembers of the company

Lifting of Corporate VeilLifting of Corporate Veil
As the company is As the company is a separate legal a separate legal entityentity , is has been provided with a , is has been provided with a veil, compared to that of individuals veil, compared to that of individuals who are managing the company.who are managing the company.
But if the court feels that such veil But if the court feels that such veil has to been used for any has to been used for any wrongful wrongful purposepurpose, the court lifts the corporate , the court lifts the corporate veil and makes the veil and makes the individual liable individual liable for such acts which they should not for such acts which they should not have done or doing in the name of have done or doing in the name of the companythe company

Circumstances to lift the Circumstances to lift the corporate veil…corporate veil…The corporate veil can be lifted eitherThe corporate veil can be lifted eitherunder the under the Statutory provisionsStatutory provisions or or Judicial interpretationsJudicial interpretationsThe statutory provisions areThe statutory provisions areProvided under the CompaniesProvided under the CompaniesAct, 1956Act, 1956The other circumstances are decidedThe other circumstances are decidedthrough Judicial interpretations, whichthrough Judicial interpretations, whichare based on facts of each case as perare based on facts of each case as perthe decisions of the courtthe decisions of the court

Statutory circumstances for Statutory circumstances for lifting the corporate veillifting the corporate veil Reduction in membership- Reduction in membership- Less than Less than
seven in public company and less than seven in public company and less than two if it is a private company two if it is a private company
Failure to refund application money- Failure to refund application money- After the issue of shares to the pubic, After the issue of shares to the pubic, the company has to pay back the initial the company has to pay back the initial payment to the unsuccessful applicants payment to the unsuccessful applicants (SEBI Guidelines- 130 Days), if they fail (SEBI Guidelines- 130 Days), if they fail to do so, the corporate veil can be lifted.to do so, the corporate veil can be lifted.
Mis-description of companies name- Mis-description of companies name- While signing a contract if the While signing a contract if the company’s name is not properly company’s name is not properly described, then the corporate veil can described, then the corporate veil can be lifted.be lifted.

continuedcontinued Misrepresentation in the prospectus- Misrepresentation in the prospectus- (Derry (Derry
Vs Peek) In case of misrepresentation, the Vs Peek) In case of misrepresentation, the promoters, directors and every other person promoters, directors and every other person responsible in this matter can be held liable. responsible in this matter can be held liable.
Fraudulent Conduct- Fraudulent Conduct- In case the company In case the company is carried on with an intent to defraud the is carried on with an intent to defraud the creditors, then the court may lift the creditors, then the court may lift the corporate veil.corporate veil.
Holding and subsidiary companies-Holding and subsidiary companies- A A subsidiary has a distinct legal entity from subsidiary has a distinct legal entity from the holding company other than in a few the holding company other than in a few circumstances, so if otherwise shown, the circumstances, so if otherwise shown, the court may under the Act , lift the corporate court may under the Act , lift the corporate veil of the subsidiary company.veil of the subsidiary company.

Circumstances to lift the corporateCircumstances to lift the corporateveil through judicial interpretations veil through judicial interpretations
When the court feels that there are When the court feels that there are no statutory provisions which can no statutory provisions which can pierce the corporate veil, and pierce the corporate veil, and the the identity of the company is not the identity of the company is not the one which has to exist, and the one which has to exist, and the court has to interfere in order to court has to interfere in order to avoid the activities that are done in avoid the activities that are done in the name of the company by persons the name of the company by persons managing themmanaging them, it has been , it has been empowered to do so…… empowered to do so……
The circumstances are…..The circumstances are…..

Judicial interpretations by the Judicial interpretations by the court are as follows:court are as follows: Protection of Revenue-Protection of Revenue- When ever a When ever a
company uses its name for the purpose of company uses its name for the purpose of tax evasion or to circumvent tax obligationstax evasion or to circumvent tax obligations
Prevention of fraud or Improper conduct- Prevention of fraud or Improper conduct- The incorporation has been used for The incorporation has been used for fraudulent purpose, like defrauding the fraudulent purpose, like defrauding the creditors, defeating the purpose of law etc..creditors, defeating the purpose of law etc..
Determination of the character of the Determination of the character of the company- company- Enemy company or all the Enemy company or all the members being the citizens of the enemy members being the citizens of the enemy country. (Daimler Co. Ltd V. Continental country. (Daimler Co. Ltd V. Continental Tyre & Rubber Co. Ltd)Tyre & Rubber Co. Ltd)

Other circumstancesOther circumstances
Where a company is used to avoid Where a company is used to avoid welfare legislation-welfare legislation- If a company is If a company is formed in order to avoid the benefits formed in order to avoid the benefits to the workers like bonus, or other to the workers like bonus, or other statutory benefits..statutory benefits..
For determining the technical For determining the technical competence of the company- competence of the company- To look To look into the competency of the company into the competency of the company or the shareholders or promoters or the shareholders or promoters
(New Horizon’s Ltd and Another V. Union of India (New Horizon’s Ltd and Another V. Union of India (1994)(1994)

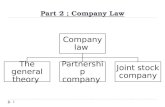
Types of CompaniesTypes of Companies
Limited Company ( Limited by Limited Company ( Limited by share or by guarantee)share or by guarantee)
Unlimited companyUnlimited company Government CompanyGovernment Company Foreign CompanyForeign Company Private CompanyPrivate Company Public CompanyPublic Company

Limited CompanyLimited Company Limited by Shares-Limited by Shares- In such companies, the In such companies, the
liability is only the amount which remains liability is only the amount which remains unpaid on the shares.unpaid on the shares.
Limited by Guarantee not having share Limited by Guarantee not having share capital-capital-In this type of companies the In this type of companies the memorandum of Association limits the memorandum of Association limits the members’ liability. It will be based on the members’ liability. It will be based on the undertaking that has been given in MOA for undertaking that has been given in MOA for their contribution in case of a winding up.their contribution in case of a winding up.
Limited by guarantee having share capital-Limited by guarantee having share capital- In In such cases , the liability would be based on such cases , the liability would be based on the MOA towards the guaranteed amount and the MOA towards the guaranteed amount and the remaining would be from the unpaid sums the remaining would be from the unpaid sums of the shares held by the person concerned.of the shares held by the person concerned.

