COCONNSSEERVATRVATIIOONN P PLALANN · Ganga Action Plan Phase – I Expenditure: Rs. 452 crores 1....
Transcript of COCONNSSEERVATRVATIIOONN P PLALANN · Ganga Action Plan Phase – I Expenditure: Rs. 452 crores 1....

NATIONAL RIVER NATIONAL RIVER CONSERVATION PLAN CONSERVATION PLAN
Ministry of Environment & Forests March 15, 2010

• •45,000 km of riverine length 45,000 km of riverine length
• •12 major river basins, 46 12 major river basins, 46 medium river basins, 14 minor medium river basins, 14 minor and desert river basins and desert river basins
• •Ganga Basin: largest, lies in Ganga Basin: largest, lies in 11 States 11 States
• •Lifeline of the people Lifeline of the people
• •Closely linked with culture Closely linked with culture and tradition and tradition
Rivers in India Rivers in India


Main Water Quality Threats Main Water Quality Threats
• • Water Scarcity Water Scarcity § § Distribution of rainfall Distribution of rainfall § § Over Over exploitation of water resources exploitation of water resources
• • Pathogenic Pollution Pathogenic Pollution
• • Oxygen depletion Oxygen depletion
• • Salinity Salinity
• • Toxicity Toxicity

Major Cause for Water Quality Degradation Major Cause for Water Quality Degradation
Ø Ø Point Sources of Pollution Point Sources of Pollution l l Domestic Wastewater Domestic Wastewater
l l Industrial Wastewater Industrial Wastewater
Ø Ø Non Non Point Sources of Pollution Point Sources of Pollution l l Rural and Slum Population, open defecation, garbage etc Rural and Slum Population, open defecation, garbage etc
l l Agricultural Run Agricultural Run off off
l l Half Half burnt bodies burnt bodies
l l Storm water Storm water
l l Cattle wallowing Cattle wallowing
l l Deposition of Air pollutants Deposition of Air pollutants

Main Sources of Pollution Main Sources of Pollution
DISPOSAL OF DEAD BODIES & ANIMAL
CARCASSES
OPEN DEFECATION
& CATTLE
WALLOWING
RUNOFF FROM SOLID &
MEDICAL WASTES &
AGRICULTRAL FIELDS
NON NON POINT POINT
SOURCES SOURCES
30%
MUNICIPAL SEWAGE MUNICIPAL SEWAGE
INDUSTRIAL INDUSTRIAL POLLUTION POLLUTION
70%
POINT SOURCES POINT SOURCES

Magnitude of the Problem Magnitude of the Problem Ø Ø Around 33,000 mld domestic wastewater Around 33,000 mld domestic wastewater
generated from class I & II towns generated from class I & II towns
Ø Ø Generation of sewage increasing rapidly with Generation of sewage increasing rapidly with growth in urban population growth in urban population
Ø Ø Sewage treatment capacity of only 7000 mld Sewage treatment capacity of only 7000 mld exists, of which 4000 mld created under NRCP exists, of which 4000 mld created under NRCP
Ø Ø Present sanctioned schemes of NRCP would Present sanctioned schemes of NRCP would add 2000 mld leaving a very large gap add 2000 mld leaving a very large gap

15438
10852
2033
33000
6600 5200
0
5000
10000
15000
20000
25000
30000
35000
Wastewater gen (mld) BOD Generation (t/d) BOD Discharge (t/d)
Comparison of pollution load generation from domestic and industrial sources
Industrial Domestic

S. No
Level of Pollution
Pollution Criteria
Riverine length (Km.)
Riverine length (percentage)
1. Severely polluted
BOD more than 6 mg/l
6086 14
2. Moderately polluted
BOD 3-6 mg/l
8691 19
3. Relatively clean
BOD less than 3 mg/l
30242 67
Water Quality Status of Rivers Water Quality Status of Rivers Analysis of 10 years data with respect to BOD values as indicator of organic pollution

