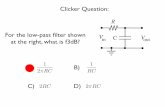
Clicker Question
description
Transcript of Clicker Question
1
Clicker Question Room Frequency BA
By Pascal’s Principle, the applied pressure is the same every in the fluid (at the same depth).
A force of 200 lbs is applied as FIN. Assume that AIN is 1 cm2 and AOUT is 20 cm2
. What’s POUT?
A) 200 lb/cm2 B) 400 lb/cm2 C) 2000 lb/cm2 D) 4000 lb/cm2
2
• CAPA assignment #13 is due on Friday at 10 pm.• This week in Section: Assignment #6• Start reading Chapter 11 on Vibrations and Waves• Prof. Nagle will have his regular office hours this
afternoon at 2-3pm (in his office).• Prof. Uzdensky’s office hours Tuesday 11am are
canceled this week
Announcements
3
Pressure as a function of depth
Pressure only depends on the depth; at a given depth the pressure is the same.
Ph =Patm + ρWateρhg
4
Forces on a Small Box of Water
h
Δy
Consider again a small imaginary cubic box at depth h
We argued last time that in static fluids, the net force on the box must be zero.
Again we conclude that the side forces all cancel and only the top and bottom forces are left.
Fnet = Ftop + Fbottom = 0Using our depth formula we can find thatFnet =−ρWateρg(h−Δy)A+ ρWateρghA−mWateρg=0
ρWatergΔyA = mWatergThe pressure difference between top and bottom is just the weight of the water in the box
5
Forces on a Small Box of Gold
h
Δy
Now suppose the cubic box is a block of gold at depth h
The fluid outside the block is the undisturbed, so the pressures are not changed. The net force however is no longer necessarily zero!!!
Again we conclude that the side forces all cancel and only the top and bottom forces are left.
Fnet = Ftop + Fbottom Using our depth formula we can find thatFnet =−ρWateρg(h−Δy)A+ ρWateρghA−m Goldg
ρWatergΔyA = mWatergThe pressure difference between top and bottom is just the weight of the water in the box
6
Buoyant Force
h
Δy
So we conclude that the net force is
The fluid exerts an upward force of mwaterg on the gold cube. This is known as the buoyant force.
Fnet =ρWateρgΔyA−m Goldg=m wateρg−m Goldg
FBuoyancy =ρFluidgΔyA=m Fluidg
You can show that this is true for any shape volume V!
For some general fluid, we can write
FBuoyancy =ρFluidgV =m Fluidg
7
Archimedes Principle
A solid body, either partially or totally submerged in a fluid, will experience an upward buoyant force equal to the weight of the displaced fluid.
FBuoyancy =ρFluidgV =m Fluidg
Let’s check with a demonstration!
8
Two identical bricks are held under water in a bucket. One of the bricks is lower in the bucket than the other. The upward buoyant force on the lower brick is…..
Fbuoy =m fluidg=ρ fluidV g
Clicker Question Room Frequency BA
The weight of displaced fluid does not depend on depth
9
A solid piece of plastic of volume V and density ρplastic would ordinarily float in water, but it is held under water by a string tied to the bottom of bucket as shown. (The density of water is ρwater.)
What is the buoyant force on the plastic?
A) Zero B) ρplastic V C) ρwater V D) ρwater V g E) ρplastic V g
Clicker Question Room Frequency BA
Fbuoy =m fluidg=ρ fluidV g
FB
10
Motion of Submerged objects
When will an object sink or float?
Object will rise: Fbuoy > Fg (mfluid > mobject)
Object will sink: Fbuoy < Fg (mfluid < mobject)
Object will be in equilibrium: Fbuoy = Fg (mfluid = mobject)
Fbuoyant
Fg
Fbuoy = mfluidg
Fg = mobjectg Δy
Fnet =m Fluidg−m Objectg
11
Motion of Submerged objects
Fbuoyant
Fg
Δy
Since Fbuoy and Fg both depend on the same volume V we can also write
Object will rise: ρfluid > ρobject
Object will sink: ρfluid < ρobject
Object will be in equilibrium: ρfluid = ρobject
Diet vs Regular Pepsi!
12
Example. A block of copper (Cu) with mass 400 g and density ρCU = 8.9 g/cm3 is suspended by a string while under water. How does the tension in the string compare with the weight of the copper block?
0 =Fnet = F∑ =FT + FB −Fg
=FT + m fluidg−m CUg
FT =g(m CU −m fluid )=g(0.4kg−(0.4 / 8.9)kg)=g(0.355kg)=0.345N
Fg =(0.4kg)g=0.392N
FTFg
=0.345N0.392N
=88% The buoyant force helps support the weight of the block.
13
A carefully-made sphere, when placed under water, remains at rest, in equilibrium as shown above. How does the magnitude of the upward buoyant force FB compare to the weight mg of the sphere?
A) FB > mg
B) FB = mg
C) FB < mg
mg
FB
Clicker Question Room Frequency BA
Net force = 0
14
A helium-filled balloon of volume V can carry a total mass M (M includes the mass of the rubber balloon but not the mass of the Helium inside). What is the correct expression for the buoyant force FB
on the balloon?
A) ρair V g B) ρhelium V g C) Mg D) (ρair– ρhelium) V g
Clicker Question Room Frequency BA
Weight of displaced fluid
15
A helium-filled balloon of volume V can carry a total mass M (M includes the mass of the rubber balloon but not the mass of the Helium inside). What is the correct expression for the net force on the balloon?
A) ρair V g -Mg B) (ρair+ ρhelium) V g - Mg C) ρhelium V g - Mg D) (ρair– ρhelium) V g - Mg
Clicker Question Room Frequency BA
Helium has weight!
16
Floating Object: Displaces a mass of water equal to its mass.
FB =mgρ fluidV displaced g =ρobjectV objectg
m ass of fluid displaced = m ass of the object oρV displaced
V object
=ρobject
ρ fluid
Floating objects
Vdispl
17
VdisplacedVobject
=ρobject
ρ fluid
What fraction of a piece of Aluminum will be submerged if it is placed in a tank of Mercury?(ρAl = 2.7 x 103 kg/m3, ρHg = 13.6 x 103 kg/m3)
A) 20%B) 40%C) 60%D) 80%
Vdisplaced =ρobject
ρ fluid
⎛⎝⎜
⎞⎠⎟V object =
2.7x103
13.6x103
⎛⎝⎜
⎞⎠⎟V object =0.2V object
The volume of the Mercury displaced is the amount of the Aluminum that will be submerged.
Clicker Question Room Frequency BA
18
Waterfall Death Trap
Every year several people drown near/underneath waterfalls!
Why?
Foamy, frothy water is much less dense than regular water!!! Hence the force of buoyancy is much less! Humans rapidly sink deep under the surface.
Also “explains” mysterious disappearance of ships in the Bermuda Triangle: Seabed releases of large quantities of gas (“avalanches” at the edge of the continental shelf) just under the ship. The ship immediately sinks below the surface.