Unlimited Company Unlimited Company
There is There is no limit on the liability of the no limit on the liability of the members.members. The liability in such cases would The liability in such cases would extend to the whole amount of the extend to the whole amount of the company’s debts and liabilities.company’s debts and liabilities.
Here the Here the members cannot be directly sued members cannot be directly sued by the creditorsby the creditors..
When the company is wound up, the When the company is wound up, the official liquidator will call upon the members official liquidator will call upon the members to discharge the liability.to discharge the liability.
The details of the number of members with The details of the number of members with which the company is registered and the which the company is registered and the amount of share capital has to be stated in amount of share capital has to be stated in the Articles of Association (AOA).the Articles of Association (AOA).

Government CompanyGovernment Company When When 51%51% of the paid up share of the paid up share
capital is held by the government.capital is held by the government. The share can be held by the The share can be held by the central central
government or state governmentgovernment or state government. . Partly by central and partly by two or Partly by central and partly by two or more governments.more governments.
As the legal status of the company As the legal status of the company does not change by being a does not change by being a government company, there are no government company, there are no special privileges given to them.special privileges given to them.

Foreign CompanyForeign Company
A company incorporated A company incorporated outside India, but outside India, but having a place having a place of business in Indiaof business in India..
If it does not have a place of If it does not have a place of business in India but only has business in India but only has agents in India it cannot be agents in India it cannot be considered to be foreign considered to be foreign company. company.

Private CompanyPrivate Company A company which has a A company which has a minimum of two minimum of two
personspersons. They have to subscribe to the . They have to subscribe to the MOA and AOAMOA and AOA
It should be have a It should be have a minimum paid up minimum paid up capital of 1 lakh or morecapital of 1 lakh or more as prescribed by as prescribed by the article.the article.
The maximum number of members to be The maximum number of members to be fiftyfifty ( it does not include members who are ( it does not include members who are employed in the company, persons who employed in the company, persons who were formerly employed)were formerly employed)
The The rights to transfer the shares are rights to transfer the shares are restrictedrestricted in the Private companies in the Private companies
continued….continued….

Prohibits any invitation to the public to Prohibits any invitation to the public to subscribesubscribe and therefore it cannot issue and therefore it cannot issue a prospectus inviting the public to a prospectus inviting the public to subscribe for any shares in, or subscribe for any shares in, or debentures of the companydebentures of the company
It It prohibits acceptance of depositsprohibits acceptance of deposits from from persons other than its members, persons other than its members, directors or their relatives.directors or their relatives.
If If two or more are holding one or more two or more are holding one or more sharesshares in a company in a company jointly,jointly, they shall they shall for the purpose of this definition, be for the purpose of this definition, be treated as treated as a single member.a single member.
As there is As there is no public accountabilityno public accountability like like a public company, there is a public company, there is no rigorous no rigorous surveillance.surveillance.

Exemption and Privileges of a Exemption and Privileges of a Private companyPrivate company It can have a It can have a minimum of two minimum of two
members.members. It can It can commence business commence business
immediatelyimmediately after obtaining after obtaining certificate of incorporation.certificate of incorporation.
It need It need not issue prospectusnot issue prospectus or or statement in lieu of prospectus.statement in lieu of prospectus.
It can have a It can have a minimum of 2 directors.minimum of 2 directors. It It need not hold statutory meetingneed not hold statutory meeting or or
file statutory report with the ROC.file statutory report with the ROC.

Public CompanyPublic Company A Public company means a company-A Public company means a company- > Which is > Which is not a private companynot a private company > Which has a > Which has a minimum paid-up minimum paid-up
capital of Rs 5 lakh or such higher capital of Rs 5 lakh or such higher paid-uppaid-up capital, as may be prescribed capital, as may be prescribed
> Which is > Which is a private company and is a a private company and is a not a subsidiary ofnot a subsidiary of a company, which is a company, which is private company. private company.
>It includes- any company which is a >It includes- any company which is a public company with a paid up capital public company with a paid up capital of less than 5 lakh, then it has to of less than 5 lakh, then it has to enhance its paid up capital as per the enhance its paid up capital as per the statutory requirementstatutory requirement

Conversion of CompanyConversion of Company
The Act provides for The Act provides for conversion of conversion of public company into a private public company into a private company and vice versacompany and vice versa
A private company is converted into A private company is converted into a public company either a public company either by default or by default or by choiceby choice in compliance with the in compliance with the statutory requirements. statutory requirements.
Once the action for conversion takes Once the action for conversion takes place then, place then, a petition can be filed a petition can be filed with the central government with the with the central government with the necessary documents for its decision necessary documents for its decision on the matter of conversionon the matter of conversion

Registration and IncorporationRegistration and Incorporation Association of persons or partnership or Association of persons or partnership or
more than more than 20 members ( 10 in case of 20 members ( 10 in case of banking) can register to form a company banking) can register to form a company under the Companies Act, 1956under the Companies Act, 1956
If they do not register they can be If they do not register they can be considered to be illegal association. The considered to be illegal association. The contract entered into by this illegal contract entered into by this illegal association is association is void and cannot be void and cannot be validated. validated. Its illegality will Its illegality will not affect its not affect its tax liability or its chargeabilitytax liability or its chargeability
The certification of incorporation is the The certification of incorporation is the conclusive evidence, that all the conclusive evidence, that all the requirements for the registration have requirements for the registration have been complied with the been complied with the

Incorporation of a CompanyIncorporation of a Company The persons who The persons who conceive an ideaconceive an idea of a of a
company decide and do the necessary company decide and do the necessary work for formation of a company are called work for formation of a company are called the the promoterspromoters of the Company. of the Company.
The Promoters are the persons who decide The Promoters are the persons who decide on the on the formation of the company.formation of the company.
The promoters of a company stand The promoters of a company stand undoubtedly in a undoubtedly in a fiduciary positionfiduciary position though though they are not the agent or a trustee of a they are not the agent or a trustee of a company. They are the ones “who create company. They are the ones “who create and mould the company”. and mould the company”.
They may have to enter into They may have to enter into pre-pre-incorporation contractsincorporation contracts , which can be , which can be validated after the incorporation of the validated after the incorporation of the company for obtaining certificate of company for obtaining certificate of incorporation.incorporation.