• • Minimum ecological flows important for Minimum ecological flows important for biodiversity, aquatic life, and biodiversity, aquatic life, and water quality water quality
• • Competing demands for irrigation, drinking Competing demands for irrigation, drinking water, industries and power water, industries and power
• • Large scale abstraction for Large scale abstraction for
§ § hydroelectric projects in upper reaches hydroelectric projects in upper reaches
§ § canals in central plains for irrigation canals in central plains for irrigation
Diminishing flows Diminishing flows

v v Pollution abatement works in major rivers in the country Pollution abatement works in major rivers in the country commenced with the launching of Ganga Action Plan commenced with the launching of Ganga Action Plan Phase Phase I in 1985 I in 1985
v v GAP GAP I extended as GAP I extended as GAP II in II in 1993 to cover shortfall and 1993 to cover shortfall and Gomti, Yamuna, Mahananda Gomti, Yamuna, Mahananda and Damodar rivers and Damodar rivers
v v Programme broad based in Programme broad based in 1995 to include other major 1995 to include other major rivers and renamed NRCP rivers and renamed NRCP
National River Conservation Plan National River Conservation Plan

• Ganga Project Directorate (GPD) set up in MoEF in 1985 for coordinating implementation of Ganga Action Plan
• NRCD evolved out of Ganga Project Directorate in 1996 as more rivers taken up for conservation
• NRCD entrusted with implementation of NRCP & NLCP
• Organizational Structure of NRCD – headed by Project Director, and consists mostly of technical officers
National River Conservation Directorate National River Conservation Directorate

River Action Plans River Action Plans Objectives: Objectives: Reduction of pollution load Reduction of pollution load into river through schemes of: into river through schemes of: • • interception & diversion of sewage interception & diversion of sewage
• • sewage treatment sewage treatment
• • crematoria (electric & improved wood) crematoria (electric & improved wood)
• • low cost sanitation low cost sanitation
• • river front development river front development
• • afforestation afforestation
• • public participation public participation

v Initially 100% funding by Centre
v From 1993, equal sharing of funds between Centre and States
v 100% by the Centre with effect from 1.4.1997
v projects approved after March 2001 are being funded on 70:30 cost sharing basis
v Operation and maintenance (O&M) of assets created is the responsibility of the State Government/ULB
v v Initially 100% funding by Centre Initially 100% funding by Centre
v v From 1993, equal sharing of funds between From 1993, equal sharing of funds between Centre and States Centre and States
v v 100% by the Centre with effect from 1.4.1997 100% by the Centre with effect from 1.4.1997
v v projects approved after March 2001 are being projects approved after March 2001 are being funded on 70:30 cost sharing basis funded on 70:30 cost sharing basis
v v Operation and maintenance (O&M) of assets Operation and maintenance (O&M) of assets created is the responsibility of the State created is the responsibility of the State Government/ULB Government/ULB
Funding Pattern Funding Pattern Funding Pattern

• • Town centric, focussed on Town centric, focussed on interception, interception, diversion and treatment schemes diversion and treatment schemes
• • Investment of Rs 900 crore; treatment Investment of Rs 900 crore; treatment capacity of around 1000 mld created in 73 capacity of around 1000 mld created in 73 towns towns
• • Despite industrial & urban growth, BOD Despite industrial & urban growth, BOD and DO values at most locations improved and DO values at most locations improved
Ganga Action Plan Ganga Action Plan

• • 25 towns of U.P., Bihar, 25 towns of U.P., Bihar, West Bengal covered West Bengal covered
• • Amount spent Amount spent Rs. 452 Rs. 452 crore. crore.
• • 869 million litres per day 869 million litres per day (mld) sewage treatment (mld) sewage treatment capacity created capacity created
STP at Kolkata
Ganga Action Plan Phase Ganga Action Plan Phase I I

• • Sanctioned cost Sanctioned cost Rs. 2367.11 crore Rs. 2367.11 crore
• • Schemes sanctioned Schemes sanctioned 701 701
• • Schemes completed Schemes completed 544 544
• • Amount spent Amount spent Rs.1612.38 crore Rs.1612.38 crore
Ganga Action Plan Phase Ganga Action Plan Phase II II

