CLASSIFICATION Part 1 The 3 Domains for Booklet. Next > 3 Domains – Bacteria, Archaea, Eukaryota...
-
Upload
ambrose-evans -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
0
Transcript of CLASSIFICATION Part 1 The 3 Domains for Booklet. Next > 3 Domains – Bacteria, Archaea, Eukaryota...

CLASSIFICATIONPart 1
The 3 Domains
for Booklet

Next >
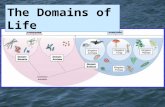
3 Domains – Bacteria, Archaea, EukaryotaCurrently all life is divided into three large groups called domains:
Bacteria
Archaea
Eukaryota

Next >
3 Domains –Bacteria and Archaea and Eukaryota
With the exception of plants, animals, fungi and slime molds within the domain Eukaryota, most life forms are microscopic.
These are called microorganisms.

Next >
Domains –Archaea
Archaebacteria has been on Earth for at least 3 billion years.
Are known as “ancient” bacteria.
Live in places where most living things cannot live.

Next >
Domain –Archaea
Can live in areas of extreme heat or extreme cold.
Some are autotrophic and some are heterotrophic
Composed of plasma and cell walls.
Reproduce asexually.
Ex. Thermophiles (thermal vents), halophiles (salty-Red Sea), acidophiles (extreme acidic conditions such as methanogens in animal guts)

Next >
Domain–Bacteria“True” Bacteria
Are tiny organisms that live in almost every place on and near Earth’s surface.
Even live on and inside the human body!
Complex, prokaryotic organisms
Single celled autotrophs.
Reproduce asexually and sometimes
sexually (conjugation)Blue green algae
Streptococcus

Next >
Domain– Eukarya
Contains all other kingdoms since they are all Eukaryotes.
Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia

CLASSIFICATIONPart 2
The 6 Kingdoms
for Booklet

Next >
The Six Kingdoms

Next >
The Six Kingdoms
The Cavalier-Smith six kingdom classification system divides all known organism types into the following kingdoms:
1) Plantae (plants)
2) Animalia (animals)
3) Fungi (mushrooms and molds)

Next >
The Six Kingdoms
6) Protista (microscopic organisms that are not bacteria, plants or animals) “catch all” for those that don’t fit anywhere else
4) Eubacteria (true bacteria)
5) Archaebacteria (ancient bacteria that live in extremely hostile conditions)

Next >
Kingdom Plantae
The plant kingdom consists of organisms that are:
Some plants reproduce sexually, others reproduce asexually. Primarily sexual
multicellular eukaryotic autotrophic
Members of the plant kingdom have strong cell walls that provide support.

Next >
Kingdom Animalia
The animal kingdom consists of organisms that are:
Most animals reproduce sexually, but some, such as starfish, can reproduce asexually (regeneration). Primarily sexual.
multicellular eukaryotic heterotrophic

Next >
Kingdom Fungi
The fungi kingdom consists of organisms that are:
multicellular or unicellular
eukaryotic
heterotrophic

Next >
Kingdom Fungi
Members of the fungi kingdom are similar to plants in that they have cell walls.
Fungi reproduce by producing spores.
Some reproduce sexually, others reproduce asexually…so…BOTH
However they do not contain chlorophyll which is why they cannot make their own food.

Next >
Kingdom EubacteriaThe eubacteria kingdom consists of organisms that are:
Bacteria can be grouped depending on the thickness of a substance in their cell walls. It is shown using a gram stain.
unicellular
prokaryotic
autotrophic or heterotrophic
able to reproduce asexually by binary fission or sexually by conjugation
Gram positive bacteria – thick layer of substance
Gram negative bacteria – thin layer of substance

Next >
Kingdom Archaebacteria
The archaebacteria kingdom consists of organisms that are:
able to reproduce asexually
unicellular prokaryotic autotrophic or
heterotrophic

Next >
Kingdom Archaebacteria
Members of this kingdom are found in extreme conditions where other organisms could not survive.
For example in extreme temperatures or regions of high salt levels.
Thermophiles – survive in areas of extreme temperature.Halophiles – survive in areas with high salt levels.
Methanogens – produce methane and live in the guts of animals.

