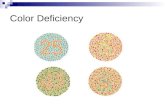
Color is the light reflected from a surface.
description
Transcript of Color is the light reflected from a surface.

• Color is the light reflected from a surface.
• Visible light is made up of the wavelengths of light between infrared and ultraviolet radiation (between 400 and 700 nanometers).
What is Color?

Additive Model RGB, Light
Color Models
Subtractitive Model CMYK, Pigment

Sergei Mikhailovich Prokudin-Gorskii. Dmitrievskii Church, 1911.
Additive Color

HueThe ‘color’ of the color. Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, Violet
ValueLightness (tint) or darkness (shade) of a color.
Saturation (Chroma)Intensity of the hue in the color. Desaturated colors tend to look gray.
Describing Color

Color Contrast
Contrast Of Hue
Contrast Of Value
Contrast Of Saturation
Low Contrast High Contrast

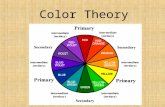
A color circle, based on red, yellow and blue, is traditional in the field of art. Sir Isaac Newton developed the first circular diagram of colors in 1666.
Newton’s Color Model
Graphics taken from www.colormatters.com

Primary Colors
Primary colors are the most basic colors; they cannot be broken down into component colors. The primary colors are different depending on which color model you are using. The primary colors in the Newtonian color model are red, yellow, and blue.
Graphics taken from www.colormatters.com

These are the colors formed by mixing the primary colors.
Secondary Colors
Graphics taken from www.colormatters.com

These are the colors formed by mixing one primary and one secondary color.
Tertiary Colors
Graphics taken from www.colormatters.com

Color Relationships
Analogous Colors
located close together on a color wheel.
Complementary Colors
Located opposite each other on a color wheel
Primary Colors
Essential colors, cannot be broken down into component colors
Secondary Colors
Mixture of two primary colors
Monochromatic Colors
Shades and tints of the same color
Newtonian (Artist’s) Color Wheel
Shade and Tint
Add black or white
Intensity
Amount of saturation) Graphics taken from www.worqx.com/color

Color Temperature
COOL
WARM
Temperature can be measured absolutely, or relatively.
For example, yellow-green is warmer than cyan-green, but both are cool colors.
An approximate separation of absolute color temperature is denoted below:
Nearly any color could appear as either warm or cold depending on the surrounding colors, especially those near the dividing line.

Red appears more brilliant against a black background and somewhat duller against the white background. In contrast with orange, the red appears lifeless; in contrast with blue-green, it exhibits brilliance. Notice that the red square appears larger on black than on other background colors.
Color Context
Graphics taken from www.colormatters.com