Physical Progress Physical Progress S. No. Item Target Achievement
Ganga Action Plan Phase – I Expenditure: Rs. 452 crores 1. No of schemes 261 260 2. Treatment capacity 882 mld (35 STPs) 869 mld (34 STPs) 3. No. of Interception &
Diversion schemes 88 88
4. No. of Low Cost Sanitation schemes
43 43
5. No. of Crematoria schemes 28 28 6. No. of River Front
Development schemes 35 35
Ganga Action Plan Phase – II Expenditure: Rs. 437.53 crores 1. No of schemes 322 218 2. Treatment capacity 281 mld (38STPs) 156 mld (24STPs) 3. No. of Interception &
Diversion schemes 120 67
4. No. of Low Cost Sanitation schemes
26 24
5. No. of Crematoria schemes 19 9 6. No. of River Front
Development schemes 49 35

• • States covered States covered 20 20
• • Towns covered Towns covered 167 167
• • Rivers covered Rivers covered 38 38
• • Sanctioned cost Sanctioned cost Rs. 4691.55 crore Rs. 4691.55 crore of schemes of schemes
• • Expenditure Expenditure Rs. 3521.85 crore Rs. 3521.85 crore
Present Coverage of NRCP Present Coverage of NRCP

Cumulative Status of NRCP Cumulative Status of NRCP (Physical) (Physical)
• • Schemes sanctioned Schemes sanctioned 1085 nos. 1085 nos.
• • Schemes completed Schemes completed 802 nos. 802 nos.
• • STP capacity sanctioned STP capacity sanctioned 4246 mld 4246 mld
• • STP capacity created STP capacity created 3095 mld* 3095 mld*
* Adding 869 mld capacity created under GAP * Adding 869 mld capacity created under GAP I, an I, an aggregate treatment capacity of 3964 mld has aggregate treatment capacity of 3964 mld has been created so far been created so far

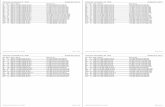
S.No. Name of River No. of towns covered
Sanctioned Cost (Crore)
Expenditure (Crore)
STP Capacity Created (mld)
1 Adyar 1 404.25 380.74 264.00
2 Cooum
3 Beehar 1 19.44 1.69
4 Betwa 3 8.23 5.63 15.20
5 Bhadra 1 3.77 4.14 5.83
6 Brahmini 4 84.70 43.19
7 Cauvery 13 269.10 261.57 151.93
8 Chambal 3 154.06 3.58 9.00
9 Diphu and Dhansiri 1 31.74
10 Damodar 12 4.40 4.29 13.17
11 Ganga 59 635.66 404.40 155.95
12 Godavari 7 118.98 112.61 185.46
13 Gomti 3 318.79 276.57 47.00
14 Khan 1 40.19 39.56 90.00
15 Krishna 2 28.74 21.95 28.00
16 Kshipra 1 18.05 17.33 55.46
17 Mahanadi 1 8.04 8.04 33.00
18 Mandakini 1 6.20
19 Mandovi 1 14.10 10.92 12.50
National River Conservation Plan National River Conservation Plan

S.No. Name of River No. of towns covered
Sanctioned Cost (Crore)
Expenditure (Crore)
STP Capacity Created (mld)
20 Mahananda 1 54.88 18.03
21 Musi 1 335.66 314.85 542.00
22 Narmada 2 14.33 3.31
23 Pamba 1 18.44 1.47
24 Panchganga 1 74.29
25 Pennar 1 46.27 35.94
26 Ranichi 3 37.39 14.67
27 Sabarmati 1 101.96 95.08 232.00
28 Satluj 6 215.68 293.06 413.20
29 Subarnrekha 3 3.76 0.98
30 Tapti 1 4.81 3.88 6.00
31 Tapi 1 2.44
32 Tunga 1 3.70 2.60
33 Tungabhadra 2 7.16 6.22 28.29
34 Tamrabarani 1 54.93 54.27 24.20
35 Vennar 1 62.75 63.31 28.05
36 Vaigai 1 130.24 107.95
37 Wainganga 3 1.01 0.94 1.95
38 Yamuna 21 1353.37 909.08 753.25
National River Conservation Plan National River Conservation Plan



