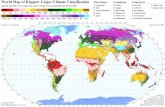
Classification of Climate
-
Upload
universiti-teknologi-mara-uitm-malaysia -
Category
Education
-
view
3.694 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Classification of Climate

CLASSIFICATION OF CLASSIFICATION OF CLIMATESCLIMATES

22
A tropical climate is a kind of climate typically in the tropicsA tropical climate is a kind of climate typically in the tropics
Defined as non-arid climate in which all Defined as non-arid climate in which all 12 months have 12 months have
mean temperature above 64.4 °F (18.0 °C)mean temperature above 64.4 °F (18.0 °C)
Cover the Cover the largest area of earth largest area of earth (20% of land surface and (20% of land surface and
43% of ocean surface) - the home to almost half of the 43% of ocean surface) - the home to almost half of the
world ’s populationworld ’s population
South Florida, The Caribbean, Central Africa, Coastal South Florida, The Caribbean, Central Africa, Coastal
India, Southeast Asia, North Queensland, Hawaii, India, Southeast Asia, North Queensland, Hawaii, Central Central
America, or most of Brazil.America, or most of Brazil.
CLASSIFICATIONCLASSIFICATION

33
CLASSIFICATIONCLASSIFICATION

44
Can be divided into Can be divided into 3 major 3 major climatic zones climatic zones and 3 sub-groups :-and 3 sub-groups :-
I.I. Warm-humid equatorial climateWarm-humid equatorial climate warm-humid island or trade-wind climatewarm-humid island or trade-wind climate
II.II. Hot-dry desert or semi-desert climateHot-dry desert or semi-desert climate hot-dry maritime desert climatehot-dry maritime desert climate
III.III. Composite or monsoon climate (combination Composite or monsoon climate (combination of I & II)of I & II)
tropical upland climatetropical upland climate
CLASSIFICATIONCLASSIFICATION

Type of Tropical Climate
Warm Humid Island Climate
Hot Dry Maritime Desert Climate
Tropical Upland Climate
Warm Humid Climate
Warm Humid Climate
Hot Dry Desert Climate
Hot Dry Desert Climate
Composite or Monsoon Climate
Composite or Monsoon Climate
CLASSIFICATIONCLASSIFICATION
Sub-Group

Found in a belt Found in a belt near the Equator near the Equator extending to extending to about about 15º North and South15º North and South
Examples: Examples: Malaysia, Jakarta, Singapore, Hawaii, Malaysia, Jakarta, Singapore, Hawaii, USUS
WARM HUMID CLIMATE WARM HUMID CLIMATE

WARM HUMID ELEMENTSWARM HUMID ELEMENTSWARM HUMID CLIMATEWARM HUMID CLIMATE|ELEMENTS||ELEMENTS|

WARM HUMID ELEMENTSWARM HUMID ELEMENTSWARM HUMID CLIMATEWARM HUMID CLIMATE|ELEMENTS||ELEMENTS|

99
WallWall - is still warm at night because of the - is still warm at night because of the high solar radiation during the dayhigh solar radiation during the day
Pitch roof Pitch roof - is used act as a buffer to - is used act as a buffer to reduce the entering of heat into the housereduce the entering of heat into the house
GuttersGutters are built are built Plastered single layer wall Plastered single layer wall – to prevent – to prevent
heat captured in the househeat captured in the house
WARM HUMID CLIMATEWARM HUMID CLIMATE|BUILDING CHARACTERISTIC||BUILDING CHARACTERISTIC|

1010
WindowWindow hoods and balcony hoods and balcony - to reduce the - to reduce the entering of solar radiation and daylight into entering of solar radiation and daylight into the housethe house
More More windows and the opening windows and the opening are wideare wide ApronsAprons - to prevent dirt on the wall - to prevent dirt on the wall Wide doors Wide doors – wind shaft is built to enable – wind shaft is built to enable
heated air go outsideheated air go outside Ceiling (high ceiling) Ceiling (high ceiling) – to prevent direct – to prevent direct
heat into the househeat into the house
WARM HUMID CLIMATEWARM HUMID CLIMATE|BUILDING CHARACTERISTIC||BUILDING CHARACTERISTIC|

1111

• Island Island within the Equatorial belt within the Equatorial belt and in the and in the trade wind zonetrade wind zone
• Examples: Examples: Carribbeans, Philipines and Carribbeans, Philipines and other island groups in Pacific Oceanother island groups in Pacific Ocean
WARM HUMID ISLAND CLIMATEWARM HUMID ISLAND CLIMATE

1313
Caribbean
Philippine

WARM HUMID ELEMENTSWARM HUMID ELEMENTSWARM HUMID ISLANDWARM HUMID ISLAND|ELEMENTS||ELEMENTS|

WARM HUMID ELEMENTSWARM HUMID ELEMENTSWARM HUMID ISLANDWARM HUMID ISLAND|ELEMENTS||ELEMENTS|

◊ Occur in Occur in 2 belts at latitude 15º and 30º2 belts at latitude 15º and 30º North and South.North and South.
◊ Examples: Examples: Baghdad, Saudi Arabia, India, Baghdad, Saudi Arabia, India, South Afrika.South Afrika.
HOT-DRY DESERT CLIMATEHOT-DRY DESERT CLIMATE

