Clicker Question #1 - Physics Coursescourses.physics.ucsd.edu/2013/Fall/physics1a/Clicker Question...
Transcript of Clicker Question #1 - Physics Coursescourses.physics.ucsd.edu/2013/Fall/physics1a/Clicker Question...
A. At time tB, both trains have the same velocity.
B. Both trains increase speed all the time.
C. Both trains have the same velocity at some time before tB.
D. Somewhere on the graph, both trains have the same
acceleration.
The graph shows
position as a function of
time for two trains
running on parallel
tracks.
Which statement is true?
Clicker Question #1
A particle with zero instantaneous acceleration must have zero instantaneous velocity
A. True
B. False
Clicker Question #2
A particle with zero instantaneous velocity must have zero
instantaneous acceleration
A. True
B. False
Clicker Question #3
A particle with zero instantaneous velocity must have zero
instantaneous acceleration
A. True
B. False
Clicker Question #3
A. True
B. False
C. None of the above
A particle with zero instantaneous velocity must have zero
instantaneous displacement
Clicker Question #4
A. Train A travels the further distance by time tB
B. Train B travels the further distance by time tB
C. Both trains travel the same distance by time tB
D. There is too little information to determine the relative
distances travelled
The graph shows velocity
as a function of time for two
trains starting at rest and
running on parallel tracks.
Which of the following is
true?
Clicker Question #5
velocity
Register clicker
• From a 10 m height you throw ball A up at 5 m/s, and you throw a ball B down at 5 m/s. When the two balls hit the ground are they:
A. Going at the same speed
B. Going at different speeds
C. Land simultaneously
D. Ball A never reaches the ground
Clicker Question #6
For a given initial velocity, at what angle would you maximize the time of flight?
A. θ = 0º
B. θ = 45º
C. θ = 60º
θ
Clicker Question #7
D. θ = 90º
For a given initial velocity, at what angle would you maximize the range?
A. θ = 0º C. θ = 60º
D. θ = 90º
θ
Clicker Question #8
B. θ = 45º
A battleship simultaneously fires two shells at enemy
ships. If the shells follow the parabolic trajectories
shown, which ship gets hit first?
A. A
B. B
C. both at the same time
D. need more information
Clicker Question #9
What is the trajectory of the monkey? CQ#11
A. Stays put B. Down, constant v C. Down, constant a D. Up, constant v
In the absence of gravity, where would we aim our
gun? CQ#12
A. Above the monkey B. At the monkey C. Below the monkey
With gravity, where do we aim the gun? CQ#13
A. Above the monkey B. At the monkey C. Below the monkey
Which object accelerates faster? CQ#14
A. The projectile B. The monkey C. They accelerate the same D. Need to know initial
conditions
A hammer-thrower builds up speed by spinning around as fast as possible before releasing hammer.
If thrower A spins 3 times as fast as thrower B, how much more centripetal acceleration does thrower A apply?
A. The same
B. 3x as much
C. 1/3 as much
spin rate
Clicker Question #15
D. 9x as much
If thrower A has a hammer that is 3 times as long as thrower B’s, and both spin at the same rate, how much more centripetal acceleration does thrower A have to apply?
A. The same C. 1/3 as much
D. 9x as much
radius
Clicker Question #16
B. 3x as much
If thrower A has a hammer that is 3 times as long as thrower B’s, and both spin at the same rate, how much faster is thrower A’s hammer moving in space (speed)?
A. The same B. 1/3 as much
D. 9x as much
Clicker Question #17
C. 3x as much
At what angle with respect to horizontal should she release the hammer to get maximal range?
A. 0º
C. 45º
B. 90º
D. It depends on the speed of rotation
Clicker Question #18
On the Moon...
A. Your weight is the same, but your mass is less.
B. Your weight is less, but your mass is the same.
C. Your weight is more, but your mass is the same.
D. Your weight is more, but your mass is less.
Clicker Question #19
Acceleration can occur in a direction perpendicular of net force
A. True
B. False
Clicker Question #20
Acceleration can occur in a direction directly opposite of net force
A. True
B. False
can’t be negative
Clicker Question #21
A bee and a train collide. What is true about this collision?
A. The bee experiences the greater magnitude of force
B. The train experiences the greater magnitude of force
C. The bee experiences the greater magnitude of acceleration
D. Both A and C are true
Clicker Question #22
Consider a car at rest. We can conclude that
the downward gravitational pull of Earth on
the car and the upward contact force of Earth
on it are equal and opposite because
1. the two forces form an interaction pair
2. the net force on the car is zero
3. neither of the above
Clicker Question #23
26
If tilt angle = 0º, what happens to the friction force Ff?