Experience with NRCP: Mixed Success Experience with NRCP: Mixed Success
• • Visible improvement lacking, coliform levels Visible improvement lacking, coliform levels unacceptably high unacceptably high
• • In critically polluted stretches, BOD values In critically polluted stretches, BOD values do not meet bathing water quality standards do not meet bathing water quality standards
• • Counterfactual; but for NRCP, problem Counterfactual; but for NRCP, problem would have gotten worse; further would have gotten worse; further deterioration arrested deterioration arrested
• • Step in right direction, inadequate Step in right direction, inadequate investment, resources thinly spread investment, resources thinly spread

Shortcomings Shortcomings
• • Town centric, focussed on Town centric, focussed on interception, interception, diversion and treatment schemes diversion and treatment schemes
• • Implementation slow Implementation slow
• • sub sub optimal utilization of assets optimal utilization of assets
• • Weak enforcement by State Pollution Control Weak enforcement by State Pollution Control Boards Boards
• • Lack of civil society involvement Lack of civil society involvement

• • Huge treatment capacity deficit Huge treatment capacity deficit
• • Focused attention required on critically Focused attention required on critically polluted stretches e.g. Kannauj to Varanasi polluted stretches e.g. Kannauj to Varanasi on Ganga on Ganga
• • Tackling non Tackling non point sources point sources (agricultural (agricultural runoff, solid wastes, cattle runoff, solid wastes, cattle wallowing, idol wallowing, idol immersions, etc.) immersions, etc.) and fecal coliform and fecal coliform
• • Restoring natural ecosystem of the rivers Restoring natural ecosystem of the rivers
Challenges Challenges

• • Technical, managerial & financial constraints Technical, managerial & financial constraints of ULBs & implementing organizations of ULBs & implementing organizations
• • Strengthening capacity of SPCBs to address Strengthening capacity of SPCBs to address weak compliance & enforcement weak compliance & enforcement
• • Community involvement for improved Community involvement for improved sanitation sanitation
• • Augment flows through water conservation, Augment flows through water conservation, reuse of treated wastewater, storage projects reuse of treated wastewater, storage projects
Challenges Challenges

Challenges Challenges
• • Industrial hotspots along the rivers Industrial hotspots along the rivers
• • Concentration of polluting industries : Concentration of polluting industries : Sugar, distilleries, paper, tanneries, Sugar, distilleries, paper, tanneries, chemical, etc chemical, etc
• • 30% by volume, toxic and non 30% by volume, toxic and non biodegradable biodegradable
• • Major problem with small scale Major problem with small scale industries; lack of common effluent industries; lack of common effluent treatment facilities treatment facilities

New Initiative: NGRBA New Initiative: NGRBA
• • Constituted on 20.02.2009. Joint Centre Constituted on 20.02.2009. Joint Centre State structure. Empowered under State structure. Empowered under EPA. EPA. Chaired by PM. Includes CMs. Strong Chaired by PM. Includes CMs. Strong presence of experts and civil society presence of experts and civil society
• • Planning, financing, monitoring & Planning, financing, monitoring & coordinating body. implementation through coordinating body. implementation through States and SPVs States and SPVs

Functions of NGRBA Functions of NGRBA • • Development of river basin management plan Development of river basin management plan
• • Planning, financing and execution of Planning, financing and execution of programme for abatement of pollution in the programme for abatement of pollution in the river Ganga river Ganga
• • Maintenance of minimum ecological flows Maintenance of minimum ecological flows
• • Creation of special purpose vehicles, as Creation of special purpose vehicles, as appropriate appropriate
• • Promotion of water conservation practices Promotion of water conservation practices