PromotersPromoters They can be They can be remunerated for their remunerated for their
services, but they have to enter into a services, but they have to enter into a contract before the incorporation of the contract before the incorporation of the company through a pre incorporationcompany through a pre incorporation of of the companythe company
They will usually act as They will usually act as nominees or as nominees or as the first directorsthe first directors of the company of the company
They enter into contracts after the They enter into contracts after the incorporation and before the incorporation and before the commencement of business.commencement of business.
But they need But they need not compulsorily participate not compulsorily participate in the formation of the company.in the formation of the company.

Sometimes , a few persons may only act Sometimes , a few persons may only act as as professionals who help the professionals who help the promoters on behalf of the company.. promoters on behalf of the company.. like the solicitor, chartered accountant like the solicitor, chartered accountant etc.. and get paid for their servicesetc.. and get paid for their services..
The promoters in most of the cases The promoters in most of the cases decide as to …What is the type of a decide as to …What is the type of a companycompany to be formed? to be formed?
In IndiaIn India promoters generally secure the promoters generally secure the management of the company that is management of the company that is formed and have a controlling interest in formed and have a controlling interest in the company’s managementthe company’s management

Legal Position of the Legal Position of the PromotersPromoters They They cannot make profitcannot make profit at the expense at the expense
of the company, which they have of the company, which they have promoted promoted without the knowledge and without the knowledge and consent of the company.consent of the company. In case they In case they do so , they may be compelled to do so , they may be compelled to account for it.account for it.
They They cannot sell their property to the cannot sell their property to the company at a profit unless all the company at a profit unless all the material factsmaterial facts are disclosed at the are disclosed at the independent board of directors or the independent board of directors or the shareholders of the company.shareholders of the company.
If they do so, the company may If they do so, the company may repudiate the contract of sale or confirm repudiate the contract of sale or confirm the sale after recovering the profit made the sale after recovering the profit made by the promoter.by the promoter.

Promoters have the following Promoters have the following liabilities under the Companies liabilities under the Companies Act, 1956Act, 1956 They can be They can be liable for non complianceliable for non compliance of the of the
provisions of the Actprovisions of the Act Severe penaltySevere penalty may be imposed may be imposed The court may The court may suspend the promoter from suspend the promoter from
taking part in the managementtaking part in the management of the company of the company Liable for any untrue statement in the Liable for any untrue statement in the
prospectusprospectus to the person who has subscribed to the person who has subscribed for any shares or debentures on the faith of the for any shares or debentures on the faith of the prospectusprospectus
The The liabilities areliabilities are …. …. a) to set aside the allotment of shares, a) to set aside the allotment of shares, b) sued for damages, b) sued for damages, c) sued for compensation c) sued for compensation d) criminal proceedingsd) criminal proceedings

The requirements are as The requirements are as followsfollows Application for availability of nameApplication for availability of name Preparation of MOA and AOAPreparation of MOA and AOA Selection and finalization of MOA Selection and finalization of MOA
and AOA- Its printing, stamping and and AOA- Its printing, stamping and signingsigning
Preparation of other necessary Preparation of other necessary documentsdocuments
Filling of the required documents for Filling of the required documents for RegistrationRegistration to obtain certificate of to obtain certificate of incorporation and Certificate of incorporation and Certificate of commencement of businesscommencement of business

Memorandum of AssociationMemorandum of Association It is the It is the chartercharter of the company of the company It contains the It contains the fundamental conditions upon fundamental conditions upon
which the company can be incorporatedwhich the company can be incorporated It contains the It contains the objects objects of the company’s of the company’s
formationformation The company has to The company has to act within objects act within objects
specifiedspecified in the MOA in the MOA It It defines as well as confinesdefines as well as confines the powers of the powers of
the companythe company Any thing done beyond the objects Any thing done beyond the objects
specified in the MOA will be specified in the MOA will be ultra vires. ultra vires. Their transactions will be null and voidTheir transactions will be null and void
The outsider have The outsider have to transactto transact looking into looking into the MOAthe MOA

Conditions of the MOAConditions of the MOA
It should be It should be printedprinted Divided into Divided into paragraph and numbers paragraph and numbers
consecutivelyconsecutively SignedSigned by at least seven persons or by at least seven persons or
two in case of public and private two in case of public and private company respectively.company respectively.
The signature should be in the The signature should be in the presence of a witness, who will have presence of a witness, who will have to attestto attest the signature the signature
Members have to take Members have to take shares and shares and write the number of shareswrite the number of shares taken taken with full addresswith full address

The MOA of the Limited The MOA of the Limited CompanyCompany The name of the company with ‘The name of the company with ‘limited’limited’
as the last wordas the last word The name of the The name of the state where the state where the
registered officeregistered office of the company is to be of the company is to be situatedsituated
The objects of the company stating the The objects of the company stating the ‘Main objects’ and the ‘other objects’‘Main objects’ and the ‘other objects’
The declaration about the The declaration about the liability of the liability of the membersmembers is is limitedlimited ( limited by shares or ( limited by shares or guarantee)guarantee)
The amount of the The amount of the authorized share authorized share capital, divided into shares of fixed capital, divided into shares of fixed amounts.amounts.

