Color Theory - part 1
-
Upload
malomatia-qsc -
Category
Education
-
view
152 -
download
3
Transcript of Color Theory - part 1


Color Theory: Overview• Color is one of the most expressive
elements because• its quality affects our emotions directly
and immediately.• In representational art, color serves to
identify objects• and to create the effect of illusionistic
space

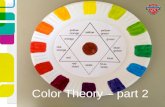
The Color WheelThe Color Wheel•The color wheel shows relationships between the colors.
•The color wheel is divided into three categories: primary, secondary, and tertiary.
•Artists often use the color wheel to help understand how colors relate to one another.

The Color WheelThe Color Wheel
Primary, Secondary, & Tertiary Colors
Warm ColorsCool ColorsNeutralsColor SchemesMixing ColorsHistory and BackgroundEmotional Response to
colourPhysiologiacal
principals of colours
Let’s learn about Color!

It's easy to mix paints to make new colors. You can use the primary colors (red, blue, and yellow) plus black and white to get all of the colors of the rainbow!
COLOR MIXING Primary + Secondary

COLOR MIXING Primary + Secondary
•When you mix the Primary Colors together, you get the Secondary Colors.•The three primary colors are red, yellow and blue.•These colors are considered to be foundation colors because they are used to create all other colors.
What colors do these make?Red + Yellow =
Red + Blue =
Blue + Yellow =
Orange
Green
Purple

COLOR MIXING Primary + Secondary
• By combining two of the primary colors, three secondary colors are formed. They are orange, green and violet.
• The six tertiary colors are made by combining a primary and an adjacent secondary color. These colors are red-orange, red-violet, yellow-green, yellow-orange, blue-green and blue-violet.

COLOR MIXING Tints and Shades
Making Tints and Shades•A shade of color is made by mixing that color with black. •A tint of color is made by mixing that color with white.

Graphic Designer – Qualification
A bachelor’s degree in graphic design is usually required for most entry-level and advanced graphic design positions.
Veda conduct a Diploma Course “Diploma in Graphics Designing & Creative writing”.
Course Duration : 1 Year
https://www.veda-edu.com

Warm Colors• The warm colors are red, orange,
yellow, and anything in between.• They are called warm because they
remind you of the sun or fire. • Warm colors seem to come out at
you in space.
The Fighting Temeraire by William TurnerIn The Fighting Temeraire by William Turner, the warm colors of the sunset give a feeling of brightness and heat. Look at the red spreading from the setting sun and the deep golden glow on the water. If you're feeling cold, looking at colors like these can actually make you feel warmer!

Cool Colors
Artist: Pablo Picasso
Year: 1939
Title: Femme Allongée Lisant
•The Cool colors are blue, green,
purple and anything in between.
•They are called cool because they
remind you of the earth or a cool creek.
•Cool colors seem to recede from you in space.

Neutrals
• Neutrals don't usually show up on the color wheel. Neutrals include black, white, gray, and sometimes brown and beige. They are sometimes called “earth tones.”
• There are a few different ways to make neutrals. You can blend black and white to make gray. You can create brown in two ways—by blending two complementary colors together or by blending all three primary colors together.

Color schemes
• A monochromatic scheme consists of different values (tints and shades) of a single color. An example of a monochrome color scheme could include any color mixed with white or above black. The example is a green monochromatic color scheme. • A shade of green is made
by mixing green and black.
• A tint of green is made by mixing green and white.
Monochromatic Colors

• These colors are located next to each other on the wheel, such as:• Blue, Blue-green, Green
• Red, Red-Orange, and Orange
• Analogous colors are sometimes called harmonious colors.
.
Analogous Colors

• Complementary colors are the colors that are directly across from each other on the color wheel• Blue & Orange• Red & Green• Purple & Yellow
• When used together in a design they make each other seem
brighter and more intense. (example: red and green) Mixed together makes brown.
Complementary Colors

• A split-compliment color scheme includes a main color and the two colors on each side of its complementary (opposite) color on the color wheel.
• An example of a split-compliment color scheme could be green, violet-red, and red-orange.
Split-Complement Color Scheme

• A double split-complement (also called tetradic) uses two pairs of complements, one space apart on the color wheel.
• An example is red, green, orange, and blue.
Double Split-Complement Color Scheme

Triadic Color Scheme• A triadic color scheme
uses colors at the points of an equilateral triangle (three colors spaced equally on the color wheel).
• These are sometimes called balanced colors.
• An example of a triadic color scheme could be red, blue, and yellow; green, orange, and purple, etc.

Color History & Physiological Principles of Color will be continue in the next parts.

MCE Society’s P.A. Inamdar College of Visual Effects,Design & Art
Ground floor, Hotel Management Building,Azam Campus, Camp,
Pune – 411001.Maharashtra, India.Contact No:(020) 64013441/44Email :enquiry[at]veda-edu[dot]comWeb : https://www.veda-edu.com
For any question or admission query please contact
Disclaimer: Images used in this presentation is purely for the reference purpose. We do not own any copyright onImages other then Veda college. Source of images : www.teachkidsart.net, www.dreamhomedecorating.com, www.learning4kids.net, www.edu230fall2014.wikispaces.com, www.designschool.canva.com, www.atpm.com, www.ceenphotography.com, www.wikiart.org, www.pablo-ruiz-picasso.net, www.blog.mitchalbala.com, www.incredibleart.org, www.golbaharfun.com, www.allemstudio.blogspot.in, www.katiestarr.wordpress.com, www.123rf.com, www.incolororder.com, www.jsgtlr.com, www.diknows.com, www.doubledare.typepad.com, www.colorscence.blogspot.in, www.en.wikipedia.org, www.prismfilmworks.com/PRISMABOUT.html

THANK YOU