Next >
Kingdom Protista
The protista kingdom consists of organisms that are: mostly unicellular
but some multicellular
Eukaryotic-”catch all” kingdom
mostly heterotrophic but some are autotrophic
Heterotrophic
Autotrophic
Protozoa
Protista
Neat fact: Algae produce most of the oxygen on earth

Next >
Kingdom Protista
This kingdom contains microscopic organisms that are not plants, animals or bacteria.
Some protists reproduce sexually, others reproduce asexually.
Heterotrophic
Autotrophic
Protozoa
Protista

CLASSIFICATIONPart 3
The 7 Levels of Classification for
Booklet

Flowering
Non-flowering
Ferns
Gymnosperms
Plants with seeds and flowers
Next >
Separating Species
The kingdoms are populated according to characteristics of the organisms and how they are related to each other.
Groups of organisms are then broken down according to differences found between them.

Flowering
Non-flowering
Ferns
Gymnosperms
Plants with seeds and flowers
Next >
Separating Species
Plants may be flowering or non-flowering.
Then differences within each group can enable the organisms to be separated further.
Animals may have backbones, but may not.

Next >
7 Levels of Classification- Carl Linneaus
Until the 1700’s, scientists divided organisms into two groups, plants and animals. But scientists found that some living things didn’t really fit into either group. In the 1700’s, a Swedish physician and botanist named Carl Linneaus solve the problem. Linneaus founded taxonomy. Linneaus tried to classify all known living things based on their shape and structure. He came up with a seven-level system of classification, which is still used today.

7 Levels of Classification- Kingdom
Every living thing is classified into one of six kingdoms.
Kingdoms are the largest, most general groups.
All animals are in the kingdom Animalia.

Next >
7 levels of Classification - Kingdom
This kingdom consists of organisms that satisfy their nutrition needs from consuming other organisms.

Invertebrates
(no backbone)
(with backbone)
Mollusks
Segmented worms
Roundworms
Flatworms
Coelenterates
Echinoderms
Arthropods Insects
Arachnids
Myriapods
Crustaceans
Mammals
Birds
Reptiles
Amphibians
Fish
Animalia
Vertebrates
Next >
7 Levels of Classification - Phylum
All living things are then sorted into several phyla (singular, phylum).

7 Levels of Classification-Phylum
The members of one phylum are more like each other than they are like members of other phyla.
All animals in the phylum Chordata have a hollow nerve cord and most have a backbone.

7 Levels of Classification-Class
All of the living things in a phylum are further sorted in classes.
Animals in the Class Mammalia have a backbone. They also nurse their young.

7 Levels of Classification- Order
Each class is divided into one or more orders.Animals in the order Carnivora have a backbone and nurse their young. They also have special teeth for tearing meat.

7 Levels of Classification- Family
Orders are separated into families.Animals in the family Felidae are cats. They have a backbone, nurse their young and have special teeth for tearing meat. Their claws can be drawn back into their paws.

7 Levels of Classification- Genus
Families are broken into genera (singular genus).Animals in the genus Felis have traits of other animals in the same family. However, they cannot roar, they can only purr.

7 Levels of Classification- Species
Genera are sorted into species.Species Felis domesticus is the common house cat. It has traits of all the levels above it, but it also has special traits.

Scientific NamesFelis domesticus is the scientific name of a common house cat.Scientific names are use in place of common names because they can have several different common names depending on where they are.The scientific name is either in italics or underlined. The first letter of the Genus is capitalized and the species is all lower case.

Dichotomous Keys
Dichotomous Keys are special guides that help to identify unknown organisms.
A dichotomous key has several pairs of descriptive statements and the person trying to make an identification looks at the first pair of statements and chooses the best one that describes the organism.
By working through the statements in the key, the person will be able to identify the organism.

Which picture is the only one to show an organism that is a vertebrate?
A) Picture A
B) Picture B
C) Picture C
D) Picture D
Picture A Picture B
Picture C Picture D
Next >

Which picture is the only one to show an organism that is a vertebrate?
A) Picture A
B) Picture B
C) Picture C
D) Picture D
Picture A Picture B
Picture C Picture D
Next >

Which of these is the broadest category for the organism shown?
A) Domain Eukaryota
B) Kingdom Plantae
C) Flowering plant
D) Seed-producing plant
Next >

Next >
Which of these is the broadest category for the organism shown?
A) Domain Eukaryota
B) Kingdom Plantae
C) Flowering plant
D) Seed-producing plant