The Compulsory ClausesThe Compulsory Clausesin MOAin MOA The Name Clause – it decides on the The Name Clause – it decides on the name name
of the companyof the company based on the capital based on the capital involvedinvolved
The Registered Office Clause- where it has The Registered Office Clause- where it has registered its head officeregistered its head office and other branch and other branch office ( The registered office can be office ( The registered office can be changed with the permission of the ROC)changed with the permission of the ROC)
The Object Clause- The Object Clause- Main object, ancillary Main object, ancillary object and the other objectsobject and the other objects of the of the company are clearly specified ( Ashbury company are clearly specified ( Ashbury Railway Carriage Co V. Riche). The Railway Carriage Co V. Riche). The applicable doctrine here is the applicable doctrine here is the “ Doctrine of “ Doctrine of Ultra Vires” beyond the powers of the Ultra Vires” beyond the powers of the company (opposed to Intra Vires)company (opposed to Intra Vires)

The Liability Clause-The Liability Clause- What is the liability of What is the liability of its members.. limited by shares or its members.. limited by shares or guarantee or unlimited, there can be guarantee or unlimited, there can be alteration in the liability clausealteration in the liability clause
The Capital ClauseThe Capital Clause - The amount of the - The amount of the nominal capital of the company, number of nominal capital of the company, number of shares in which it is to be divided… shares in which it is to be divided… alteration of the capital clause etcalteration of the capital clause etc
The Association or Subscription clause- The Association or Subscription clause- Where the subscribers to the MOA declare Where the subscribers to the MOA declare that they respectively agree to take the that they respectively agree to take the number of the shares in the capital. It has number of the shares in the capital. It has to have the following:to have the following:
a) They have to sign in the presence of two a) They have to sign in the presence of two witnesses, who attest the signatures, witnesses, who attest the signatures,
b) The subscriber to take at least one b) The subscriber to take at least one share. share.
c) After the name the subscriber has to c) After the name the subscriber has to write the number of shares takenwrite the number of shares taken

““Doctrine of Ultra Vires”Doctrine of Ultra Vires” The powers exercisable by the company are The powers exercisable by the company are
to be confined to the objects to be confined to the objects specified in the specified in the MOA.MOA.
So it is better to define and include the So it is better to define and include the provisions regarding the provisions regarding the acquiring of business, acquiring of business, sharing of profits, promoting company and sharing of profits, promoting company and other financial, gifts , political party funds etcother financial, gifts , political party funds etc
If the company acts beyond the powers or the If the company acts beyond the powers or the objects of the company that is specified in the objects of the company that is specified in the MOA, the acts are considered to be of MOA, the acts are considered to be of ultra ultra viresvires. Even if it is ratified by the all the . Even if it is ratified by the all the members, the action is considered to be members, the action is considered to be ineffective.ineffective.
Even the charitable contributions have to be Even the charitable contributions have to be based on the object clause. based on the object clause. ( A ( A Lakshmanaswami Mudaliar V. LIC of India)Lakshmanaswami Mudaliar V. LIC of India)

The The consequences of the consequences of the ultra ultra viresvires transactions are as follows transactions are as follows::
a)a) Injunction Injunction b)b) Directors’ personal liability.Directors’ personal liability.c)c) If a property has been purchased If a property has been purchased
and it is an and it is an ultra viresultra vires act, the act, the company can have a right over that company can have a right over that property.property.
d)d) The doctrine to be used exclusively The doctrine to be used exclusively for the companies’ interest.for the companies’ interest.
e)e) But the others cannot use this But the others cannot use this doctrine as a tool to attack the doctrine as a tool to attack the companycompany

Articles of AssociationArticles of Association It is the companies It is the companies bye- laws or rules bye- laws or rules
to governto govern the management of the the management of the company for its company for its internal affairs and the internal affairs and the conduct of its businessconduct of its business..
AOA defines the AOA defines the powers of its officers powers of its officers and also establishes a contract and also establishes a contract between the company and the between the company and the members and between the members members and between the members inter seinter se
It can be originally framed and altered It can be originally framed and altered by the company under previous or by the company under previous or existing provisions of law.existing provisions of law.

AOA AOA AOA plays a AOA plays a subsidiary partsubsidiary part to the MOA to the MOA Any thing Any thing done beyond the AOA will be done beyond the AOA will be
considered to be irregular and may be ratified considered to be irregular and may be ratified by the shareholdersby the shareholders..
The content of the AOA may differ from The content of the AOA may differ from company to company as the Act has not company to company as the Act has not specified any specific provisionsspecified any specific provisions
Flexibility is allowed to the persons who form Flexibility is allowed to the persons who form the company to adopt the AOA within the the company to adopt the AOA within the requirements of the company lawrequirements of the company law
The AOA will have to be conversant with the The AOA will have to be conversant with the MOA, as they are contemporaneous MOA, as they are contemporaneous documents to be read together.documents to be read together.
Any Any ambiguity and uncertainty in one of them ambiguity and uncertainty in one of them may be removed by reference to the other.may be removed by reference to the other.

Contents of the AOA may be Contents of the AOA may be as follows:as follows: Share capitalShare capital Lien on sharesLien on shares Calls on sharesCalls on shares Transfer and transmission of sharesTransfer and transmission of shares Forfeiture of the sharesForfeiture of the shares Surrender of the sharesSurrender of the shares General meetingsGeneral meetings Alteration of the capitalAlteration of the capital Directors etc..Directors etc.. Dividends and reservesDividends and reserves Account and auditAccount and audit Borrowing powersBorrowing powers Winding upWinding up Adoption of the preliminary contracts etc….Adoption of the preliminary contracts etc….