A. It remains the same.
B. It becomes zero.
C. It remains the same but is balanced by the normal force.
D. It remains the same but is balanced by a second friction force.
30º
Clicker Q. #24
27
If tilt angle = 0º, what happens to the friction force Ff?
A. It remains the same.
B. It becomes zero.
C. It remains the same but is balanced by the normal force.
D. It remains the same but is balanced by a second friction force.
30º
Clicker Q. #24
28
In the phrase “A 9,000 N automobile” to what does 9,000 N refer?
A. The mass.
B. The weight.
C. The acceleration.
D. The cost.
Clicker Q. #24b
Clicker Question #27
A. Pushing downward on her shoulders B. Pulling upward on a rope C. No difference
A father tries to slide his daughter on a sled over snow. Which is easier?
A. Parallel to the velocity
B. Antiparallel to velocity
C. Perpendicular to velocity
D. For a constant velocity, there is no friction force acting
A car drives on a level road at constant velocity; in which direction does friction act?
N
Mg
Clicker Question #29A
A. Up the hill.
B. Down the hill.
C. Perpendicular to the hill.
D. For a constant velocity, there is no friction force acting.
A car drives downhill at constant velocity; in which direction does friction act?
potential acceleration without friction
friction force
Mg
Clicker Question #29
Force of static Friction A. Always equals μsN B. Exceeds μsN C. Balances Fapplied when Fapplied < μsN D. Acts normal to the surface
Clicker Question #30
Clicker Question #31
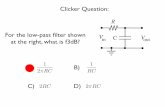
What are the dimensions of the spring constant k?
A. M L-1
B. M T-2
C. L T-2
D. M L T2
[k] = [F]/[x]
= M L T-2 / L
= M T-2
k
A mass is supported by a spring with spring constant k. It’s equilibrium displacement is 50 cm. If I double the mass, the new equilibrium displacement is:
A. 50 cm B. 100 cm C. 25 cm D.200 cm
M
Clicker Question #32
35
k
A mass is supported by one spring with spring constant k has an equilibrium displacement is 50 cm. If I add another spring with the same spring constant k, the new equilibrium displacement is:
A. 50 cm B. 100 cm C. 25 cm D.200 cm
Mg
kΔx
@ Equilibrium ΣF = 0 => kΔx + kΔx – Mg = 0 => Δx = Mg/2k
kΔx M
Clicker Question #33
How does the gravitational force between two objects change if one object’s mass triples?
A. the force increases by a factor of three B. the force remains the same C. the force decreases by a factor of three D. the force decreases by a factor of nine
Clicker Question #34
How does the gravitational force between two objects change if the distance between them triples?
A. the force increases by a factor of three B. the force remains the same C. the force decreases by a factor of three D. the force decreases by a factor of nine
Clicker Question #35
If you have two planets, one three times as massive as the other, how much larger is the force on that planet as compared to the lower mass one?
A. the force is bigger by a factor of three B. the force is the same C. the force is smaller by a factor of three D. the force is smaller by a factor of nine
Newton’s 3rd law – equal and
opposite forces
Clicker Question #36
CQ #40: Last time we talked about the mass-spring system. Which forces are
conservative?
A. Force of the spring B. Force of gravity C. Both D. Neither
M
Mg
F = kΔx
CQ #41: What is a isolated system?
A collection of objects that is sufficiently isolated from the rest of the Universe so that no energy can be transferred
Fixed in place
No friction
A. Isolated B. Not Isolated
CQ #42: Sam and Cathy are standing on a roof 100 m high. Sam throws a ball up with an initial speed of 10 m/s. Cathy throws a ball down with an initial speed of 10 m/s. Which ball will have a
greater speed when it hits the ground?
A. The ball that Sam threw B. The ball that Cathy threw C. Both have the same final speed D. Neither one hits the ground
Two hikers climb the same hill. The first hiker
takes a steep, direct route and gets to the top in
about 1 hour. The other takes a more gentle
sloping route that is 4 times longer, but can walk 2
times faster and makes it to the top in 2 hours. The
power expended by the first hiker is
A. four times as large
B. twice as large
C. the same
D. half as large
as the power expended by the second hiker.
Clicker Question #43
A sports car accelerates from 0 mph to 30 mph in
1.5 s. How long does it take for it to accelerate from
0 mph to 60 mph, assuming the power of the engine
to be independent of velocity and ignoring friction?
