Comonent of bone
Transcript of Comonent of bone
What’s collagen?
▶ Collagen is a family of protein present in all tissues and organs, it provides the framework that gives the tissues their form and strength.
▶ It is a fibrous protein which is produced by a variety of cell types.
▶ They consist of amino acid, organic molecule made from carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
▶ Fibroblast are the cells that most commonly produce collagen.
What’re Minerals?
▶ Minerals are natural occurring means they are made by nature.
▶ They are inorganic and are not made by organism.▶ They have definite composition which means
occurrences of minerals varies within a specific limited range.
▶ They have ordered internal structure which means that the atoms in a mineral are arranged in a systematic and repeating pattern.
Minerals In Bone ▶ Bone minerals is an organic compound, it gives bones
their strength.▶ Many functions of the bone in the body are regulated by
minerals.▶ In addition to the mechanical functions of the bone it is
a reservoir for minerals.▶ The mineral component is composed of hydroxyapatite,
which is an insoluble salt of calcium and phosphorus. About 65% of adult bone mass is hydroxyapatite.
▶ The bone stores 99% of the body's calcium and 85% of the phosphorus.
▶ It is very important to keep the blood level of calcium within a narrow range. If blood calcium gets too high or too low, the muscles and nerves will not function.
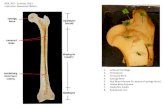
Components Of Bone▶ Bone is a tissue in which
the extracellular matrix has been hardened to accommodate a supporting function. The fundamental components of bone, like all connective tissues, are cells and matrix. The cells build up and break down bone matrix, which is composed of organic and inorganic material.
Organic Portion Of Bone
▶ Osteoid (form organic portion ), which is the unmineralized matrix composed mainly of type I collagen and other protein molecules( proteoglycans , glycoproteins)
Inorganic Portion Of Bone
▶ Hydroxyapatite (form the inorganic portion ), calcium phosphate in the form of hydroxyapatite crystals Ca10 (PO4)6(OH)2 , that gives bone its strength and rigidity.
• The minerals in your bones serve two primary functions. As components of mixed crystals, minerals transform spongy bone matrix into a rigid structure
• Your bones also function as a mineral storage depot, releasing dissolved calcium, phosphorus and magnesium into your bloodstream if needed.
• Although the quantity of magnesium in your bones is significantly less than that of calcium and phosphorus, magnesium remains an important contributor to bone strength.
• fluoride supports your bone strength by forming crystals in open spaces between the more numerous calcium phosphate crystals.
Function Of Minerals In Bone
Location Of Different Types Of Cartilage
There are over 11 types of collagen characterized by having 19 unique chains. They are divided into three general classes:∙ A molecule containing a length greater than 30
nm in uninterrupted helical chain.∙ 301 nm molecules in which the helical chain is
interrupted.∙ Relatively short molecules in which the helical
region may be continuous and uninterrupted.
Class 1 (300 nm triple helix)Type I – Skin, bone, ligamentType II – Cartilage, disc, eyeType III – Skin, blood vessels, ligamentType V – With type IType XI – With type I
Class 2 (basement membranes)Type IV – Basal lamina
Class 3 (short-chain<300 nm molecules)
Type IX – Cartilage (with type II)Type X – Hypertrophic cartilage
All things composed of elements:-
Phosphate- phosphorus containing molecule. 99% of body store”
Mostly collagen and other molecules. Contains over 99% of body calcium.
Roughly 4% of body potassium. 35% of total body sodium.50% of body magnesium.
Properties of collagen ▶ They are readily recognized
in tissues
▶ They are generally white
▶ Possess high tensile strength
▶ Low extensibility
▶ They tend to swell in concentrated solution
▶ They contract on heating
▶ It is in soluble in the body fluid
1- Most minerals have a distinctive color that can be used for identification.2-Hardness is a measure of the mineral’s resistance to scratching3-Minerals tend to break along lines or smooth surfaces when hit sharply. Different minerals break in different ways showing different types of cleavage.4-Mineral crystals occur in various shapes and sizes. The particular shape is determined by the arrangement of the atoms, molecules or ions that make up the crystal and how they are joined5-Diaphaneity is a mineral’s degree of transparency or ability to allow light to pass through it. The degree of transparency may also depend on the thickness of the
Properties of Minerals