Doctrine of Constructive notice Doctrine of Constructive notice and Indoor Managementand Indoor Management
Persons dealing with the company have to Persons dealing with the company have to satisfy themselves. But need not know the satisfy themselves. But need not know the internal irregularity. Royal British Bank V. internal irregularity. Royal British Bank V. Turquand (Turquand Rule) Directors Turquand (Turquand Rule) Directors issuing a bond. issuing a bond.
The doctrine of Constructive notice can be The doctrine of Constructive notice can be invoked by the company to operate against invoked by the company to operate against the persons dealing with the company.the persons dealing with the company.
The outsider cannot embark, but only can The outsider cannot embark, but only can acquaint upon the MOA and AOA. (Official acquaint upon the MOA and AOA. (Official Liquidator, Manasube &Co Pvt Lid V. Liquidator, Manasube &Co Pvt Lid V. Commissioner of Police)Commissioner of Police)

Exceptions to the Doctrine of Exceptions to the Doctrine of Where the outsider cannot claim Where the outsider cannot claim the relief on the grounds of the relief on the grounds of “Indoor management”“Indoor management”
Knowledge of irregularityKnowledge of irregularity No knowledge of articlesNo knowledge of articles NegligenceNegligence ForgeryForgery Non- Existent authority of the Non- Existent authority of the
companycompany

Raising of Capital From PublicRaising of Capital From Public
The companies can raise money by The companies can raise money by offering securitiesoffering securities for sale to the for sale to the public. public.
They can invite the public to buy They can invite the public to buy shares, which is known as shares, which is known as public public issue.issue.
For this purpose the company may For this purpose the company may issue a issue a prospectus, which may prospectus, which may include a notice circular, include a notice circular, advertisement or other documentsadvertisement or other documents which are issued to invite public which are issued to invite public deposits.deposits.

Prospectus Prospectus It is an It is an invitation invitation issued to the public issued to the public to to
purchase or subscribe shares or purchase or subscribe shares or debenturesdebentures of the company. of the company.
Every Every prospectus must be datedprospectus must be dated. The date . The date of publication and the date of issue must of publication and the date of issue must be specifically stated in the prospectus.be specifically stated in the prospectus.
The The golden rulegolden rule of the prospectus is that of the prospectus is that every detail has to be given in strict and every detail has to be given in strict and scrupulous accuracy. The material facts scrupulous accuracy. The material facts given in the prospectus are presumed to be given in the prospectus are presumed to be true.( New Brunswick and Canada Railway. true.( New Brunswick and Canada Railway. Land & Co. Vs. Muggerridge).Land & Co. Vs. Muggerridge).

Various forms in which the Various forms in which the prospectus can be issued.prospectus can be issued. Shelf ProspectusShelf Prospectus: Prospectus is normally : Prospectus is normally
issued by financial institution or bank for issued by financial institution or bank for one or more issues of the securities or one or more issues of the securities or class of securities mentioned in the class of securities mentioned in the prospectus. prospectus.
There can be There can be deemed prospectusdeemed prospectus also if it also if it is issued by the issue houseis issued by the issue house
‘‘Information MemorandumInformation Memorandum’: It means a ’: It means a process, which is undertaken prior to the process, which is undertaken prior to the filing of prospectus. filing of prospectus.
Even anEven an Advertisement Advertisement , that the shares , that the shares are available is considered to be are available is considered to be prospectusprospectus

Contents of the prospectus Contents of the prospectus General informationGeneral information Capital structureCapital structure Terms of present issueTerms of present issue Management and projectsManagement and projects Management and perception of Management and perception of
risk factorrisk factor
It is compulsory to register the It is compulsory to register the prospectus with the Registrarprospectus with the Registrar

Civil Liability for MisstatementsCivil Liability for MisstatementsIn case of any untrue statement in In case of any untrue statement in the prospectusthe prospectus The liability will be on the director of The liability will be on the director of
the company , whose name was the company , whose name was written during the time of issuewritten during the time of issue
The persons who have authorized The persons who have authorized their names to be theirs in the their names to be theirs in the prospectus to be named as directorsprospectus to be named as directors
PromoterPromoter Every person including the person Every person including the person
who is an expert and has authorized who is an expert and has authorized his name to be issued with the his name to be issued with the prospectus prospectus

Remedies for misstatements Remedies for misstatements in the prospectus in the prospectus Relying on the prospectus if any Relying on the prospectus if any
person buys shares, the person mayperson buys shares, the person may Rescind the contract ( only when Rescind the contract ( only when
there is misrepresentation relating to there is misrepresentation relating to the material facts.the material facts.
The rescission has to be done within The rescission has to be done within a reasonable timea reasonable time
Claim damages- it can be claimed Claim damages- it can be claimed from the directors, promoters or from the directors, promoters or other persons who has authorized other persons who has authorized their name to be written during the their name to be written during the issue of the prospectusissue of the prospectus

Share CapitalShare Capital Share: Share: Share is defined as “an interest Share is defined as “an interest
having a money value and made up of having a money value and made up of diverse rights specified under the articles of diverse rights specified under the articles of association”. association”.
Share capital: Share capital: Share capital means the Share capital means the capital raised by the company by issue of capital raised by the company by issue of sharesshares. .
A share is a share in the share capital of A share is a share in the share capital of the company including the stock.the company including the stock.
Share gives a right to participate in the Share gives a right to participate in the profits of the company, or a share in the profits of the company, or a share in the assets when the company is going to be assets when the company is going to be wound up.wound up.

Other features of a shareOther features of a share A share is not a negotiable instrument, but A share is not a negotiable instrument, but
it is a movable property. it is a movable property. It is also considered to be goods under the It is also considered to be goods under the
Sale of Goods Act, 1930.Sale of Goods Act, 1930. The company has to issue the share The company has to issue the share
certificate.certificate. It is subject to stamp duty.It is subject to stamp duty. The ‘Call’ on Shares is a demand made for The ‘Call’ on Shares is a demand made for
payment of price of the shares allotted to payment of price of the shares allotted to the members by the Board of Directors in the members by the Board of Directors in accordance with the Articles of Association.accordance with the Articles of Association.
The call may be for full amount or part of it.The call may be for full amount or part of it.