A. 2 s
B. 3 s
C. 4.5 s
D. 6 s
Clicker Question #44
A stone is launched upward into the air. In addition to the force of gravity, the stone is subject to a frictional force due to air resistance. The time the stone takes to reach the top of its flight path is A. larger than B. equal to C. smaller than the time it takes to return from the top to its original position.
Clicker Question #45
Which of the following forces never does work?
A. Gravity B. Friction C. Tension D. Normal force E. Spring force
Clicker Question #46
A bee and a train collide. Which experiences the greater
magnitude of force?
A. The bee
B. The train
C. They experience the same force
Clicker Question #47
A bee and a train collide. Which experiences the greater
magnitude of acceleration?
A. The bee
B. The train
C. They experience the same magnitude of acceleration
Clicker Question #48
Consider two carts, of masses m and 2m, at rest on
an air track. If you push both carts for the same
lengths of time with equal force, the momentum of
the less massive cart is
A. four times
B. twice
C. equal to
D. one-half
the momentum of the more massive cart.
Clicker Question #50
Consider two carts, of masses m and 2m, at rest on
an air track. If you push both carts for the same
lengths of time with equal force, the kinetic energy
of the less massive cart is
A. larger than
B. equal to
C. less than
the kinetic energy of the more massive cart.
Clicker Question #51
A person attempts to knock down a large wooden bowling
pin by throwing a ball at it. The person has two balls of equal
size and mass, one made of rubber and the other of putty.
The rubber ball bounces back, while the ball of putty sticks to
the pin. Which ball is most likely to topple the bowling pin?
A. the rubber ball
B. the ball of putty
C. makes no difference
D. need more information
Clicker Question #52
An object of mass 1 and speed 1 comes in from the left, and starts a series of elastic collisions (see above). Which of the following best represents the motion of the objects after all collisions have occurred?
Check: total p = 1 total K = 0.5
violates p-conservation
violates E-conservation
violates p-conservation
Clicker Question #53
Clicker Question #55
None of these
A.
B.
C.
D.
A wheel initially at rest is spun with a constant angular acceleration of 3 radians/s2. In how many seconds does it complete one full revolution?
Which equation would you use?
Clicker Question #56
None of these
A.
B.
C.
D.
Which equation would you use?
What angular acceleration is required to get a wheel spinning at 3 revolutions/minute to come to rest in 20 minutes?
Clicker Question #57
None of these
A.
B.
C.
D.
Which equation would you use?
What angular acceleration is required to get a wheel spinning at 3 revolutions/minute to come to rest in 10 revolutions?
Two ladybugs sit on a spinning merry-go-round, one
at the outer edge and one halfway out. The merry-
go-round spins at a constant rate. The inner
ladybug’s tangential speed is:
A. the same as the outer ladybug’s
B. half the outer ladybug’s
C. twice the outer ladybug’s
D. impossible to determine
CQ #58
Two ladybugs sit on a spinning merry-go-round, one
at the outer edge and one halfway out. The merry-
go-round spins at a constant rate. The inner
ladybug’s angular speed is:
A. half the outer ladybug’s.
B. the same as the outer ladybug’s.
C. twice the outer ladybug’s.
D. impossible to determine.
CQ #59
Point in the direction of the angular velocity of the minute hand of a clock
Into the wall
Clicker Question #60
Point in the direction of the angular velocity of the minute hand of a clock
Point in the direction of the angular velocity of the hour hand of a clock
Into the wall
Clicker Question #60
Point in the direction of the angular velocity of the minute hand of a clock
Point in the direction of the angular velocity of the hour hand of a clock
Which vector has the greater magnitude: of the hour hand or of the minute hand?
A. hour hand B. minute hand C. they are the same
Clicker Question #60
Point in the direction of the angular velocity of the minute hand of a clock
Point in the direction of the angular velocity of the hour hand of a clock
Which vector has the greater magnitude: of the hour hand or of the minute hand?
ωminute = 2π/(1 min) ωhour = 2π/(60 min) < ωminute
Clicker Question #60
You are using a wrench and trying to loosen a rusty nut. Which of the arrangements shown is most effective in loosening the nut?
Clicker Question #61
D C
B A
Clicker Question #63
You are using a wrench and trying to loosen a rusty nut. What is the direction of the resulting angular acceleration?
A. right B. left C. into screen D. out of screen
A disk and a hoop, both with the same mass and outer radius, have a force of 10 N applied to their sides for a total of 10 s. Which ends up spinning the fastest?
A. the hoop
B. the disk
C. they end up with the same rotation speed
CQ#68