How new approach is different How new approach is different
• • Empowered Authority Empowered Authority
• • Shift from town centric to river basin approach Shift from town centric to river basin approach
• • Integrated approach, no standalone investment Integrated approach, no standalone investment
• • Sewerage infrastructure, catchment area Sewerage infrastructure, catchment area treatment, tackling industrial effluents, river treatment, tackling industrial effluents, river front development front development
• • Dovetailing with JNNURM & UIDSSMT schemes Dovetailing with JNNURM & UIDSSMT schemes
• • Emphasis on minimum ecological flows Emphasis on minimum ecological flows

• • Apex Council chaired by PM Apex Council chaired by PM
• • Standing Committee under Finance Standing Committee under Finance Minister Minister
• • Empowered Steering Committee; fast track Empowered Steering Committee; fast track project approval mechanism project approval mechanism
• • State River Conservation Authorities State River Conservation Authorities
• • Implementation by States, ULBs and SPVs Implementation by States, ULBs and SPVs
Institutional Redesign Institutional Redesign

• • Development of river basin management plan Development of river basin management plan
• • Mission Clean Ganga Mission Clean Ganga
§ § No untreated sewage or industrial effluents to flow No untreated sewage or industrial effluents to flow into Ganga by 2020; into Ganga by 2020;
§ § Estimated investment of Rs 15,000 crore over next Estimated investment of Rs 15,000 crore over next 10 years required 10 years required
• • Identifying initial portfolio of projects Identifying initial portfolio of projects
• • State Governments preparing DPRs State Governments preparing DPRs
Action Program Action Program

Finance Finance
• • Centre and States committed to provide Centre and States committed to provide required resources for Mission Clean Ganga required resources for Mission Clean Ganga
• • Rs 100 crore provided in the FY 2009 Rs 100 crore provided in the FY 2009 10, and 10, and Rs 500 crore for the FY 2010 Rs 500 crore for the FY 2010 11 11
• • 13 13 th th Finance Commission approached to help Finance Commission approached to help meet O&M needs meet O&M needs
• • External finance External finance – – World Bank, JICA World Bank, JICA
• • Private capital through PPP in SPVs Private capital through PPP in SPVs

Engagement with World Bank Engagement with World Bank
World Bank has in World Bank has in principle agreed to principle agreed to
• • support NGRBA as a priority project support NGRBA as a priority project
• • mobilize initial funds for creation of a world mobilize initial funds for creation of a world class executive, knowledge base and Basin class executive, knowledge base and Basin Management Plan Management Plan
• • mobilize substantial resources for a major mobilize substantial resources for a major investment program investment program

• • Projects based on comprehensive approach Projects based on comprehensive approach
• • PPP models proposed in States for better PPP models proposed in States for better implementation implementation
• • Tripartite Memorandum of Agreement Tripartite Memorandum of Agreement
• • Project appraisal by reputed independent Project appraisal by reputed independent institutions institutions
Measures for Improving Outcomes Measures for Improving Outcomes

• • Empowered State River Conservation Empowered State River Conservation Authorities Authorities
• • Third party evaluation by independent Third party evaluation by independent institutions institutions
• • City City level citizen committees level citizen committees
• • Community mobilization Community mobilization
Measures for Improving Outcomes Measures for Improving Outcomes

• • Water Quality Monitoring by reputed Water Quality Monitoring by reputed institutions like IITs institutions like IITs
• • Online data transmission, public access to Online data transmission, public access to WQM data, additional parameters & bio WQM data, additional parameters & bio indicators to be included indicators to be included
• • Research Advisory Committee set up to Research Advisory Committee set up to encourage Innovative technologies encourage Innovative technologies
Measures for Improving Outcomes Measures for Improving Outcomes

Vision Vision
• • Gaumukh to Ganga Gaumukh to Ganga Sagar : a clean river Sagar : a clean river
• • Return of Gangetic Return of Gangetic Dolphins at Sangam Dolphins at Sangam (Gangetic Dolphins are (Gangetic Dolphins are facing extinction, only facing extinction, only few hundreds survive, few hundreds survive, apex of the food chain of apex of the food chain of Ganga ecosystem) Ganga ecosystem)

Thank You Thank You