Share Certificate and Share Share Certificate and Share WarrantWarrant Share CertificateShare Certificate:: The Share Certificate is a The Share Certificate is a
document issued by the companydocument issued by the company and is prima facie and is prima facie evidence to show that the person named therein is evidence to show that the person named therein is the holder ( title) of the specified number of shares the holder ( title) of the specified number of shares stated therein.stated therein.
Share certificate is issued by the company to the Share certificate is issued by the company to the ( share holder) allottee of shares.( share holder) allottee of shares.
The company has to issue within 3 months from The company has to issue within 3 months from the date of allotment. In case of default the allottee the date of allotment. In case of default the allottee may approach the central governmentmay approach the central government
Share WarrantShare Warrant: : The share warrant is a The share warrant is a bearer bearer documentdocument issued by the company under its issued by the company under its common seal. As share warrant is a negotiable common seal. As share warrant is a negotiable instrument, it is transferred by endorsement and by instrument, it is transferred by endorsement and by mere delivery like any other negotiable instrumentmere delivery like any other negotiable instrument. .

Kinds of sharesKinds of shares>Preference shares->Preference shares- It can be further It can be further
classified as classified as Participating preferential shares.Participating preferential shares. Cumulative preferential sharesCumulative preferential shares Non Cumulative preferential sharesNon Cumulative preferential shares>Redeemable Shares>Redeemable Shares and and>Irredeemable Shares>Irredeemable Shares>Equity or ordinary shares>Equity or ordinary shares>Shares at premium>Shares at premium>Shares at discount>Shares at discount>Bonus shares>Bonus shares>Right shares>Right shares

Transfer and Transmission of Transfer and Transmission of sharesshares AOA provides for the procedure of transfer AOA provides for the procedure of transfer
of shares. It is a voluntary action of the of shares. It is a voluntary action of the shareholder.shareholder.
It can be made even by a blank transfer –In It can be made even by a blank transfer –In such cases such cases the transferor only signs the the transferor only signs the transfer form without making any other transfer form without making any other entries. entries.
In case it is a forged transfer, the In case it is a forged transfer, the transferor’s signature is forged on the transferor’s signature is forged on the share transfer instrument. share transfer instrument.
Transmission of sharesTransmission of shares is by operation of is by operation of law, e.g. by death, insolvency of the law, e.g. by death, insolvency of the shareholder etc.shareholder etc.

Buy-Back of SecuritiesBuy-Back of Securities The company may purchase its securities The company may purchase its securities
back and it is popularly known as buy back back and it is popularly known as buy back of sharesof shares
To do so , the company has to be To do so , the company has to be authorized under the AOA.authorized under the AOA.
The company has to comply with the The company has to comply with the provisions of the Company law to buy back provisions of the Company law to buy back its securities.its securities.
The listed company has to seek permission The listed company has to seek permission from the SEBI (SERA 1998). Specifically from the SEBI (SERA 1998). Specifically for the private company etc, the Buy Back for the private company etc, the Buy Back Securities Rules1999 will be applicable.Securities Rules1999 will be applicable.

DividendsDividends
The The sharing of profitssharing of profits in the going concerns in the going concerns and the distribution of the assets after the and the distribution of the assets after the winding up can be called as dividendswinding up can be called as dividends
It will be distributed among the shares holdersIt will be distributed among the shares holders The dividends can be The dividends can be declared and paid out of:declared and paid out of: Current profitsCurrent profits ReservesReserves Monies provided by the government and the Monies provided by the government and the
depreciation as provided by the companies.depreciation as provided by the companies. It can be paid after presenting the balance It can be paid after presenting the balance
sheet and profit and loss account in the AGMsheet and profit and loss account in the AGM

DividendDividend Other than the equity shareholders, Other than the equity shareholders,
even the preferential shareholders even the preferential shareholders can get the dividends. Rather they can get the dividends. Rather they are the first ones to get the are the first ones to get the dividends.dividends.
Dividends are to be only in cash, if Dividends are to be only in cash, if otherwise specified in the AOA.otherwise specified in the AOA.
In exceptional cases, even the In exceptional cases, even the central government may permit the central government may permit the payment of interest to shareholders , payment of interest to shareholders , even though there is no profit.even though there is no profit.

DirectorsDirectorsThe Legal Status of the directorThe director occupies the position of a: As a Trustee- In relation to the company As Agents- When they act o n behalf of the company As Managing Partner-As they are entrusted
with the responsibility of the company Qualification Shares In case there is requirement as per the
AOA for the director is bound to buy qualification shares
If acts are done by the director prior to he or she being disqualified, the acts are considered to be valid.

DisqualificationsDisqualifications
As per the company law, the followingAs per the company law, the followingpersons are persons are disqualified disqualified from been appointedfrom been appointedas a director:as a director: Unsound mindUnsound mind An undischarged insolventAn undischarged insolvent A person who is convicted by the courtA person who is convicted by the court Who has applied for being adjudged Who has applied for being adjudged
insolventinsolvent Not paid for the call on sharesNot paid for the call on shares Persons who are already directors in Persons who are already directors in
maximum number of companies as per the maximum number of companies as per the provisions of the Act orprovisions of the Act or
Any other person who has been disqualified Any other person who has been disqualified by the court for any other reasonby the court for any other reason

Appointment of DirectorsAppointment of Directors
The appointment can sometimes be by based on the proportional representation like minority shareholders.
There can be alternate directors, additional directors, casual directors.
The third parties can appoint the directors Other than the shareholders and the first directors ,the central government and NCLT may also appoint directors.