HOT-DRY DESERT CLIMATEHOT-DRY DESERT CLIMATE|ELEMENTS||ELEMENTS|

WARM HUMID ELEMENTSWARM HUMID ELEMENTSHOT-DRY DESERT CLIMATEHOT-DRY DESERT CLIMATE|ELEMENTS||ELEMENTS|

1919
Flat roof Flat roof - is used because of sandstorms – - is used because of sandstorms – not obstruct the wind flownot obstruct the wind flow
Pitch roof Pitch roof - should be built as double layers- should be built as double layers Small windows Small windows - to prevent sand and dust - to prevent sand and dust
from entering the housefrom entering the house
HOT-DRY DESERT CLIMATEHOT-DRY DESERT CLIMATE|BUILDING CHARACTERISTIC||BUILDING CHARACTERISTIC|

2020
Thick wall Thick wall – the entering of heat into the house – the entering of heat into the house during daytime become slower and at night the during daytime become slower and at night the cold air push the warm air to flow outside and the cold air push the warm air to flow outside and the building is maintained cold (ie: pyramid)building is maintained cold (ie: pyramid)
ConcreteConcrete houses are built houses are built Colors of the buildings Colors of the buildings - light / bright- light / bright MaterialsMaterials - crack and break up cause by high - crack and break up cause by high
daytime temperature and rapid cooling at nightdaytime temperature and rapid cooling at night
HOT-DRY DESERT CLIMATEHOT-DRY DESERT CLIMATE|BUILDING CHARACTERISTIC||BUILDING CHARACTERISTIC|

2121

2222
Occur in the Occur in the same latitude belts same latitude belts as the as the hot-dry desert climatehot-dry desert climate
Two season – Two season – hot and coolhot and cool Example:Example: Kuwait, Karachi Kuwait, Karachi
HOT-DRY MARITIME DESERTHOT-DRY MARITIME DESERT

HOT-DRY MARITIME DESERTHOT-DRY MARITIME DESERT|ELEMENTS||ELEMENTS|

WARM HUMID ELEMENTSWARM HUMID ELEMENTSHOT-DRY MARITIME DESERTHOT-DRY MARITIME DESERT|ELEMENTS||ELEMENTS|

2525
Usually occur in : Usually occur in : large land masses near large land masses near the tropics the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, which of Cancer and Capricorn, which are are far from Equator.far from Equator.
Examples: Examples: Lahore, Mandalay, New DelhiLahore, Mandalay, New Delhi Two seasons Two seasons – 2/3 of the year is hot dry – 2/3 of the year is hot dry
and 1/3 is warm humid.and 1/3 is warm humid. Localities further North and South often Localities further North and South often
have a third season, have a third season, best described as best described as cool-dry.cool-dry.
COMPOSITE / MONSOON COMPOSITE / MONSOON CLIMATECLIMATE

2626
COMPOSITE / MONSOON COMPOSITE / MONSOON ||ELEMENTS|ELEMENTS|
1
Season Hot-dry Warm-humid Cool-dry
Daytime mean max
32 – 43 27-32 Up to 27
Night-time mean min
21 – 27 24 – 27 4 – 10
Diurnal mean range
11 – 22 3 – 6 11 – 22
Humidity2
• RH is low throughout the dry periods at 20 – 55%• Wet season : rises to 55 – 95%

COMPOSITE / MONSOON COMPOSITE / MONSOON ||ELEMENTS|ELEMENTS|

2828
Courtyard type Courtyard type buildings are very suitablebuildings are very suitable A moderate dense, low rise developmentA moderate dense, low rise development Large projecting eaves and wide verandahs Large projecting eaves and wide verandahs are are
needed in the warm-humid season needed in the warm-humid season as out door as out door living areasliving areas - to reduce sky glare, keep out the - to reduce sky glare, keep out the rain and provide shaderain and provide shade
Shading devices Shading devices should preferably be of low should preferably be of low thermal capacitythermal capacity
COMPOSITE / MONSOON COMPOSITE / MONSOON ||BUILDING CHARACTERISTIC|BUILDING CHARACTERISTIC|

2929
Roof and external walls Roof and external walls - constructed of solid - constructed of solid masonry and concrete.masonry and concrete.
Resistance insulation Resistance insulation - placed at the outside - placed at the outside surfaces of external walls or roofs.surfaces of external walls or roofs.
Large openings in opposite walls Large openings in opposite walls - preferably with - preferably with solid shutters.solid shutters.
COMPOSITE / MONSOON COMPOSITE / MONSOON ||BUILDING CHARACTERISTIC|BUILDING CHARACTERISTIC|

3030
Mountainous regions Mountainous regions - more than 900 to - more than 900 to 1200 m above sea level1200 m above sea level
Examples:Examples: Bogotá, Mexico City, Nairobi Bogotá, Mexico City, Nairobi
TROPICAL UPLAND CLIMATETROPICAL UPLAND CLIMATE

TROPICAL UPLAND CLIMATETROPICAL UPLAND CLIMATE|ELEMENTS||ELEMENTS|
Air temperature :

WARM HUMID ELEMENTSWARM HUMID ELEMENTSTROPICAL UPLAND CLIMATETROPICAL UPLAND CLIMATE|ELEMENTS||ELEMENTS|

TTHHAANNKK YYOOUU