Duties and Liabilities of the Duties and Liabilities of the DirectorsDirectorsFiduciary Duties To act honestly and with good faith Not to use confidential information of the
company for their own purpose Duty of Care and to act reasonably while
acting for the companyStatutory Duties Not to contract with company, where he/she
or his relative has an interest in the contract where he/she has a interest, they need to
inform the board or seek prior approval while entering into contract, otherwise the contract is voidable
Duty to attend and convene meetings Duty not to delegate

The directors liabilitiesThe directors liabilities The liability of the directors can be either The liability of the directors can be either
civil or criminal. civil or criminal. If provided in the MOA, the liability may be If provided in the MOA, the liability may be
unlimited, for a limited company, otherwise unlimited, for a limited company, otherwise it may be altered. it may be altered.
Liability may be for breach of fiduciary Liability may be for breach of fiduciary dutiesduties
The directors are personally liable for the The directors are personally liable for the following:following:
a) Ultra vires actsa) Ultra vires acts b) malafide actsb) malafide acts c) negligent actsc) negligent acts d) liability for the acts of third parties d) liability for the acts of third parties

Criminal LiabilityCriminal Liability Liability of the director for any untrue Liability of the director for any untrue
statement in the prospectusstatement in the prospectus Inviting any deposits in contravention Inviting any deposits in contravention
of the lawof the law Liability for false advertisementLiability for false advertisement Failure to repay the application Failure to repay the application
money, which was excessmoney, which was excess Concealing the names of the Concealing the names of the
creditorscreditors Failure to lay the balance sheet.Failure to lay the balance sheet. Failure to provide information to the Failure to provide information to the
auditor etcauditor etc

Company MeetingsCompany Meetings
A meeting may be convened by the A meeting may be convened by the director, requisitionist, or the NCLTdirector, requisitionist, or the NCLT
Notice to be given by the secretary Notice to be given by the secretary after the time and place have been after the time and place have been fixed by the directorsfixed by the directors
Even the shareholders can call a Even the shareholders can call a meeting as an extraordinary general meeting as an extraordinary general meeting (EGM)meeting (EGM)
The NCLT can call an Annual The NCLT can call an Annual General Meeting (AGM)General Meeting (AGM)

Classification of MeetingsClassification of Meetings Shareholders meetingsShareholders meetings a) a) Statutory meetingsStatutory meetings ( which ( which
happens only once in the lifetime of happens only once in the lifetime of the company)the company)
b)b) EGM EGM- Convened to transact some - Convened to transact some special or important decision to be special or important decision to be takentaken
c) c) Class meetings-Class meetings- This is the This is the meeting of the shareholders- which meeting of the shareholders- which is convened by the class of is convened by the class of shareholders based on the kind of shareholders based on the kind of shares they hold. shares they hold.
continued…..continued…..

Other meetingsOther meetings
AGMAGM-it can be conducted based on -it can be conducted based on the provisions given in the Articles or the provisions given in the Articles or by passing a resolution in one AGM by passing a resolution in one AGM for the subsequent AGM’sfor the subsequent AGM’s
Board Meetings-Board Meetings- This is conducted This is conducted for the smooth running of the for the smooth running of the company and for collectively taking company and for collectively taking the decisions. The meetings may be the decisions. The meetings may be conducted to conducted to call on shares, issue call on shares, issue debentures, borrow money, to make debentures, borrow money, to make loans, To invest the fundsloans, To invest the funds etc etc

How to conduct meeting?How to conduct meeting?
Written notice to be givenWritten notice to be given Notice to be issued under the Notice to be issued under the
authority of the companyauthority of the company In case of failure to give a In case of failure to give a
notice, the persons concerned notice, the persons concerned may be punished with fine and may be punished with fine and the proceedings of the meeting the proceedings of the meeting will be rendered invalid.will be rendered invalid.

ResolutionResolution A motion when passed is called a A motion when passed is called a
resolution.resolution. The resolution in the General body The resolution in the General body
meetings can be an meetings can be an ordinary ordinary resolution resolution
( Simple majority) ( Simple majority) andand special special resolution.resolution.
Special resolution- ( notice of 21 Special resolution- ( notice of 21 days to be given) the notice has to days to be given) the notice has to specify the purpose. specify the purpose. The number of The number of votes to be cast in favour of thevotes to be cast in favour of the resolution is to beresolution is to be three times three times the the number vote cast against. number vote cast against.

Quorum and proxy Quorum and proxy The minimum members to be present must be The minimum members to be present must be
according to the provisions of the law.according to the provisions of the law. Public company ( minimum Five) and private Public company ( minimum Five) and private
company (minimum of 2)company (minimum of 2) The quorum must be those members who are The quorum must be those members who are
eligible to vote in respect of the agenda of the eligible to vote in respect of the agenda of the meeting.meeting.
If the quorum is not present within half an hour from If the quorum is not present within half an hour from the appointed time, either the meeting stands the appointed time, either the meeting stands dissolved or may be adjourned in the same day next dissolved or may be adjourned in the same day next week or any other as may be determined by the week or any other as may be determined by the directorsdirectors
A person in case of being incapable to attend a A person in case of being incapable to attend a meeting and who is eligible to vote may appoint a meeting and who is eligible to vote may appoint a proxy in writing to attend the meeting of the member proxy in writing to attend the meeting of the member and vote on his or her behalf. The proxy can only and vote on his or her behalf. The proxy can only vote and cannot participate in the discussions.vote and cannot participate in the discussions.

Compromise, Reconstruction and Arrangement Reconstruction includes Reconstruction includes reorganization, reorganization,
arrangement and amalgamationarrangement and amalgamation.. Arrangement includes all forms of Arrangement includes all forms of
reconstructing.reconstructing. It has been broadly defined as all It has been broadly defined as all forms of forms of
capital reorganizations either by capital reorganizations either by consolidation of shares or division of consolidation of shares or division of shares or bothshares or both
Reorganization and arrangement are done Reorganization and arrangement are done when there is only one company is when there is only one company is involvedinvolved
continuedcontinued….….

Reconstruction can be effectively done Reconstruction can be effectively done through a compromise or arrangement.through a compromise or arrangement.
To do so the meeting or the members or To do so the meeting or the members or the separate class of the shareholders has the separate class of the shareholders has to be conducted or in case of winding up to be conducted or in case of winding up the meeting to be called by the liquidatorthe meeting to be called by the liquidator
Even a banking company (sick bank) may Even a banking company (sick bank) may be reconstructed or amalgamated by the be reconstructed or amalgamated by the central government on the basis of the central government on the basis of the Reserve Bank’s application for a fixed Reserve Bank’s application for a fixed period of time.period of time.
The reconstruction or amalgamation can The reconstruction or amalgamation can be done with any other banking institution.be done with any other banking institution.

Scheme to be approvedScheme to be approved
Any kind of scheme to be accepted, Any kind of scheme to be accepted, it has to get approval from the it has to get approval from the members or the members may reject members or the members may reject the scheme.the scheme.
After the scheme is approved by After the scheme is approved by voting, the court has to sanction the voting, the court has to sanction the scheme or reject, if it is against the scheme or reject, if it is against the public interest or if it feels that the public interest or if it feels that the scheme is not beneficial.scheme is not beneficial.
The legal provisions vary based the The legal provisions vary based the mode of scheme adopted by the mode of scheme adopted by the company.company.

Modes of Reconstruction or Modes of Reconstruction or AmalgamationAmalgamation By sale of undertaking- it can be the whole By sale of undertaking- it can be the whole
or part of sale ( the court will decide)or part of sale ( the court will decide) By sale of shares ( Maximum number of By sale of shares ( Maximum number of
companies adopt this scheme- In such companies adopt this scheme- In such schemes the shares are sold and schemes the shares are sold and registered in the name of the purchasing registered in the name of the purchasing company or on its behalf. The shareholders company or on its behalf. The shareholders selling the shares are compensated either selling the shares are compensated either by cash or with the shares of the acquiring by cash or with the shares of the acquiring company.company.
Amalgamation can take place even for the Amalgamation can take place even for the sake of Public interest by the central sake of Public interest by the central government. In such cases, it will be government. In such cases, it will be notified in the official gazette.notified in the official gazette.

Mergers, Acquisitions and Mergers, Acquisitions and Take over of companiesTake over of companies Merger connotes union of two or Merger connotes union of two or
more commercial interests, more commercial interests, corporations, undertakings, bodies or corporations, undertakings, bodies or any other entities.any other entities.
Fusion of two or more corporations Fusion of two or more corporations by the transfer of all property to a by the transfer of all property to a single corporation. It is used as a single corporation. It is used as a synonym for amalgamation. Even synonym for amalgamation. Even the Act makes no distinction the Act makes no distinction between merger and amalgamation.between merger and amalgamation.

The changing of legal entity The changing of legal entity after mergers and acquisitionsafter mergers and acquisitions In a merger- one of the company In a merger- one of the company
loses its corporate existence and the loses its corporate existence and the survivor company acquires the survivor company acquires the assets as well as the liabilities of the assets as well as the liabilities of the merger company.merger company.
In acquisition, it is acquiring the In acquisition, it is acquiring the ownership in the property is the ownership in the property is the purchase of a controlling interest in purchase of a controlling interest in the share capital of another existing the share capital of another existing company. It is an act of acquiring company. It is an act of acquiring asset and management of the asset and management of the company.company.

Winding upWinding up It is the process whereby the life of the It is the process whereby the life of the
company is ended and its property is company is ended and its property is administered for the benefit of its creditors administered for the benefit of its creditors and members.and members.
During this process a liquidator is During this process a liquidator is appointed to take control of the company. appointed to take control of the company. The liquidator will be responsible for the The liquidator will be responsible for the assets, debts and final distribution of the assets, debts and final distribution of the surplus to the members.surplus to the members.
It is the process for discharge of liabilities It is the process for discharge of liabilities and returning the surplus to those who are and returning the surplus to those who are entitled for it.entitled for it.
But even a company which is making profit But even a company which is making profit can be wound up is the special feature of can be wound up is the special feature of winding up , which is different from that of winding up , which is different from that of the process of insolvency.the process of insolvency.

How can be company be How can be company be wound up?wound up? By passing a special resolutionBy passing a special resolution If there is a default in holding the If there is a default in holding the
statutory meetingstatutory meeting Failure to commence the business Failure to commence the business If there is reduction in the If there is reduction in the
membership of the minimum number membership of the minimum number of members as per the statutory of members as per the statutory requirementrequirement
If it not able to pay its debtsIf it not able to pay its debts

Modes of winding upModes of winding up
Compulsory winding up under the Compulsory winding up under the supervision of the courtsupervision of the court
(Reasons as stated in the previous slide)(Reasons as stated in the previous slide) Compulsory windingCompulsory winding up may happen for up may happen for
just and equitablejust and equitable reasons also. reasons also. The just and equitable grounds can be like The just and equitable grounds can be like
loss of substratum , where there is dead loss of substratum , where there is dead lock in the management, etclock in the management, etc
Voluntary winding upVoluntary winding up ( Members voluntary ( Members voluntary winding up and creditors voluntary winding winding up and creditors voluntary winding up)up)
Voluntary winding up subject to the Voluntary winding up subject to the supervision of the court.supervision of the court.

Winding up procedureWinding up procedure
A petition for winding up has to be A petition for winding up has to be filed by the concerned person to the filed by the concerned person to the prescribed authorityprescribed authority
Liquidator to be appointed to Liquidator to be appointed to safeguard the property of the safeguard the property of the companycompany
Then the court will hear the matter Then the court will hear the matter and pass necessary orders. It can and pass necessary orders. It can dismiss the petition or pass an order dismiss the petition or pass an order of winding up of winding up

Dissolution of the companyDissolution of the company When the company ceases to exist When the company ceases to exist
as a corporate entity for all practical as a corporate entity for all practical purposes it is said to have been purposes it is said to have been dissolved. dissolved.
Dissolution has to be declared by the Dissolution has to be declared by the court.court.
It will not be extinct and will be kept It will not be extinct and will be kept under suspension for 2 Years.under suspension for 2 Years.
The order has to be forwarded by the The order has to be forwarded by the liquidator to the Registrar of the liquidator to the Registrar of the Companies within 30 days from the Companies within 30 days from the date of the order of dissolution.date of the order of dissolution.